Question: Q 4 ( a ) A car ferry, operating in pure water ( that is , = 1 0 0 0 k g m 3
Q
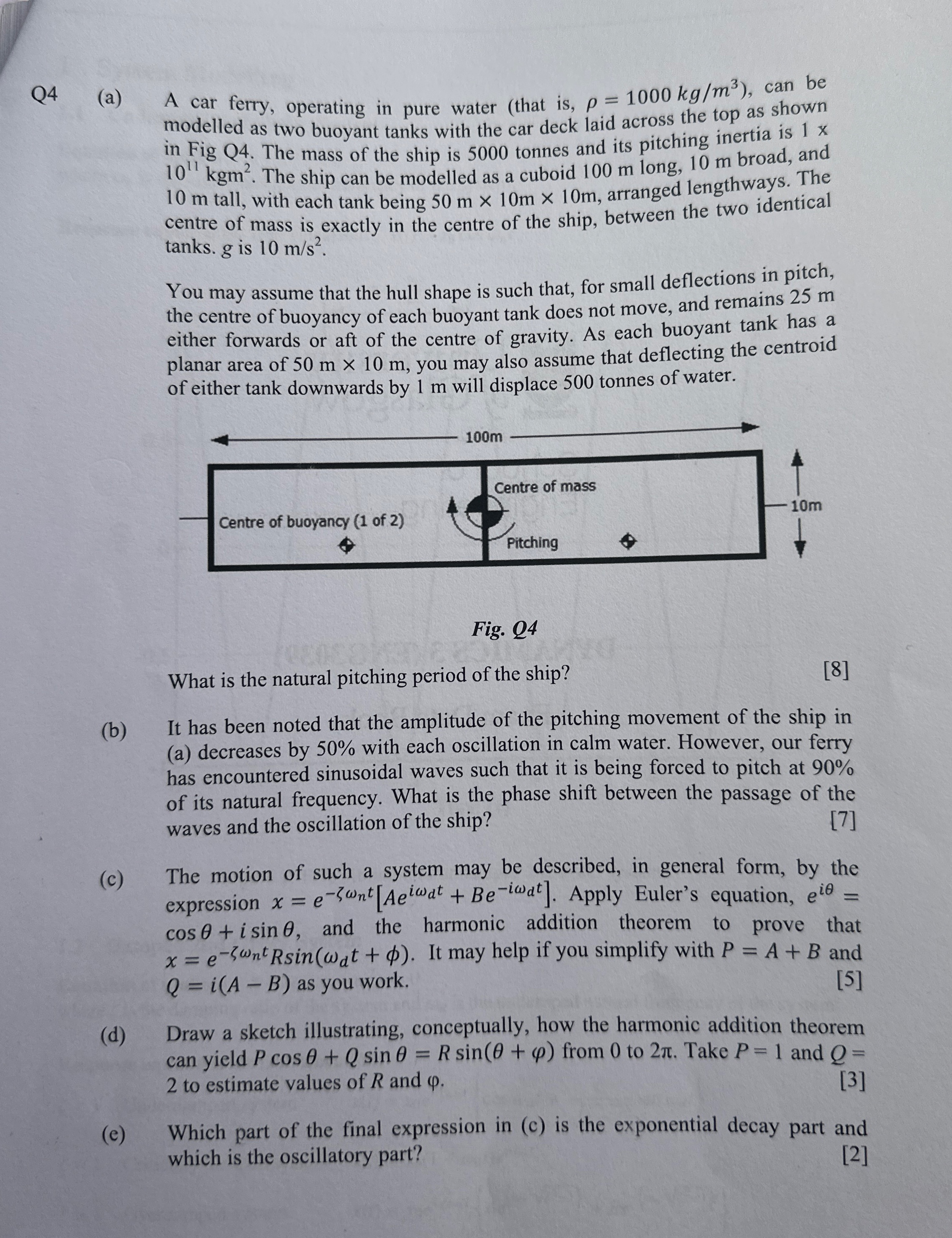
a A car ferry, operating in pure water that is can be modelled as two buoyant tanks with the car deck laid across the top as shown in Fig Q The mass of the ship is tonnes and its pitching inertia is The ship can be modelled as a cuboid m long, m broad, and m tall, with each tank being arranged lengthways. The centre of mass is exactly in the centre of the ship, between the two identical tanks. is
You may assume that the hull shape is such that, for small deflections in pitch, the centre of buoyancy of each buoyant tank does not move, and remains m either forwards or aft of the centre of gravity. As each buoyant tank has a planar area of you may also assume that deflecting the centroid of either tank downwards by m will displace tonnes of water.
Fig. Q
What is the natural pitching period of the ship?
b It has been noted that the amplitude of the pitching movement of the ship in a decreases by with each oscillation in calm water. However, our ferry has encountered sinusoidal waves such that it is being forced to pitch at of its natural frequency. What is the phase shift between the passage of the waves and the oscillation of the ship?
c The motion of such a system may be described, in general form, by the expression Apply Euler's equation, and the harmonic addition theorem to prove that Rsin It may help if you simplify with and as you work.
d Draw a sketch illustrating, conceptually, how the harmonic addition theorem can yield PcosQsinRsin from to Take and to estimate values of and
e Which part of the final expression in c is the exponential decay part and which is the oscillatory part?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


