Question: Python problem Element-wise operations. As stated above relational operations on numpy arrays are performed element-wise. Examples we mentioned before are The == operator The addition
Python problem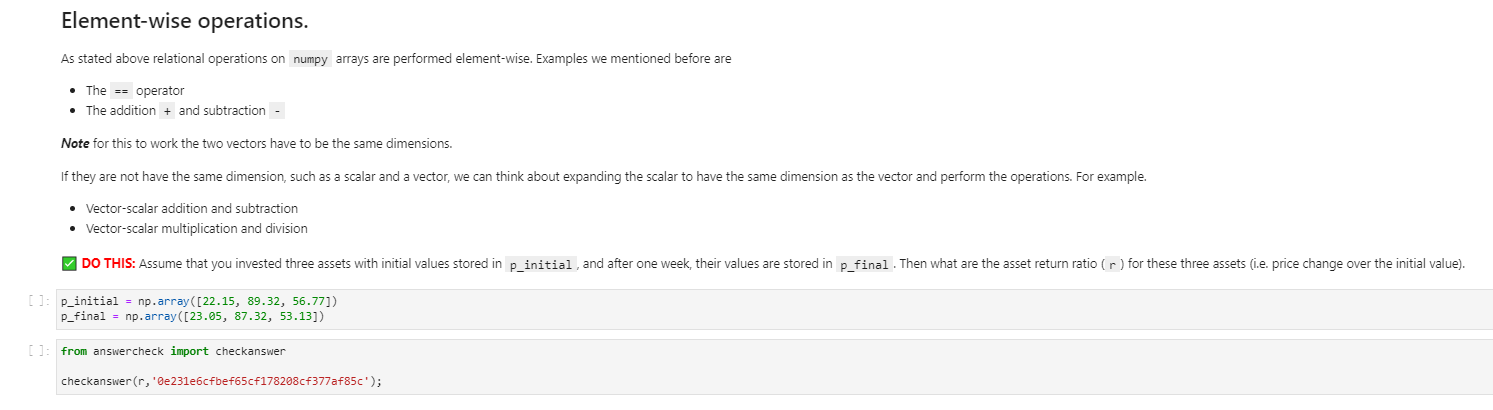
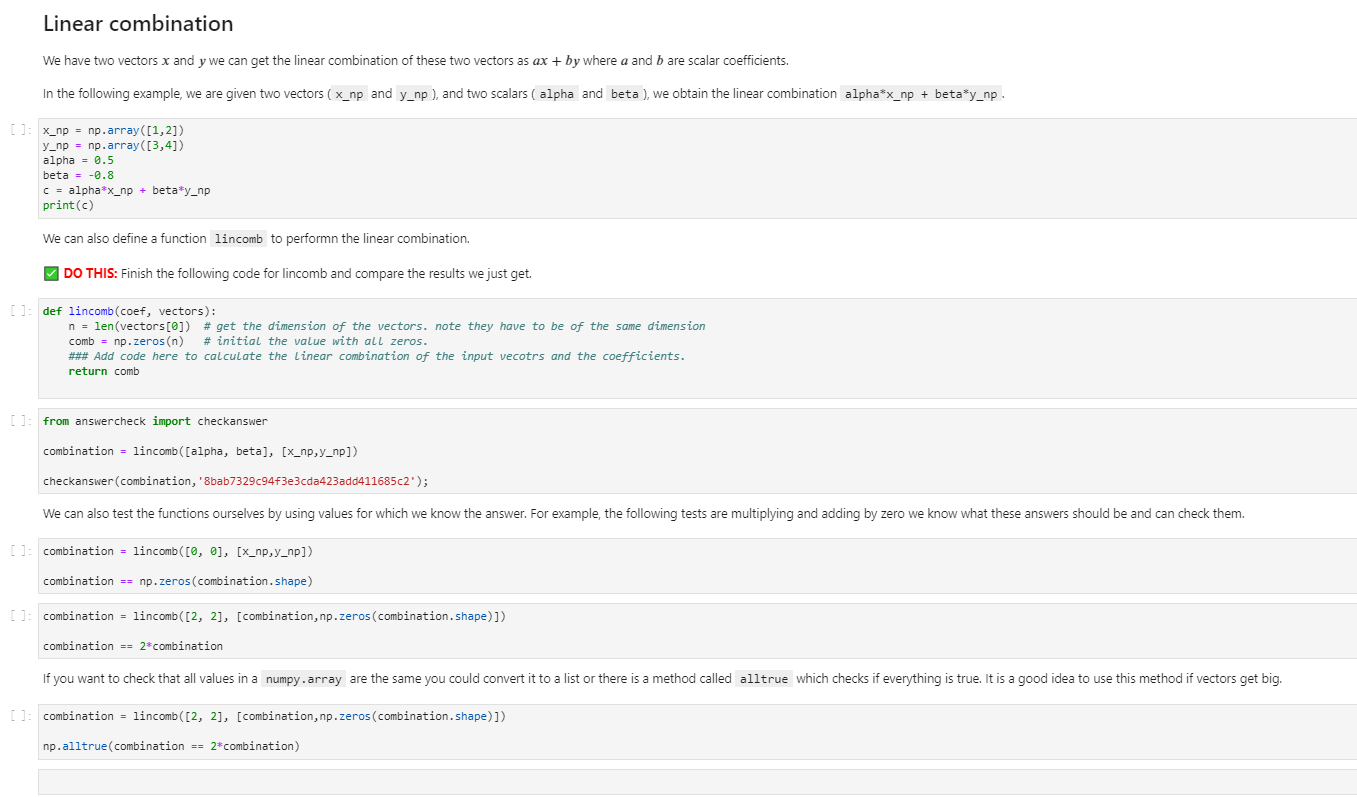
Element-wise operations. As stated above relational operations on numpy arrays are performed element-wise. Examples we mentioned before are The == operator The addition + and subtraction - Note for this to work the two vectors have to be the same dimensions. If they are not have the same dimension, such as a scalar and a vector, we can think about expanding the scalar to have the same dimension as the vector and perform the operations. For example. Vector-scalar addition and subtraction Vector-scalar multiplication and division DO THIS: Assume that you invested three assets with initial values stored in p_initial and after one week, their values are stored in p_final. Then what are the asset return ratio (r) for these three assets (i.e. price change over the initial value). [] p_initial = np.array([22.15, 89.32, 56.77]) p_final = np.array([23.65, 87.32, 53.13]) []: from answercheck import checkanswer checkanswer (r, 'Be231e6cfbef65cf178208cf377af85c'); Linear combination We have two vectors x and y we can get the linear combination of these two vectors as ax + by where a and bare scalar coefficients. In the following example, we are given two vectors (x_np and y_np ), and two scalars ( alpha and beta), we obtain the linear combination