Question: PYTHON CODE PLEASE FOLLOW THE QUESTION'S REQUIREMENTS !!!!!!! NO PRINT FUNCTION CAN BE USED, ONLY CAN USE RETURN Task 4: m-Coloring problem In this problem,
PYTHON CODE
PLEASE FOLLOW THE QUESTION'S REQUIREMENTS !!!!!!!
NO PRINT FUNCTION CAN BE USED, ONLY CAN USE RETURN
Task 4: m-Coloring problem
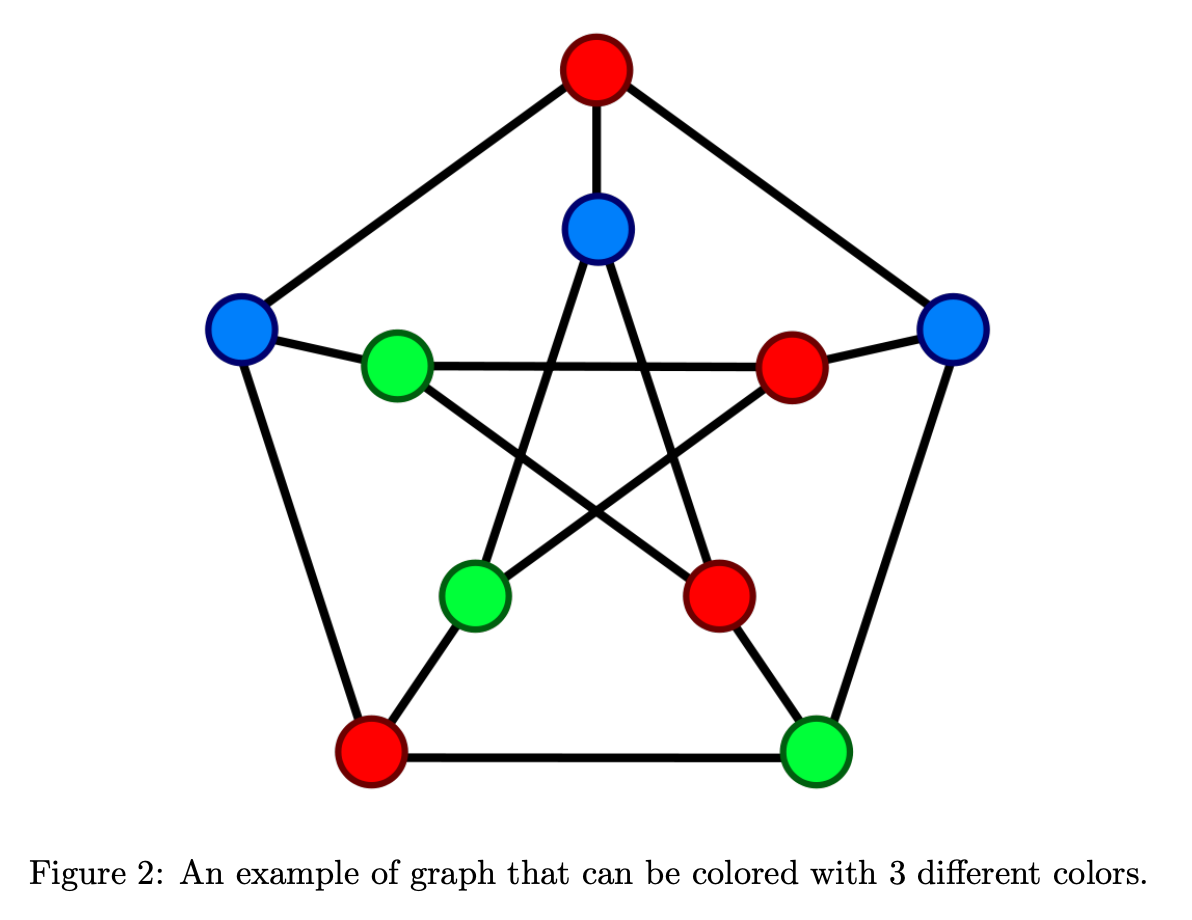
In this problem, an undirected graph is given. There is also provided m colors. The problem is to find if it is possible to assign nodes with m different colors, such that no two adjacent vertices of the graph are of the same colors. If the solution exists, then display which color is assigned on which vertex as shown in Figure 2. The graph coloring enjoys many practical applications as well as theoretical challenges. Some of the practical applications of graph coloring are pattern matching, scheduling, designing seating plans, exam timetabling, radio frequency assignment and solving Sudoku puzzles.
