Question: Python - I need help with creating a list of tuples by calling on a function that I have created. I am struggling on the
Python - I need help with creating a list of tuples by calling on a function that I have created. I am struggling on the yellow highlights, I think I may have misunderstood the structure or what am I doing wrong here? Please see my script below. Any advice is truly appreciated!!

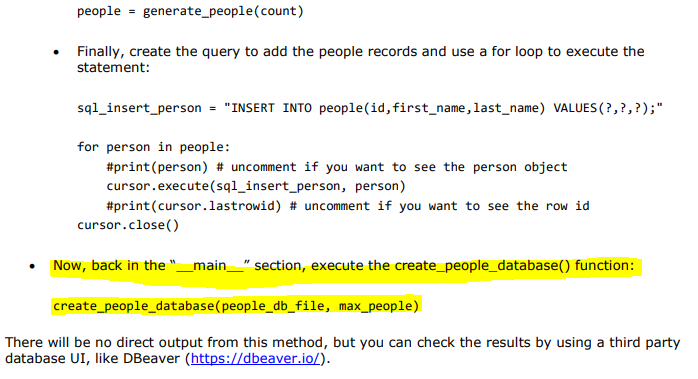
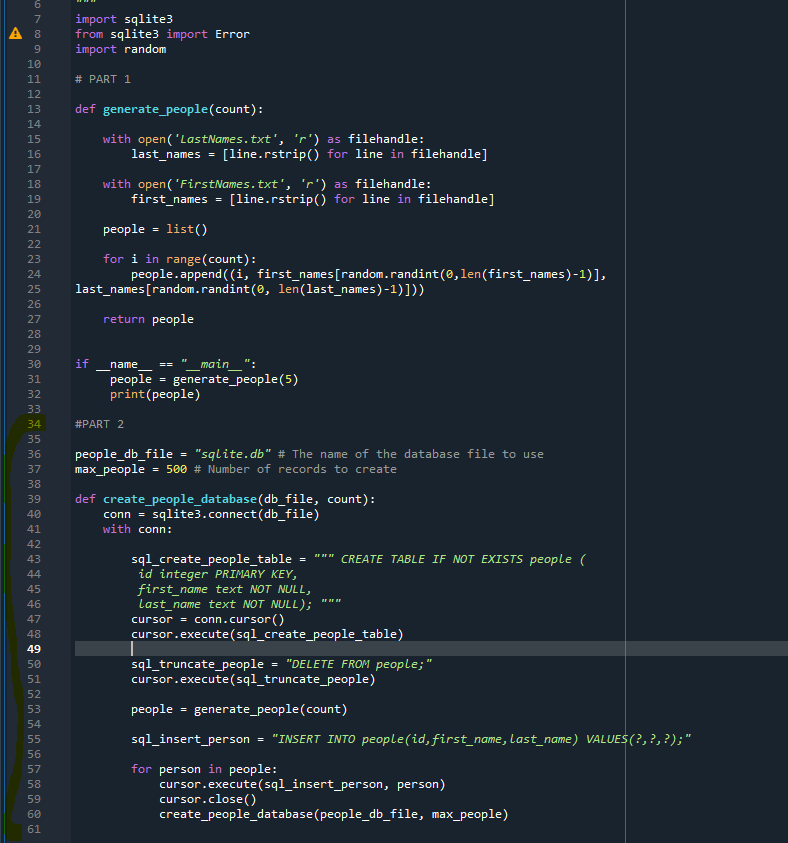
import sqlite3 from sqlite3 import Error Next create the following variables just under the import statements, outside of any method: people_db_file = "sqlite.db" # The name of the database file to use max_people = 500 # Number of records to create . Now, create the create_people_database() function: def create_people_database(db_file, count): Where: o The db_file parameter represents a filename. o The count parameter represents the number of records to generate. The method will first create a connection to SQLite and then utilize a context manager to handle its lifetime: conn = sqlite3.connect(db_file) with conn: ### The rest of the code will go here ### Next, create a SQL command string to create the "people" table, open a cursor and then execute the command (the triple quotes are important for line continuations): sql_create_people_table "" CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS people id integer PRIMARY KEY, first_name text NOT NULL, last_name text NOT NULL); cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.execute(sql_create_people_table) The next step is to truncate any existing data from the table with the following commands: sql_truncate_people = "DELETE FROM people;" cursor.execute(sql_truncate_people) Next, generate a list of person tuples by calling the generate_people() function created in the previous step: people = generate_people(count) Finally, create the query to add the people records and use a for loop to execute the statement: sql_insert_person = "INSERT INTO people(id, first_name, last_name) VALUES (?,?,?);" for person in people: #print (person) # uncomment if you want to see the person object cursor.execute(sql_insert_person, person) #print(cursor.lastrowid) # uncomment if you want to see the row id cursor.close() Now, back in the "_main_" section, execute the create_people_database() function: create_people_database (people_db_file, max_people) There will be no direct output from this method, but you can check the results by using a third party database UI, like DBeaver (https://dbeaver.io/). 6 7 A 8 9 10 11 12 import sqlite3 from sqlite3 import Error import random # PART 1 13 14 15 16 17 18 def generate_people(count): with open('LastNames.txt', 'r') as filehandle: last_names = [line.rstrip() for line in filehandle] with open('FirstNames.txt', 'r') as filehandle: first_names [line.rstrip() for line in filehandle] people list() for i in range(count): people.append((i, first_names[random.randint(0, len(first_names)-1)], last_names [random.randint(0, len(last_names)-1)])) 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 = return people 28 if name "_main__": people generate_people(5) print(people) 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 #PART 2 people_db_file = "sqlite.db" # The name of the database file to use max_people = 500 # Number of records to create 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 BF BF er def create_people_database(db_file, count): conn = sqlite3.connect(db_file) with conn: sql_create_people_table = CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS people ( id integer PRIMARY KEY, first_name text NOT NULL, Last_name text NOT NULL); cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.execute(sql_create_people_table) sql_truncate_people = "DELETE FROM people;" cursor.execute(sql_truncate_people) 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 people generate_people(count) sql_insert_person "INSERT INTO people(id, first_name, Last_name) VALUES (?,?,?);" 56 57 58 59 for person in people: cursor.execute(sql_insert_person, person) cursor.close() create_people_database (people_db_file, max_people) 60 61 import sqlite3 from sqlite3 import Error Next create the following variables just under the import statements, outside of any method: people_db_file = "sqlite.db" # The name of the database file to use max_people = 500 # Number of records to create . Now, create the create_people_database() function: def create_people_database(db_file, count): Where: o The db_file parameter represents a filename. o The count parameter represents the number of records to generate. The method will first create a connection to SQLite and then utilize a context manager to handle its lifetime: conn = sqlite3.connect(db_file) with conn: ### The rest of the code will go here ### Next, create a SQL command string to create the "people" table, open a cursor and then execute the command (the triple quotes are important for line continuations): sql_create_people_table "" CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS people id integer PRIMARY KEY, first_name text NOT NULL, last_name text NOT NULL); cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.execute(sql_create_people_table) The next step is to truncate any existing data from the table with the following commands: sql_truncate_people = "DELETE FROM people;" cursor.execute(sql_truncate_people) Next, generate a list of person tuples by calling the generate_people() function created in the previous step: people = generate_people(count) Finally, create the query to add the people records and use a for loop to execute the statement: sql_insert_person = "INSERT INTO people(id, first_name, last_name) VALUES (?,?,?);" for person in people: #print (person) # uncomment if you want to see the person object cursor.execute(sql_insert_person, person) #print(cursor.lastrowid) # uncomment if you want to see the row id cursor.close() Now, back in the "_main_" section, execute the create_people_database() function: create_people_database (people_db_file, max_people) There will be no direct output from this method, but you can check the results by using a third party database UI, like DBeaver (https://dbeaver.io/). 6 7 A 8 9 10 11 12 import sqlite3 from sqlite3 import Error import random # PART 1 13 14 15 16 17 18 def generate_people(count): with open('LastNames.txt', 'r') as filehandle: last_names = [line.rstrip() for line in filehandle] with open('FirstNames.txt', 'r') as filehandle: first_names [line.rstrip() for line in filehandle] people list() for i in range(count): people.append((i, first_names[random.randint(0, len(first_names)-1)], last_names [random.randint(0, len(last_names)-1)])) 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 = return people 28 if name "_main__": people generate_people(5) print(people) 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 #PART 2 people_db_file = "sqlite.db" # The name of the database file to use max_people = 500 # Number of records to create 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 BF BF er def create_people_database(db_file, count): conn = sqlite3.connect(db_file) with conn: sql_create_people_table = CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS people ( id integer PRIMARY KEY, first_name text NOT NULL, Last_name text NOT NULL); cursor = conn.cursor() cursor.execute(sql_create_people_table) sql_truncate_people = "DELETE FROM people;" cursor.execute(sql_truncate_people) 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 people generate_people(count) sql_insert_person "INSERT INTO people(id, first_name, Last_name) VALUES (?,?,?);" 56 57 58 59 for person in people: cursor.execute(sql_insert_person, person) cursor.close() create_people_database (people_db_file, max_people) 60 61
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


