Question: PV, FV, Yields, Bonds, and Trees Below is a table of fixed income yields taken from BondSource via Schwab.com. Use the table to answer the
PV, FV, Yields, Bonds, and Trees Below is a table of fixed income yields taken from BondSource via Schwab.com. Use the table to answer the following questions. Show work for partial credit. DO NOT ROUND UNTIL YOUR FINAL ANSWER!
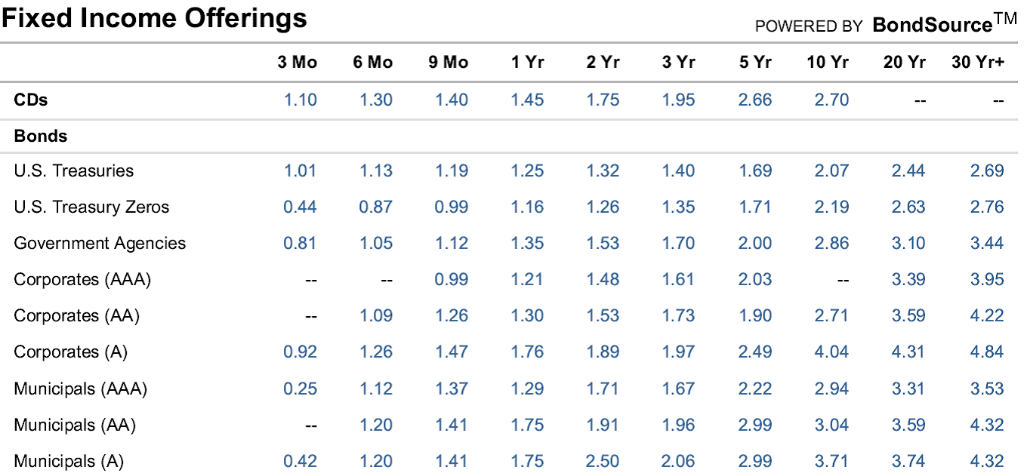 1. Use the U.S. Treasury Zeros to calculate the forward interest rates for years 2 and years 3. f2 = ___ ___ . ___ ___ % f3 = ___ ___ . ___ ___ % 2. The U.S. Treasury Zeros to calculate the discount factor () for years 1, 2 and 3. The discount factor is the present value, or price, of one dollar delivered at a future date. v1 = $ ___ . ___ ___ ___ ___ v2 = $ ___ . ___ ___ ___ ___ v3 = $ ___ . ___ ___ ___ ___ 3. Loan payments are often amortized (spread evenly through time). Consider three equal payments of $5,000. Payments are at the end of years 1, 2, and 3. Use the discount factors from question two to present value this stream of cash. $ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ . ___ ___ 4. Consider a balloon payment of $100,000 at the end of year 3. Use the discount factors from question 2 to present value this stream of cash. $ ___ ___ ___ , ___ ___ ___ . ___ ___ 5. Consider the following yields on riskless securities 1.16% for the first year, 1.26% for the second year and 1.35% for the third year. These are forward rates. What is the present value or implied price of a three-year par $100,000 zero coupon bond assuming annual compounding? What is the value assuming continuous compounding? Annual compounding $ ___ ___ ___ , ___ ___ ___ . ___ ___ Continuous compounding $ ___ ___ ___ , ___ ___ ___ . ___ ___ PV, FV, Yields, Bonds, and Trees 6. Assume there is a 2% chance of default on the balloon payment from question 4. Use a binomial tree to calculate present value and yield to maturity of the stream of cash incorporating the default possibility. $ ___ ___ ___ , ___ ___ ___ . ___ ___ ___ ___ . ___ ___ % 7. A three-year $100,000 par bond has a coupon rate of 5% paid annually. Use your answers to questions 3 and 4 to calculate the present value of the coupon bond. $ ___ ___ ___ , ___ ___ ___ . ___ ___ 8. Now consider the coupon bond from question 7 using a binomial tree to incorporate default risk. Each year there is a 2% chance that the issuer defaults and the bond owner receives nothing. There is 98% chance that the issuer survives. Draw a binomial tree for this situation and use the tree to value the bond with annual compounding. If the firm defaults during year t then the investor does not the coupon payment for that year and the investor does not receive any payment for subsequent years. Bond value $ ___ ___ ___ , ___ ___ ___ . ___ ___ 9. What is the yield to maturity on the coupon bond from question 8? You need to account for all the payments (coupons and face) in your calculation. There is no closed form solution. You can either (a) write the formula the ytm will solve or (b) solve for the yield using a financial calculator or Excel. ___ ___ . ___ ___ % 10. Consider the binomial tree of interest rates developed in class; the first year the rate is 6% and it moves up or down 2% each year with equal probability. A three-year zero coupon par $100 bond has a value of $84.08 today. What is the expected value of the bond if interest rates are more likely to go up (60% probability) than to go down (40% probability)?
