Question: Q: Explain what does Table 1 and Table 2 present in the article. 556 J.F. Super Table 1. Steps in the task engagement and learning
Q: Explain what does Table 1 and Table 2 present in the article.
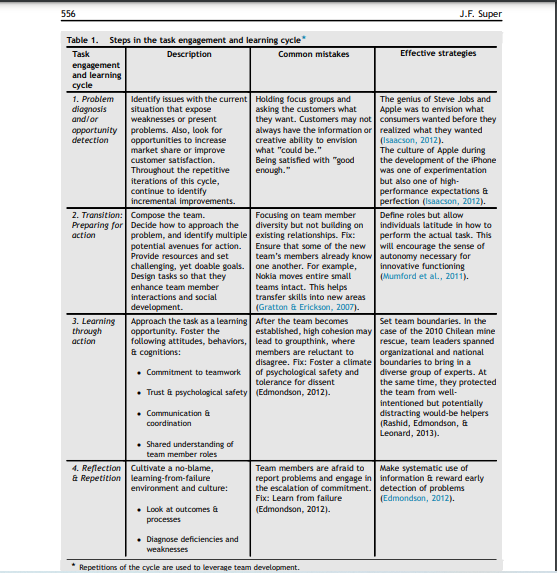
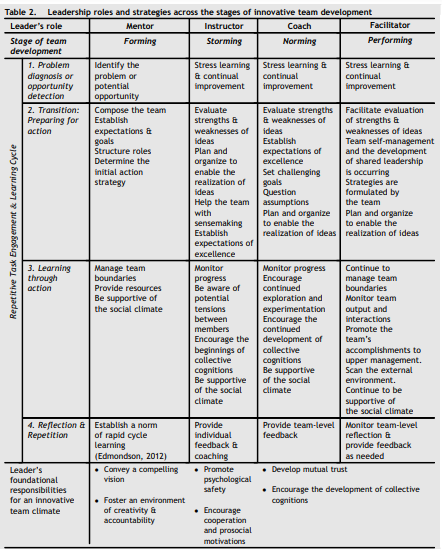
556 J.F. Super Table 1. Steps in the task engagement and learning cycle Task Description Common mistakes Effective strategies engagement and learning cycle 1. Problem Identify issues with the current Holding focus groups and The genius of Steve Jobs and diagnosis situation that expose asking the customers what Apple was to erwision what and/or weaknesses or present they want. Customers may not consumers wanted before they opportunity problems. Also, look for always have the information or realized what they wanted detection opportunities to increase creative ability to envision (Isaacson, 2012). market share or improve what "could be." The culture of Apple during customer satisfaction. Being satisfied with "good the development of the iPhone Throughout the repetitive enough." was one of experimentation iterations of this cycle, but also one of high- continue to identify performance expectations & incremental improvements. perfection (Isaacson, 2012). 2. Transition: Compose the team. Focusing on team member Define roles but allow Preparing for Decide how to approach the diversity but not building on individuals latitude in how to action problem, and identify multiple existing relationships. Fix: perform the actual task. This potential avenues for action. Ensure that some of the new will encourage the sense of Provide resources and set team's members already know autonomy necessary for challenging, yet doable goals. one another. For example, innovative functioning Design tasks so that they Nokia moves entire small (Mumford et al., 2011). enhance team member teams intact. This helps interactions and social transfer skills into new areas development. (Gratton & Erickson, 2007). 3. Learning Approach the task as a learning After the team becomes Set team boundaries. In the through opportunity. Foster the established, high cohesion may case of the 2010 Chilean mine action following attitudes, behaviors, lead to groupthink, where rescue, team leaders spanned Et cognitions: members are reluctant to organizational and national disagree. Fix: Foster a climate boundaries to bring in a Commitment to teamwork of psychological safety and diverse group of experts. At tolerance for dissent the same time, they protected the team from well- intentioned but potentially Communication a distracting would be helpers coordination (Rashid, Edmondson, Et Leonard, 2013). Shared understanding of team member roles 4. Reflection Cultivate a no-blame, Team members are afraid to Make systematic use of & Repetition learning-from-failure report problems and engage in information Et reward early environment and culture: the escalation of commitment.detection of problems Fix: Learn from failure (Edmondson, 2012). Look at outcomes & (Edmondson, 2012). processes Trust psychological safety (Edmondson, 2012). Diagnose deficiencies and weaknesses Repetitions of the cycle are used to leverage team development. Table 2. Leadership roles and strategies across the stages of innovative team development Leader's role Mentor Instructor Coach Facilitator Forming Storming Norming Performing Stage of team development 1. Problem diagnosis or opportunity detection Stress leaming & continual improvement Stress learning & continual improvement Stress learning & continual improvement 2. Transition: Preparing for action Identify the problem or potential opportunity Compose the team Establish expectations goals Structure roles Determine the initial action strategy Repetitive Task Engagement & Learning Cycle Evaluate Evaluate strengths Facilitate evaluation strengths Et & weaknesses of of strengths & weaknesses of ideas weaknesses of ideas ideas Establish Team self-management Plan and expectations of and the development organize to excellence of shared leadership enable the Set challenging is occurring realization of goals Strategies are ideas Question formulated by Help the team assumptions the team with Plan and organize Plan and organize sensemaking to enable the to enable the Establish realization of ideas realization of ideas expectations of excellence Monitor 3. Learning through action Manage team boundaries Provide resources Be supportive of the social climate progress Be aware of potential tensions between members Encourage the beginnings of collective cognitions Be supportive of the social Monitor progress Continue to Encourage manage team continued boundaries exploration and Monitor team experimentation output and Encourage the interactions continued Promote the development of team's collective accomplishments to cognitions upper management, Be supportive Scan the external of the social environment. climate Continue to be supportive of the social climate Provide team-level Monitor team-level feedback reflection et provide feedback as needed climate 4. Reflection & Establish a norm Repetition of rapid cycle learning (Edmondson, 2012) Provide individual feedback at Convey a compelling vision Develop mutual trust coaching Promote psychological safety Leader's foundational responsibilities for an innovative Encourage the development of collective cognitions team climate Foster an environment of creativity a accountability Encourage cooperation and prosocial motivations