There is two files, graph_A.txt and graph_b.txt
Inside graph_A.txt there is : 0,1,1,1 1,0,1,0 1,1,0,1 1,0,1,0
Inside graph_B.txt there is :
0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0 1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0 0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0 0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0 1,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1 1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0 0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1 0,0,1,0,0,1,0,0,0,1 0,0,0,1,0,1,1,0,0,0 0,0,0,0,1,0,1,1,0,0
Part A: Get graph from text-file
Write a function graph from file(file name) that reads in a file containing a graph and returns the contents of the file as a Python-readable table.
Input: a file name file name, where the file contains n lines, and each line contains n entries separated by commas.
Output: a table represented as a nested list, where each entry in the original file is an element in the table, and all numbers have been converted to integers.
Examples
a) Calling (graph from file(graph A.txt)), returns: [[0, 1, 1, 1], [1, 0, 1, 0], [1, 1, 0, 1], [1, 0, 1, 0]]
b) Calling (graph from file(graph B.txt)), returns: [[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0], [1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0], [1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1], [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0], [0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1], [0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1], [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0]]
Part B: Valid entry
Write a function valid entry(vertex,graph,colored vertex,color) that determines whether a particular color can be entered at a particular vertex in the graph, while maintaining validity.
Input: vertex is an integer that represents the vertex that to be colored; graph is a nested list that represents the adjacency matrix of the graph; colored vertex is a list that represents that the color of the vertices. For an example, a graph with 4 vertices, colored vertex can be represented by colored vertex =[1,2,3,0] (We may assume that red = 1, green = 2, blue = 3 and not colored = 0. Assignment of colors are arbitrary, however, we assign not colored as 0). In this example, vertex 0 is colored by red, vertex 1 is colored as green, vertex 2 is colored as blue and vertex 3 is not colored; color is an integer represents the color to be added to vertex.
Output: return a Boolean is the coloring is valid; otherwise False.
Examples
Given graph A= [[0, 1, 1, 1], [1, 0, 1, 0], [1, 1, 0, 1], [1, 0, 1, 0]]
a) Calling valid entry(3,graph A,[1,2,3,0],2) returns True.
b) Calling valid entry(3,graph A,[1,2,3,0],1) returns False.
Part C: Assign colors to vertex
Write a function add color vertex(vertex,graph,colored vertex,m) that assigns all the possible valid colors to a particular vertex.
Input: vertex is an integer that represents the vertex that to be colored; graph is a nested list that represents the adjacency matrix of the graph; colored vertex is a list that represents that the color of the vertices; m represents the number of the colors.
Output: a nested list that represents all the possible valid color assignments to vertex. If no possible assignment of colors to the vertex available, then return an empty list.
a) Calling add color vertex(1,graph A,[1,0,0,0],3) returns [[1, 2, 0, 0], [1, 3, 0, 0]].
b) Calling add color vertex(2,graph A,[1, 2, 2, 0],2) returns [].
Part D: Solve m-coloring problem for the given graph
Write a function m color(file name,m) that finds the solution for the given graph.
Input: a file name, where the file contains n lines, and each line contains n entries separated by commas. This file represents the adjacency matrix of a graph. Output: a list representing the colored graph. If there are more than one possible solutions available, just return one possible solution (You may always return all possible solutions). If no possible solution available, the function should return an empty list.
Examples
a) Calling (m color(graph A.txt,3)) returns [1, 2, 3, 2] (One of the possible valid solution).
b) Calling (m color(graph A.txt,2)) returns [].
c) Calling (m color(graph B.txt,3)) returns [1, 2, 1, 2, 3, 2, 1, 3, 3, 2] (One of the possible valid solution).
Students are encouraged to validate the correctness of their functions with different graphs.
Marks are given for the correct behavior of the different functions: (a) Task 4(A): 1 mark for graph from file. (b) Task 4(B): 1 mark for valid entry. (c) Task 4(C): 3 marks for add color vertex. (d) Task 4(D): 5 marks for m solve.
THE RETURN OUTPUT MUST BE THE SAME AS THE EXAMPLE GIVEN, NO PRINT FUNCTION CAN BE USED, ONLY RETURN
THIS IS THE WHOLE QUESTION, WHAT ELSE INFO DO YOU NEED ??????????
Figure 2: An example of graph that can be colored with 3 different colors
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


