Question: Python Dictionary. Part III: Constructing a Simple Text Index from a File (4 points) Search engines like Google and Bing work by consulting an index


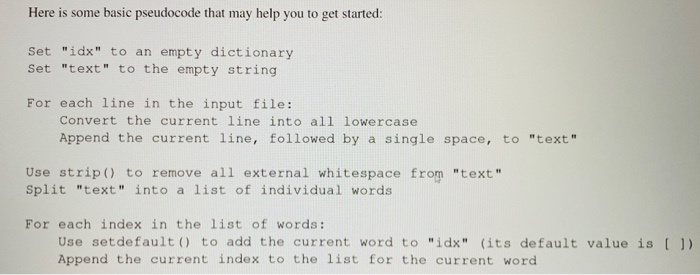
Part III: Constructing a Simple Text Index from a File (4 points) Search engines like Google and Bing work by consulting an index of the words found in each Web page that they examine. This index identifies the document(s) that contain a particular word (like "dog" or "cat"), as well as the word's position(s) in those documents. For example, Google might record that the Web page "pets.html" contains the word "cat" at positions 22, 35, 100, and 209. Later, when a user searches for the word "cat". Google will return "pets.html" as a hit for that search term. Complete the buildIndex () function. This function takes one argument: a string representing the name of a plain text file whose contents are to be indexed. buildIndex ( returns a dictionary whose keys are the unique words in the text file; each key's value is a list of integer positions where that word appears in the original text. The input file may contain multiple lines, but you may assume that every word is separated by a space, and that the file does not contain any external punctuation like periods or commas. If a word appears in varying cases, treat all of those instances as copies of the same word (for example, "Cat", "CAT", and "cat" all count as copies of a single word: "cat"). For each word in the source, if it is already present in the dictionary, append the current index of the word to the dictionary to the existing key. If the word is not yet in the dictionary, add it as a new entry. After processing the entire source file, buildIndex () returns the index of word locations. NOTE: In order for your code to work properly, your data file MUST be located in the same directory as your "lab7.py" file
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


