Question: Python 2a) As part of the floating point number representation, we need to specify an integer-valued exponent. Internally, the exponent is also represented as a
Python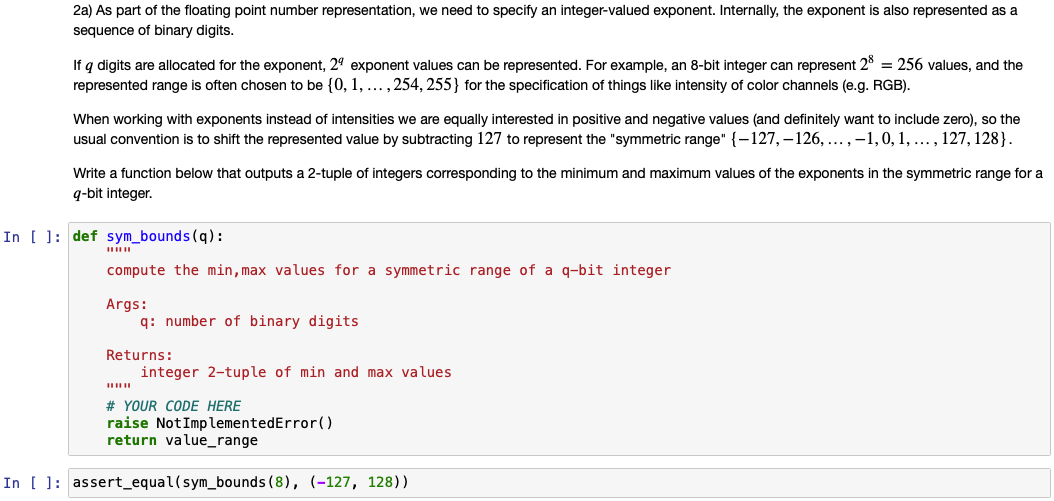
2a) As part of the floating point number representation, we need to specify an integer-valued exponent. Internally, the exponent is also represented as a sequence of binary digits. If q digits are allocated for the exponent, 29 exponent values can be represented. For example, an 8-bit integer can represent 28 = 256 values, and the represented range is often chosen to be {0, 1, ...,254, 255) for the specification of things like intensity of color channels (e.g. RGB). When working with exponents instead of intensities we are equally interested in positive and negative values and definitely want to include zero), so the usual convention is to shift the represented value by subtracting 127 to represent the "symmetric range" {-127, -126, ...,-1,0,1,..., 127, 128}. Write a function below that outputs a 2-tuple of integers corresponding to the minimum and maximum values of the exponents in the symmetric range for a q-bit integer. In [ ]: def sym_bounds(q): compute the min, max values for a symmetric range of a q-bit integer Args: q: number of binary digits Returns: integer 2-tuple of min and max values # YOUR CODE HERE raise Not ImplementedError() return value_range In [ ]: assert_equal(sym_bounds (8), (-127, 128))
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


