Question: PYTHON 3 pART 1 The Caesar cipher, also known as Caesar's cipher is one of the simplest and most widely known encryption techniques. It is
PYTHON 3
pART 1
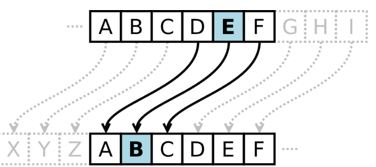
The Caesar cipher, also known as Caesar's cipher is one of the simplest and most widely known encryption techniques. It is a type of substitution cipher in which each letter in the plaintext is replaced by a letter some fixed number of positions down the alphabet. For example, with a left shift of 3, D would be replaced by A, E would become B, and so on. The method is named after Julius Caesar, who used it in his private correspondence (Wikipedia).
The function below is designed to input a message(string), it will then pass through each character of the string within a for loop. Each character is converted to its ASCII equivalent numerical value using the ord() method, then it will be increased by one. This causes a to become b, and so on Each new letter is the appended to the result string (our cipher).
The selection statement checks to see if the letter z or Z exists. If so, it reverts back to a or A.
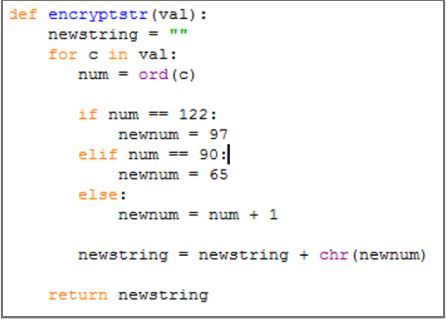
Using this code, complete the following:
Build a main function that:
Prompts the user for text
Asks the user if they wish to encrypt or decrypt that text
Call the appropriate function
Write an additional function to decrypt a message HINT: The body of this function is very similar to the encrypt function. You are simply doing the inverse of the encrypt function.
When complete your output may look similar to this:
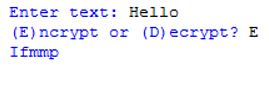 OR
OR 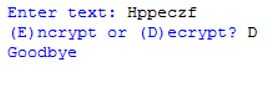
ABCIDIEFIGHI D E
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


