Question: Q 1 ) Dynamic Force Analysis a . Draw free body diagrams of links 2 , 3 , 4 , and 5 . Solve the
Q Dynamic Force Analysis
a Draw free body diagrams of links and Solve the dynamic force analysis
problem by writing a computer program which solves all the unknown variables.
Your results must contain the X and Y components of internal reaction forces and
input torque for degree increments of the input angle. Present your results in
tabular format and as plots. Discuss important points that you observe from the
plots.
b Repeat the dynamic force analysis for: a
N; and b
N
Comment on the significance of the magnitude of this external force on the dynamic
behavior of the mechanism.
c Discuss free body diagrams of the linkage for a clockwise rotation of the input link
at the same angular speed Provide insights into the distinctions observed in
internal reaction forces and crank torque.
Q Compare static and dynamic force analysis
a Modify your program in Question to perform static force analysis for degree
increments of the input link. Show the X and Y components of the internal reaction
forces, the crank torque, and any other unknown variables, for degree increments
of the input link tables and plots
b Comment on the similarities and differences with results in dynamic force analysis.
Q Power Equation Analysis
a Formulate the symbolic power equation for the linkage. Utilize the equation of
motion to generate tables and plots illustrating the crank torque at degree
intervals of the input link.
b Compare your results in c with the crank torque obtained from the dynamic force
analysis. Comment on any similarities or differences.
IF YOU SOLVE CORRECT THEN I WILL GIVE YOU GOOD REVIEW!
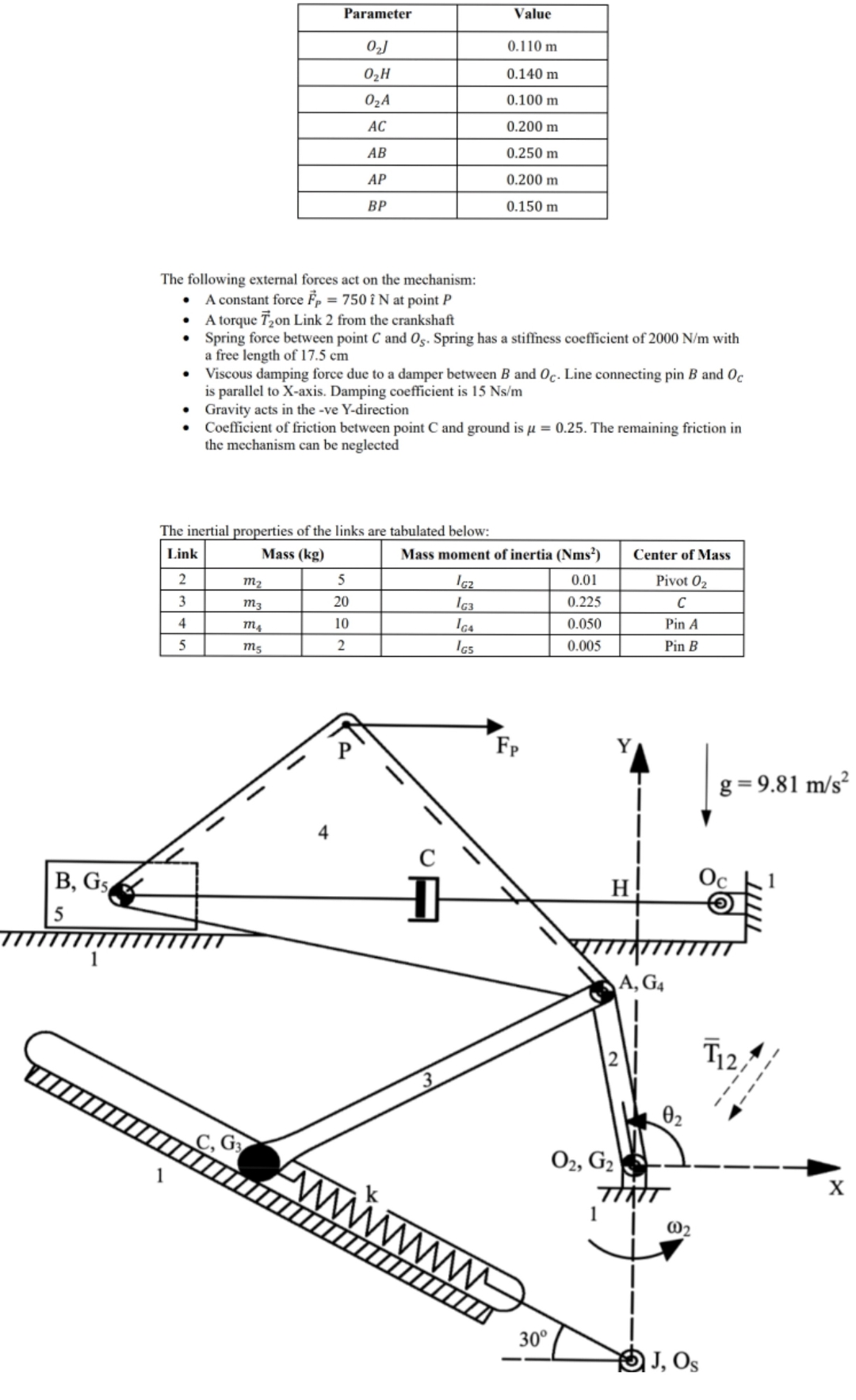
tableParameterValue m m m m m m m
The following external forces act on the mechanism:
A constant force vechat at point
A torque vec on Link from the crankshaft
Spring force between point and Spring has a stiffness coefficient of with a free length of cm
Viscous damping force due to a damper between and Line connecting pin and is parallel to X axis. Damping coefficient is
Gravity acts in the ve Ydirection
Coefficient of friction between point C and ground is The remaining friction in the mechanism can be neglected
The inertial properties of the links are tabulated below:
tableLinkMass kgMass moment of inertia Nms Center of MassPivot
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