alphax_np + beta*y_np . []: x_np = np.array([1,2]) y_np = np.array([3,4]) alpha = 0.5 beta = -0.8 C = alphax_np + beta*y_np print(c) We can also define a function lincomb to performn the linear combination. DO THIS: Finish the following code for lincomb and compare the results we just get. []: def lincomb (coef, vectors): n = len(vectors[0]) # get the dimension of the vectors. note they have to be of the same dimension comb np.zeros(n) # initial the value with all zeros. ### Add code here to calculate the Linear combination of the input vecotrs and the coefficients. return comb []: from answercheck import checkanswer combination = lincomb((alpha, beta], [x_np,y_np]) checkanswer (combination, '8bab7329c94f3e3cda423add411685c2'); We can also test the functions ourselves by using values for which we know the answer. For example, the following tests are multiplying and adding by zero we know what these answers should be and can check them. []: combination = lincomb ([0, 0], [x_np,y_np]) combination == np.zeros(combination.shape) []: combination = lincomb ([2, 2], [combination, np.zeros(combination. shape)]) combination == 2* combination If you want to check that all values in a numpy.array are the same you could convert it to a list or there is a method called alltrue which checks if everything is true. It is a good idea to use this method if vectors get big. []: combination = lincomb ([2, 2], [combination, np.zeros(combination. shape)]) np.alltrue (combination == 2*combination)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


