Question: Python Homework 4: Arcsine Laws The purpose of this python homework is to explore the so-called Arcsine laws numerically. The arcsine laws are a number
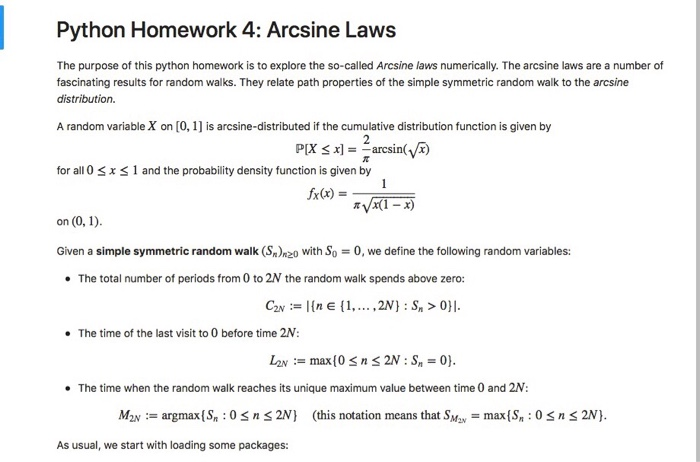
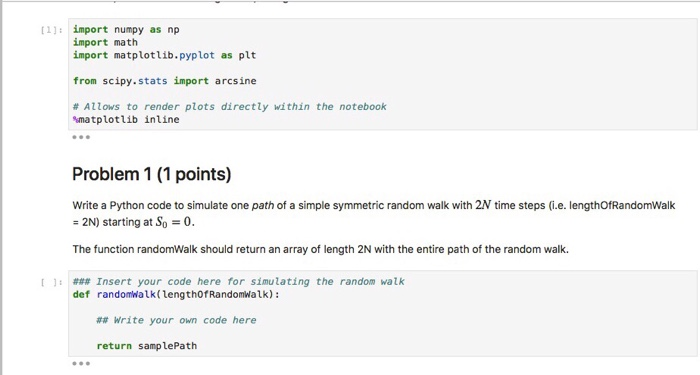
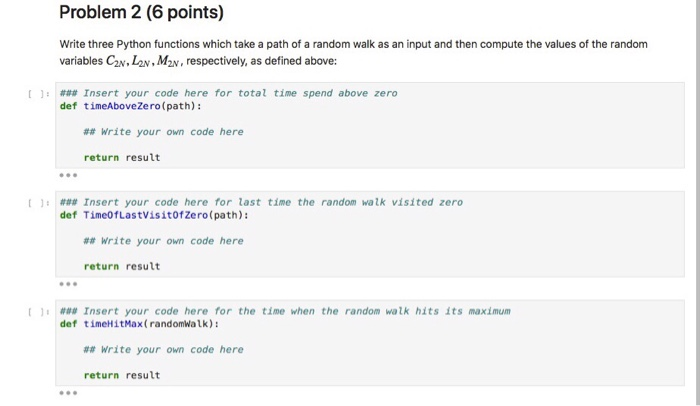
Python Homework 4: Arcsine Laws The purpose of this python homework is to explore the so-called Arcsine laws numerically. The arcsine laws are a number of fascinating results for random walks. They relate path properties of the simple symmetric random walk to the arcsine distribution. A random variable X on [0, 1] is arcsine-distributed if the cumulative distribution function is given by for all 0 sx S 1 and the probability density function is given by on (0, 1) 2 PxFarcsin(/a) Given a simple symmetric random walk (S)n20 with So0, we define the following random variables: The total number of periods from 0 to 2N the random walk spends above zero: The time of the last visit to 0 before time 2N: Lav := max(0 n 2N:S,' = 0). The time when the random walk reaches its unique maximum value between time 0 and 2N: Mav := argmax (Sn : O 2N } (this notation means that SM2v = max(Sn : 0 2N). n n As usual, we start with loading some packages: Python Homework 4: Arcsine Laws The purpose of this python homework is to explore the so-called Arcsine laws numerically. The arcsine laws are a number of fascinating results for random walks. They relate path properties of the simple symmetric random walk to the arcsine distribution. A random variable X on [0, 1] is arcsine-distributed if the cumulative distribution function is given by for all 0 sx S 1 and the probability density function is given by on (0, 1) 2 PxFarcsin(/a) Given a simple symmetric random walk (S)n20 with So0, we define the following random variables: The total number of periods from 0 to 2N the random walk spends above zero: The time of the last visit to 0 before time 2N: Lav := max(0 n 2N:S,' = 0). The time when the random walk reaches its unique maximum value between time 0 and 2N: Mav := argmax (Sn : O 2N } (this notation means that SM2v = max(Sn : 0 2N). n n As usual, we start with loading some packages
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


