Question: python. please show all 3 files needed...everything needed is shown. This week you will work again with the NetwrokTime-Experimental script. You will then add detailed
python. please show all 3 files needed...everything needed is shown.
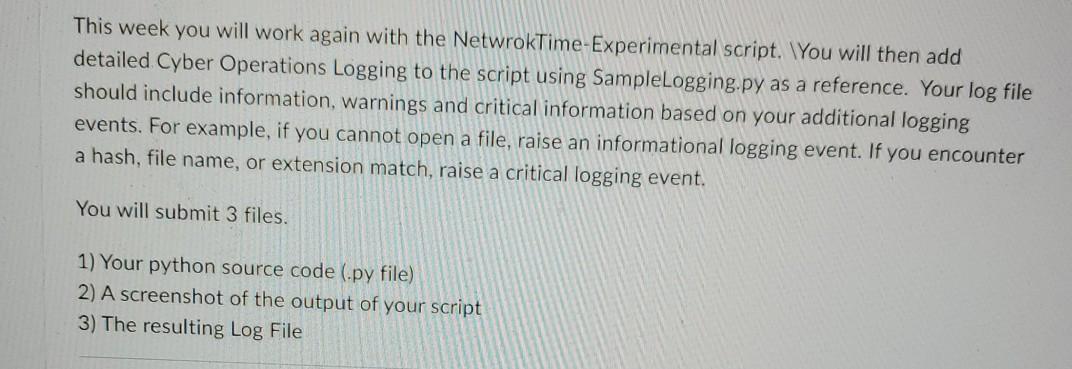
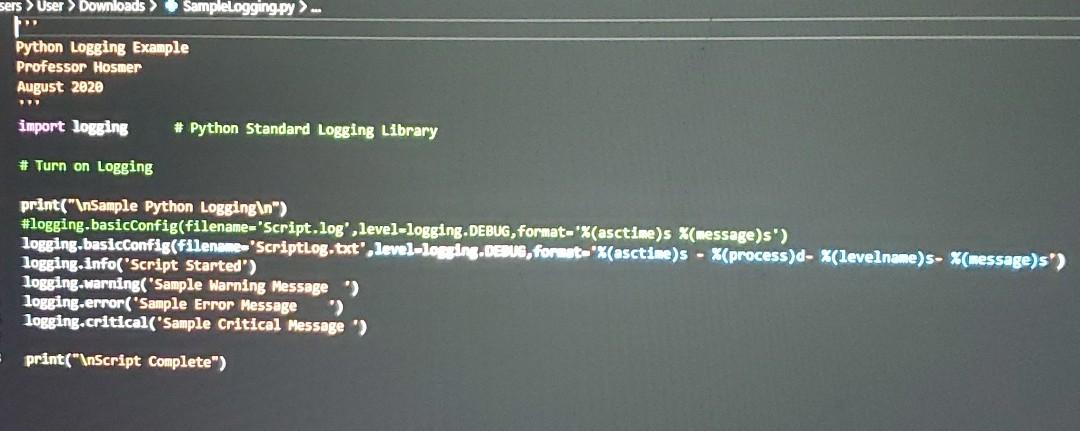
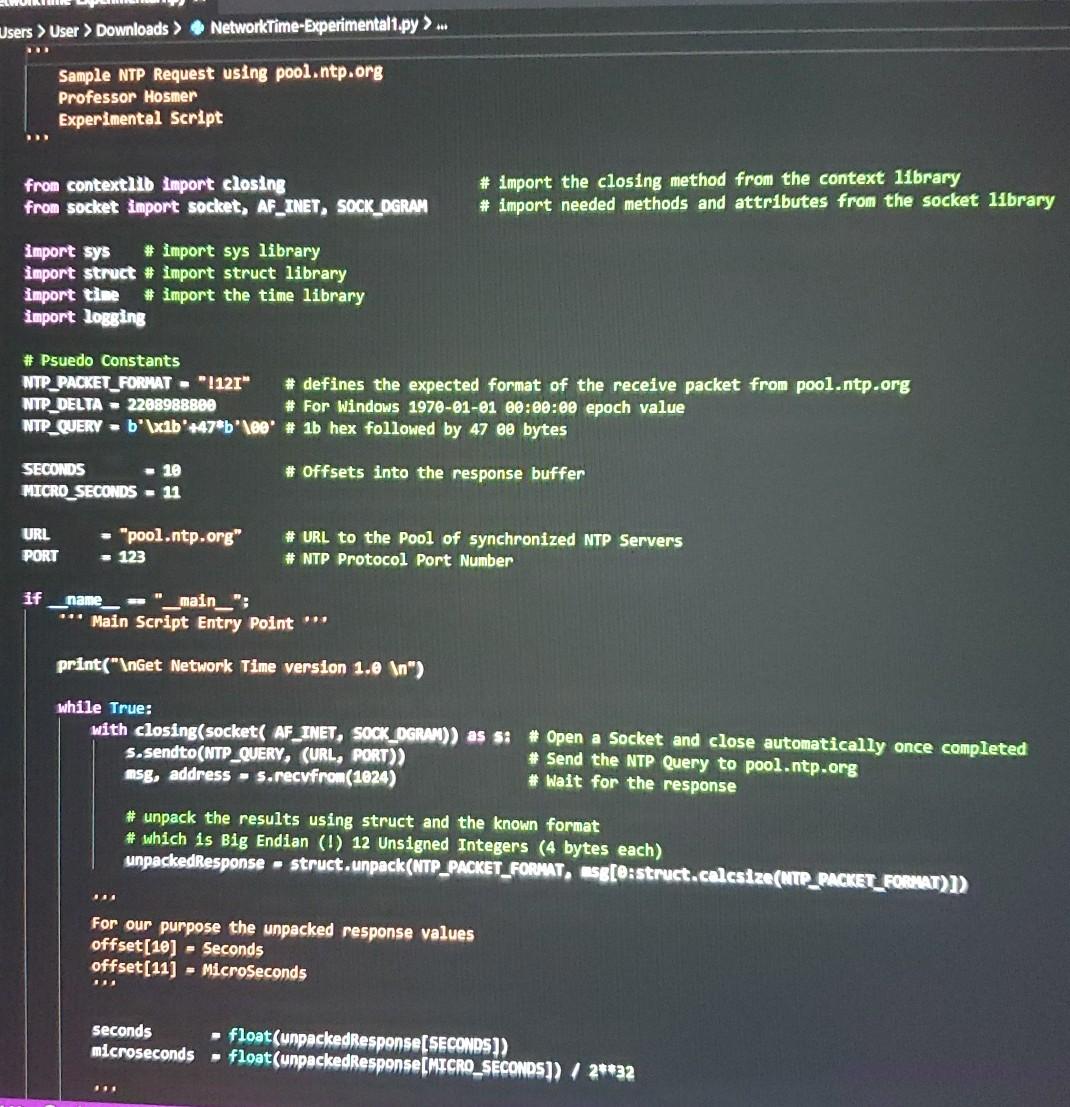
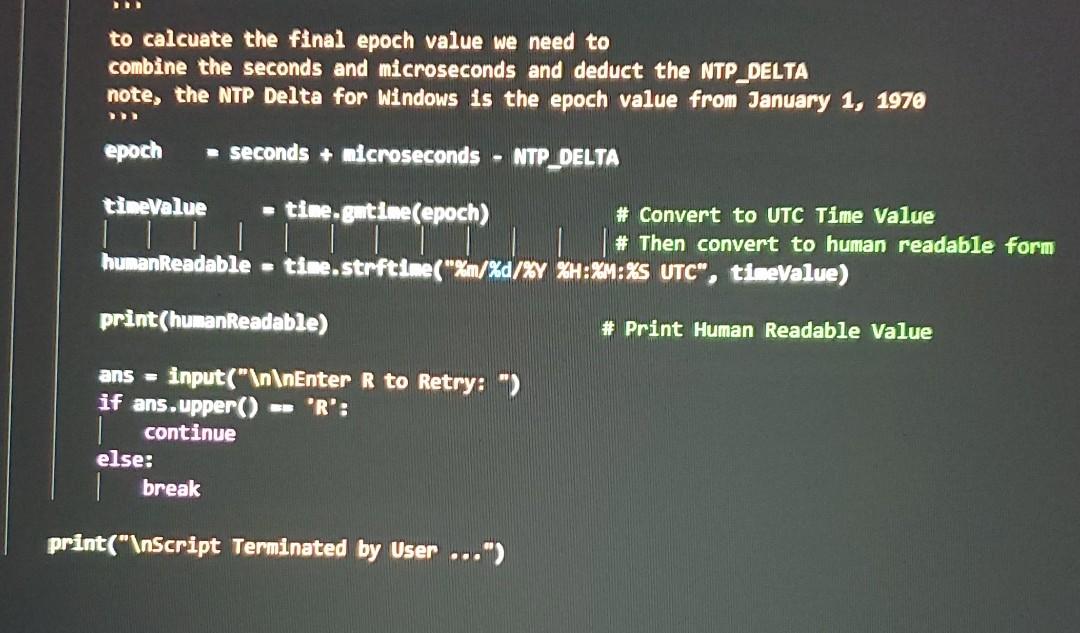
This week you will work again with the NetwrokTime-Experimental script. You will then add detailed Cyber Operations Logging to the script using SampleLogging.py as a reference. Your log file should include information, warnings and critical information based on your additional logging events. For example, if you cannot open a file, raise an informational logging event. If you encounter a hash, file name, or extension match, raise a critical logging event. You will submit 3 files. 1) Your python source code (.py file) 2) A screenshot of the output of your script 3) The resulting Log File sers > User Downloads SampleLogging.py Python Logging Example Professor Hosmer August 2020 import logging # Python Standard Logging Library # Turn on Logging print(" Sample Python Logging ") #logging.basicConfig(filename="Script.log', level-logging.DEBUG, format-'%(asctime)s X(message)s') logging basicConfig(filename 'Scriptlog.txt", level-logging.DEBUG, format X(asctime)s - X(process)d- %(levelname)s- %(message)s") logging.info('Script Started") logging.warning( "Sample Warning Message) logging.error("Sample Error Message logging.critical('Sample Critical Message > print(" Script Complete") Users > User > Downloads > NetworkTime-Experimental1.py >... Sample NTP Request using pool.ntp.org Professor Hosmer Experimental Script from contextlib Import closing from socket import