Question: python please An iterator is a convenient pattern for traversing over all of the elements in some collection (such as a list, string, tuple, etc...).
 python please
python please
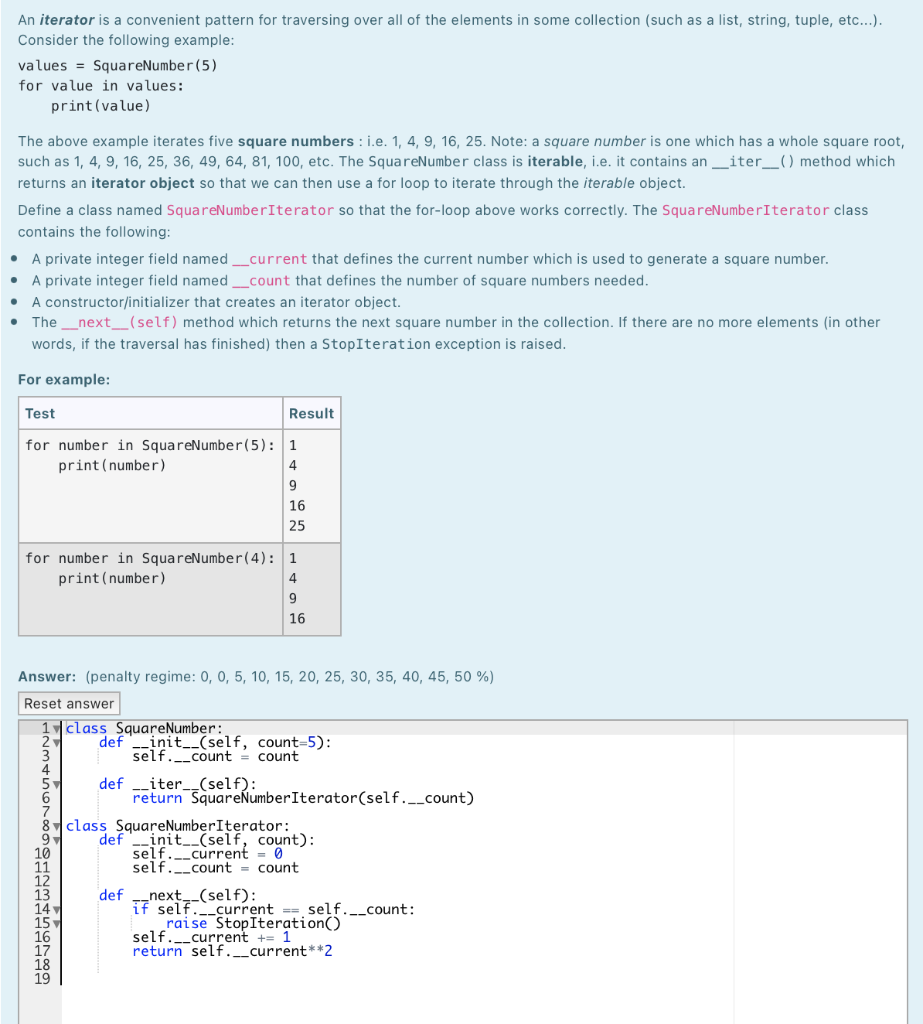
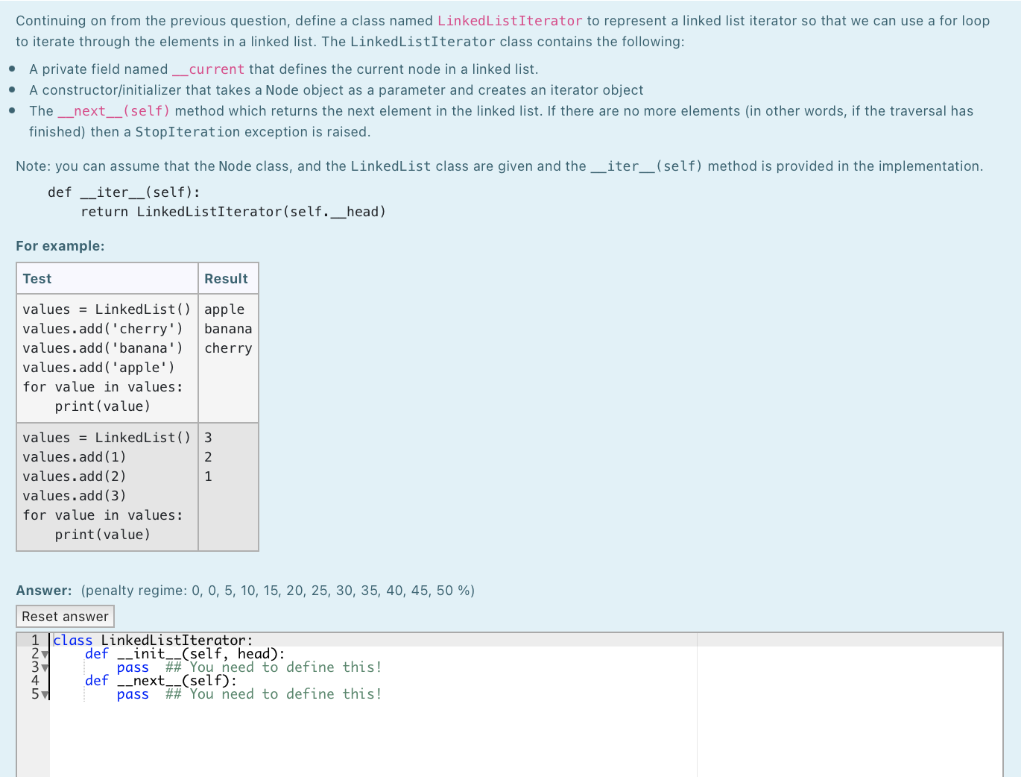
An iterator is a convenient pattern for traversing over all of the elements in some collection (such as a list, string, tuple, etc...). Consider the following example: values = SquareNumber(5) for value in values: print(value) The above example iterates five square numbers : i.e. 1, 4, 9, 16, 25. Note: a square number is one which has a whole square root, such as 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100, etc. The SquareNumber class is iterable, i.e. it contains an _iter__() method which returns an iterator object so that we can then use a for loop to iterate through the iterable object. Define a class named SquareNumberIterator so that the for-loop above works correctly. The SquareNumberIterator class contains the following: A private integer field named _current that defines the current number which is used to generate a square number. A private integer field named _count that defines the number of square numbers needed. A constructor/initializer that creates an iterator object. The __next__(self) method which returns the next square number in the collection. If there are no more elements in other words, if the traversal has finished) then a StopIteration exception is raised. . . For example: Test Result for number in SquareNumber(5): 1 print (number) 4 9 16 25 for number in SquareNumber(4): 1 print (number) 4 9 16 Answer: (penalty regime: 0, 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50 %) Reset answer 1 class SquareNumber: def __init__(self, count=5): self.