Question: python programing Average Magnitude Data For this problem, we will be using a dataset containing information about earthquakes around the world. The dataset looks like
 python programing
python programing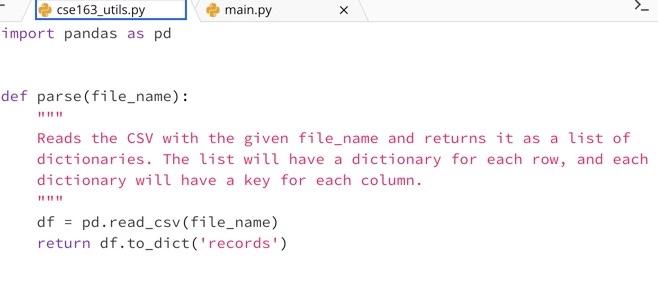
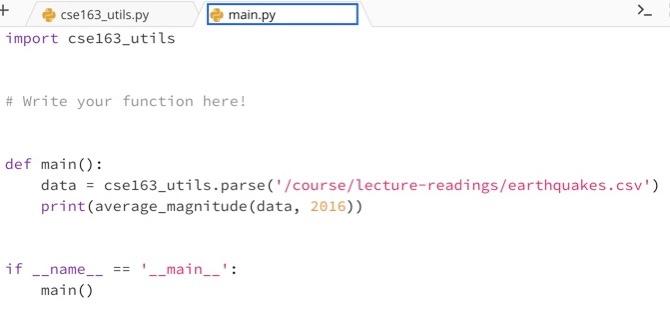
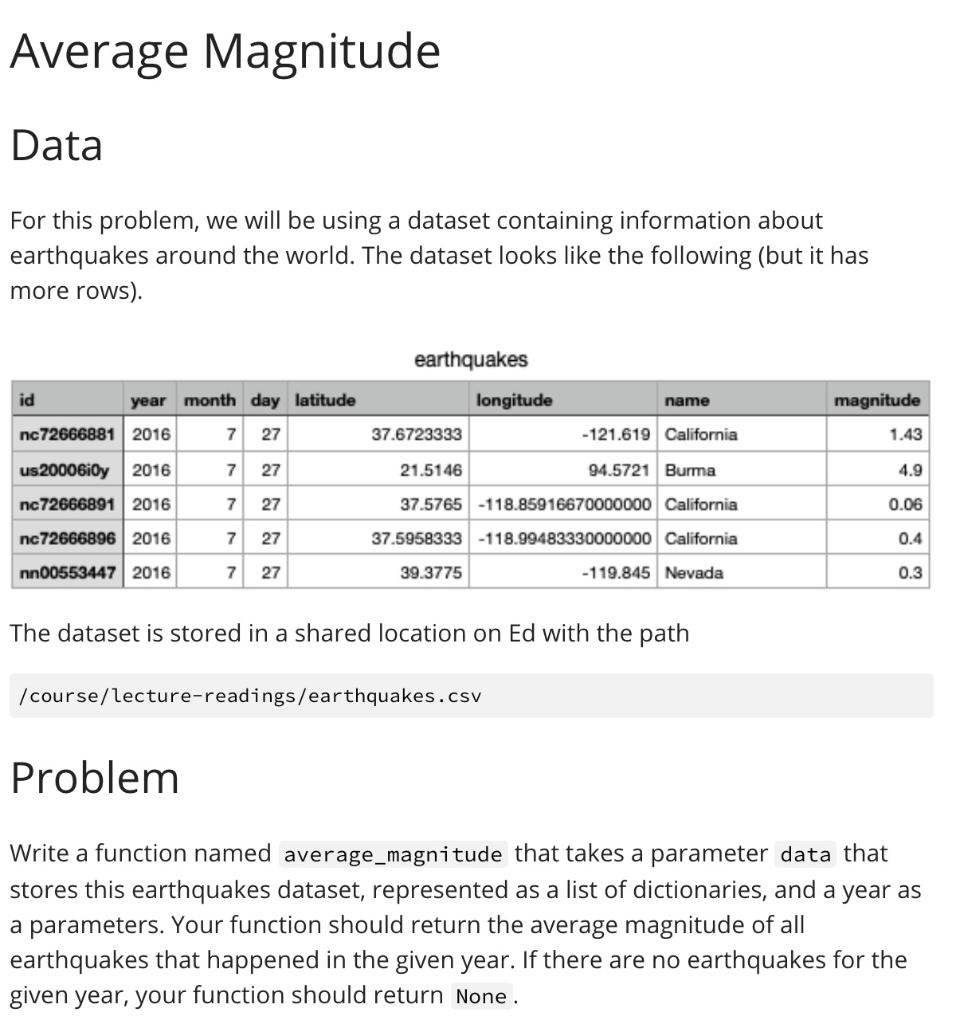
Average Magnitude Data For this problem, we will be using a dataset containing information about earthquakes around the world. The dataset looks like the following (but it has more rows). earthquakes longitude id year month day latitude name magnitude nc 72666881 2016 7 27 37.6723333 -121.619 California 1.43 us20006iOy 2016 7 27 21.5146 94.5721 Burma 4.9 nc 72666891 2016 7 27 37.5765 -118.85916670000000 California 0.06 nc72666896 2016 7 27 37.5958333 -118.99483330000000 California 0.4 nn00553447 2016 7 27 39.3775 -119.845 Nevada 0.3 The dataset is stored in a shared location on Ed with the path /course/lecture-readings/earthquakes.csv Problem Write a function named average_magnitude that takes a parameter data that stores this earthquakes dataset, represented as a list of dictionaries, and a year as a parameters. Your function should return the average magnitude of all earthquakes that happened in the given year. If there are no earthquakes for the given year, your function should return None. Problem Write a function named average_magnitude that takes a parameter data that stores this earthquakes dataset, represented as a list of dictionaries, and a year as a parameters. Your function should return the average magnitude of all earthquakes that happened in the given year. If there are no earthquakes for the given year, your function should return None. For example, if we called average_magnitude (data, 2016), where data stored a list of dictionaries representing the five rows in the image above, it would return 1.418. You should not assume the dataset passed has the exact same values or the number of rows as the one shown above. For example, you should not assume the dataset has more than one row. However, you should assume the dataset provided will have all of the columns provided for any row in the dataset (we sometimes call the set of columns of a CSV its schema). Note that you do not need to worry about how to parse the data from the CSV format to the list of dictionaries. We implemented this functionality in cse163_utils.py and already wrote the code in the main method to call that function for the earthquakes file. main.py cse163_utils.py import pandas as pd def parse(file_name): Reads the csv with the given file_name and returns it as a list of dictionaries. The list will have a dictionary for each row, and each dictionary will have a key for each column. 111111 df = pd.read_csv(file_name) return df.to_dict('records) + cse 163_utils.py import cse163_utils main.py # Write your function here! def main(): data = cse163_utils.parse("/course/lecture-readings/earthquakes.csv') print(average_magnitude (data, 2016)) if __main__': -_name_- main()
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