socket, AF_INET, SOCK_OGRAM # import the closing method from the context library # import needed methods and attributes from the socket 11brary import sys # import sys library import struct # import struct library import time # import the time library import logging # Psuedo Constants NTP_PACKET_FORMAT - 1121" # defines the expected format of the receive packet from pool.ntp.org NTP_DELTA - 2288988800 # For Windows 1970-01-01 00:00:00 epoch value NTP_QUERY -b'\xib'+47*b'\00 # 1b hex followed by 47 e0 bytes # offsets into the response buffer SECONDS - 10 MICRO_SECONDS - 11 URL PORT - "pool.ntp.org" # URL to the pool of synchronized NTP Servers # NTP Protocol Port Number - 123 if name -- "_main__": *** Main Script Entry Point print(" Get Network Time version 1.0 ") while True: with closing(socket( AF_INET, SOCK_OGRAM)) as si # Open a Socket and close automatically once completed s.sendto(NTP_QUERY, (URL, PORT)) # Send the NTP Query to pool.ntp.org msg, address - s.recvfrom (1024) # Wait for the response # unpack the results using struct and the known format # which is Big Endian (!) 12 Unsigned Integers (4 bytes each) unpackedResponse - struct.unpack(NTP_PACKET_FORMAT, Esg[e:struct.calcsize(NTP_PACKET_FORMAT)]) . For our purpose the unpacked response values offset(10) - Seconds offset(11) - MicroSeconds .. seconds microseconds float(unpackedResponse SECONDS)) float(unpackedResponse(MICRO_SECONDS]) / 2**32 to calcuate the final epoch value we need to combine the seconds and microseconds and deduct the NTP_DELTA note, the NTP Delta for Windows is the epoch value from January 1, 1970 epoch seconds + microseconds NTP_DELTA amerele de timeValue time.gmtime(epoch) # Convert to UTC Time Value TUTTI # Then convert to human readable form humanReadable = time.strftime("%m/%d/%Y %H:%M:%S