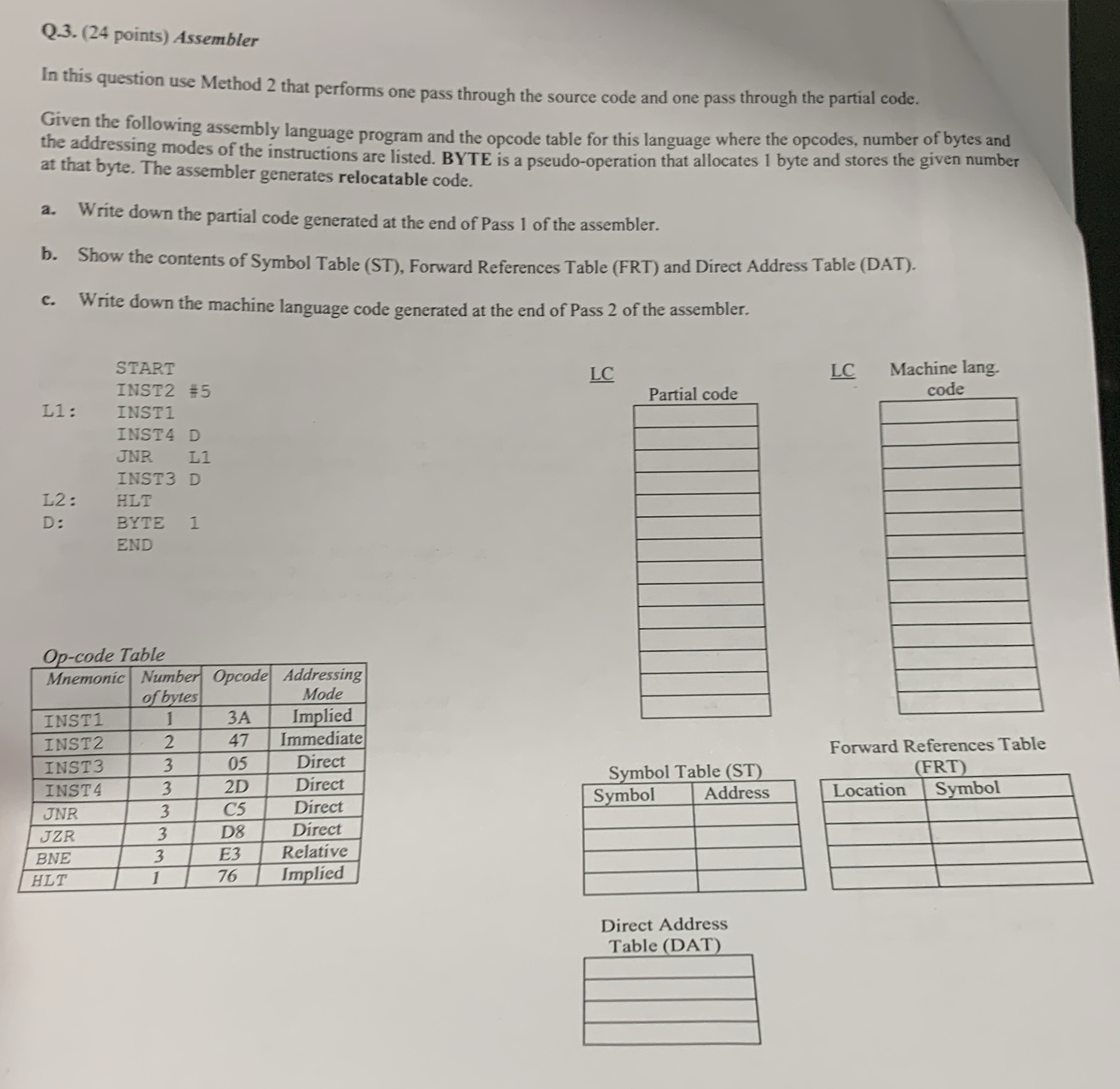
Question: Q . 3 . ( 2 4 points ) Assembler In this question use Method 2 that performs one pass through the source code and
Q points Assembler
In this question use Method that performs one pass through the source code and one pass through the partial code.
Given the following assembly language program and the opcode table for this language where the opcodes, number of bytes and the addressing modes of the instructions are listed. BYTE is a pseudooperation that allocates byte and stores the given number at that byte. The assembler generates relocatable code.
a Write down the partial code generated at the end of Pass of the assembler.
b Show the contents of Symbol Table ST Forward References Table FRT and Direct Address Table DAT
c Write down the machine language code generated at the end of Pass of the assembler.
tableSTARTINST #L:INSTINST DJNR LINST DL:HLTD:BYTE END
Opcode Table
tableMnemonictableNumberof bytesOpcode,tableAddressingModeINSTImpliedINSTImmediateINST DirectINSTDirectJNRC DirectJZRD DirectBNEE RelativeHLTImplied
Partial code
table
Symbol Table ST
tableSymbolAddress
Direct Address Table DAT
Machine lang. code
Forward References Table FRT
tableLocationSymbol
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


