Question: Python 3.x Binary Tree Recursion: Note: This question has been updated Treenode.py (This is ADT so please import): def create(data, left=None, right=None): Create a
Python 3.x Binary Tree Recursion:

Note: This question has been updated
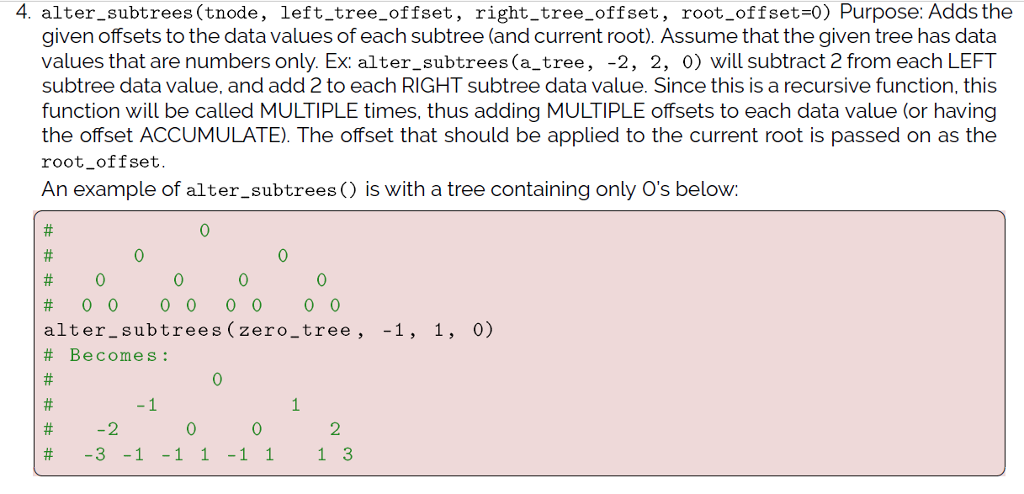
Treenode.py (This is ADT so please import):
def create(data, left=None, right=None): """ Create a new treenode for the given data. Pre-conditions: data: Any data value to be stored in the treenode left: Another treenode (or None, by default) Post-condition: none Return: the treenode created """ return {'data':data, 'left':left, 'right':right} def get_data(treenode): """ Retrieve the contents of the data field. Pre-conditions: node: a node created by create() Post-conditions: none Return the data value stored previously in the node """ return treenode['data'] def get_left(tnode): """ Retrieve the contents of the left field. Pre-conditions: tnode: a treenode created by create() Post-conditions: none Return the value stored in left field """ return tnode['left'] def get_right(tnode): """ Retrieve the contents of the right field. Pre-conditions: tnode: a treenode created by create() Post-conditions: none Return the value stored in right field """ return tnode['right'] def set_data(tnode, val): """ Set the contents of the data field to val. Pre-conditions: tnode: a node created by create() val: a data value to be stored Post-conditions: stores the new data value, replacing the existing value Return none """ tnode['data'] = val def set_left(tnode, val): """ Set the contents of left field to val. Pre-conditions: tnode: a treenode created by create() val: a treenode, or the value None Post-conditions: stores the val in left field, replacing the existing value Return none """ tnode['left'] = val def set_right(tnode, val): """ Set the contents of right field to val. Pre-conditions: tnode: a treenode created by create() val: a treenode, or the value None Post-conditions: stores the val in right field, replacing the existing value Return none """ tnode['right'] = val treefunction.py:
import treenode as TN def is_leaf(tnode): """ Purpose: Determine if tnode is a leaf. Pre-conditions: :param tnode: a treenode Return: True if the tnode has zero children """ return TN.get_left(tnode) is None and TN.get_right(tnode) is None def to_string(tnode, level=0): """ Produce a formatted string to represent the hierarchy of a tree. Tree diagrams usually have the root at the top. Here the root is at the top left. - every data value appears on its own line - the levels of a tree are columns from left to right - nodes at the same level start in the same column - very long data values might cause the presentation to get messy - subtrees appear below a parent - left subtree immediately - right subtree after the entire left subtree Pre-conditions: :param tnode: a Binary tree (treenode or None) :param level: the level of the tnode (default value 0) Return: A string with the hierarchy of the tree. """ if tnode is None: return 'EMPTY' else: result = '\t'*level result += str(TN.get_data(tnode)) if TN.get_left(tnode) is not None: result += ' '+to_string(TN.get_left(tnode), level+1) if TN.get_right(tnode) is not None: result += ' '+to_string(TN.get_right(tnode), level+1) return result
Exampletrees.py:
# Defines a few example trees import treenode as tn atree = tn.create(2) a = tn.create(7) b = tn.create(5) tn.set_left(atree, a) tn.set_right(atree, b) c = tn.create(11) d = tn.create(6) tn.set_left(a, c) tn.set_right(a, d)
Purpose: To practice recursion on binary trees. Degree of Difficulty: Easy to Moderate to Tricky You can find the treenode ADT on the assignment page. Using this ADT, implement the following functions: 1 count node_types (tnode) Purpose: Returns a tuple containing the number of leaf nodes in the tree, and the number of non-leaf nodes in the tree. A leaf node is a node without any children. The is_leaf function provided in treefunctions.py can be used to check if a node is a leaf node. Re- member, you can use circle brackets to create a tuple a tuple-("a""b") print( a_tuple [0]) # Prints out "a
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