__count count 5 def __iter-_(self): 6 return SquareNumberIterator(self.__count) 8 class SquareNumberIterator: def --init__(self, count): self.__current = 0 self.__count = count def --next--(self): if self. --current == self.__count: raise Stop Iteration self. __current += 1 return self.__current**2 7 9 BHRB4S889 . Continuing on from the previous question, define a class named LinkedListIterator to represent a linked list iterator so that we can use a for loop to iterate through the elements in a linked list. The LinkedListIterator class contains the following: A private field named current that defines the current node in a linked list. A constructor/initializer that takes a Node object as a parameter and creates an iterator object The_next__(self) method which returns the next element in the linked list. If there are no more elements (in other words, if the traversal has finished) then a Stop Iteration exception is raised. . . Note: you can assume that the Node class, and the LinkedList class are given and the _iter_(self) method is provided in the implementation. def __iter__(self): return LinkedListIterator(self._head) For example: Test Result values = LinkedList() apple values.add('cherry') banana values.add('banana') cherry values.add('apple') for value in values: print(value) values = LinkedList() 3 values.add(1) 2 values.add(2) 1 values.add(3) for value in values: print(value) Answer: (penalty regime: 0, 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50 %) Reset answer 1 class LinkedListIterator: 2-1 def _init__(self, head): 3 pass ## You need to define this! 4 def -_next__(self): 54 pass ## You need to define this
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