UTC", timeValue) print(humanReadable) # Print Human Readable Value ans = input(" Enter R to Retry:-) if ans.upper() == 'R': continue else: break print(" Script Terminated by User ...") This week you will work again with the NetwrokTime-Experimental script. You will then add detailed Cyber Operations Logging to the script using SampleLogging.py as a reference. Your log file should include information, warnings and critical information based on your additional logging events. For example, if you cannot open a file, raise an informational logging event. If you encounter a hash, file name, or extension match, raise a critical logging event. You will submit 3 files. 1) Your python source code (.py file) 2) A screenshot of the output of your script 3) The resulting Log File sers > User Downloads SampleLogging.py Python Logging Example Professor Hosmer August 2020 import logging # Python Standard Logging Library # Turn on Logging print(" Sample Python Logging ") #logging.basicConfig(filename="Script.log', level-logging.DEBUG, format-'%(asctime)s X(message)s') logging basicConfig(filename 'Scriptlog.txt", level-logging.DEBUG, format X(asctime)s - X(process)d- %(levelname)s- %(message)s") logging.info('Script Started") logging.warning( "Sample Warning Message) logging.error("Sample Error Message logging.critical('Sample Critical Message > print(" Script Complete") Users > User > Downloads > NetworkTime-Experimental1.py >... Sample NTP Request using pool.ntp.org Professor Hosmer Experimental Script from contextlib Import closing from socket import socket, AF_INET, SOCK_OGRAM # import the closing method from the context library # import needed methods and attributes from the socket 11brary import sys # import sys library import struct # import struct library import time # import the time