1. Use the U.S. Treasury Zeros to calculate the forward interest rates for years 2 and years 3. f2 = ___ ___ . ___ ___ % f3 = ___ ___ . ___ ___ % 2. The U.S. Treasury Zeros to calculate the discount factor () for years 1, 2 and 3. The discount factor is the present value, or price, of one dollar delivered at a future date. v1 = $ ___ . ___ ___ ___ ___ v2 = $ ___ . ___ ___ ___ ___ v3 = $ ___ . ___ ___ ___ ___ 3. Loan payments are often amortized (spread evenly through time). Consider three equal payments of $5,000. Payments are at the end of years 1, 2, and 3. Use the discount factors from question two to present value this stream of cash. $ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ . ___ ___ 4. Consider a balloon payment of $100,000 at the end of year 3. Use the discount factors from question 2 to present value this stream of cash. $ ___ ___ ___ , ___ ___ ___ . ___ ___ 5. Consider the following yields on riskless securities 1.16% for the first year, 1.26% for the second year and 1.35% for the third year. These are forward rates. What is the present value or implied price of a three-year par $100,000 zero coupon bond assuming annual compounding? What is the value assuming continuous compounding? Annual compounding $ ___ ___ ___ , ___ ___ ___ . ___ ___ Continuous compounding $ ___ ___ ___ , ___ ___ ___ . ___ ___ PV, FV, Yields, Bonds, and Trees 6. Assume there is a 2% chance of default on the balloon payment from question 4. Use a binomial tree to calculate present value and yield to maturity of the stream of cash incorporating the default possibility. $ ___ ___ ___ , ___ ___ ___ . ___ ___ ___ ___ . ___ ___ % 7. A three-year $100,000 par bond has a coupon rate of 5% paid annually. Use your answers to questions 3 and 4 to calculate the present value of the coupon bond. $ ___ ___ ___ , ___ ___ ___ . ___ ___ 8. Now consider the coupon bond from question 7 using a binomial tree to incorporate default risk. Each year there is a 2% chance that the issuer defaults and the bond owner receives nothing. There is 98% chance that the issuer survives. Draw a binomial tree for this situation and use the tree to value the bond with annual compounding. If the firm defaults during year t then the investor does not the coupon payment for that year and the investor does not receive any payment for subsequent years. Bond value $ ___ ___ ___ , ___ ___ ___ . ___ ___ 9. What is the yield to maturity on the coupon bond from question 8? You need to account for all the payments (coupons and face) in your calculation. There is no closed form solution. You can either (a) write the formula the ytm will solve or (b) solve for the yield using a financial calculator or Excel. ___ ___ . ___ ___ % 10. Consider the binomial tree of interest rates developed in class; the first year the rate is 6% and it moves up or down 2% each year with equal probability. A three-year zero coupon par $100 bond has a value of $84.08 today. What is the expected value of the bond if interest rates are more likely to go up (60% probability) than to go down (40% probability)?
Fixed Income Offerings TM POWERED BY BondSource 5 Yr10 Yr 20 Yr 30 Yr+ 2.66 1 Yr 2Yr3 Yr 1.40 CDs Bonds U.S. Treasuries U.S. Treasury Zero:s Government Agencies Corporates (AAA) Corporates (AA) Corporates (A) Municipals (AAA) Municipals (AA) Municipals (A) 1.10 1.30 1.45 1.75 1.95 2.70 2.44 2.19 2.63 3.10 3.39 3.59 4.31 3.31 3.59 3.74 1.40 1.19 0.440.870.99 1.05 1.12 0.99 109 1.26 1.47 1.37 1.41 1.41 1.01 1.13 1.32 1.26 1.35 1.53 1.70 1.48 1.30 1.53 1.73 1.89 1.71 1.25 1.69 2.07 1.71 2.00 2.03 1.90 2.71 2.49 2.22 2.94 2.99 2.99 2.69 2.76 3.44 3.95 4.22 4.84 3.53 4.32 4.32 1.16 1.35 0.81 2.86 1.21 1.61 1.76 1.29 1.75 1.91 1.75 0.92 4.04 1.26 1.12 1.20 1.20 1.97 1.67 1.96 2.06 0.25 3.04 0.42 2.50 3.71
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