library import logging # Psuedo Constants NTP_PACKET_FORMAT - 1121" # defines the expected format of the receive packet from pool.ntp.org NTP_DELTA - 2288988800 # For Windows 1970-01-01 00:00:00 epoch value NTP_QUERY -b'\xib'+47*b'\00 # 1b hex followed by 47 e0 bytes # offsets into the response buffer SECONDS - 10 MICRO_SECONDS - 11 URL PORT - "pool.ntp.org" # URL to the pool of synchronized NTP Servers # NTP Protocol Port Number - 123 if name -- "_main__": *** Main Script Entry Point print(" Get Network Time version 1.0 ") while True: with closing(socket( AF_INET, SOCK_OGRAM)) as si # Open a Socket and close automatically once completed s.sendto(NTP_QUERY, (URL, PORT)) # Send the NTP Query to pool.ntp.org msg, address - s.recvfrom (1024) # Wait for the response # unpack the results using struct and the known format # which is Big Endian (!) 12 Unsigned Integers (4 bytes each) unpackedResponse - struct.unpack(NTP_PACKET_FORMAT, Esg[e:struct.calcsize(NTP_PACKET_FORMAT)]) . For our purpose the unpacked response values offset(10) - Seconds offset(11) - MicroSeconds .. seconds microseconds float(unpackedResponse SECONDS)) float(unpackedResponse(MICRO_SECONDS]) / 2**32 to calcuate the final epoch value we need to combine the seconds and microseconds and deduct the NTP_DELTA note, the NTP Delta for Windows is the epoch value from January 1, 1970 epoch seconds + microseconds NTP_DELTA amerele de timeValue time.gmtime(epoch) # Convert to UTC Time Value TUTTI # Then convert to human readable form humanReadable = time.strftime("%m/%d/%Y %H:%M:%S UTC", timeValue) print(humanReadable) # Print Human Readable Value ans = input(" Enter R to Retry:-) if ans.upper() == 'R': continue else: break print(" Script Terminated by User ...")
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


