Question: Q) This assignment handles object oriented programming: Write a main class named myNumberList which has the following functions: - constructor: has an optional argument that
Q)
This assignment handles object oriented programming:
Write a main class named myNumberList which has the following functions:
- constructor: has an optional argument that will be added to the list
- add(value): will insert it at the end of the list
- remove(value): will remove the item from the list (if item is there multiple times, it removes all occurrences.
- head(): returns the value in the beginning of the list
- getList(): will return the list
- if I call print(myNumberList) the list should be printed
Write a subclass named myRevOrderedNumberList (from high to low) which has overwrites
- head() function and returns the highest value and
- overwrites the print functionality to be printed appropriately
- getList(): will return the list
Some general notes:
- your lists do only handle numbers (float + int); if a function receives anything else, print a warning and ignore it.
- if variables are used, they should be all private
myL = myNumberList()
myL.add(15)
myL.add(20)
myL.add(1)
print(myL.head()) #15
print(myL) #[15,20,1]
myL.add("5") #Only numbers can be added.
print(myL) #[15,20,1]
myL.add(15)
print(myL) #[15,20,1,15]
myL2 = myRevOrderedNumberList()
myL2.add(15)
myL2.add(20)
myL2.add(1)
myL.add("hello") #Only numbers can be added.
print(myL2) #[20, 15, 1]
print(myL2.head()) #20
ans)
class myNumberList(): def __init__(self): pass def add(self, value): if type(value) == str: print('Only numbers can be added.') elif type(value) == int: lst.append(value) return lst else: print('value is of different type!!') def remove(self, value): list(filter(lambda a: a != value, lst)) def head(self): return lst[0] def getList(self): return lst def __str__(self): return str(lst)
class myRevOrderedNumberList(myNumberList): def __init__(self): pass def head(self): lst1 = sorted(lst, reverse=True) return lst1[0] def getList(self): return lst def __str__(self): lst1 = sorted(lst, reverse=True) return str(lst1)
lst = [] myL = myNumberList() myL.add(15) myL.add(20) myL.add(1) print(myL.head()) # 15 print(myL) # [15,20,1] myL.add("5") # Only numbers can be added. print(myL) # [15,20,1] myL.add(15) print(myL) # [15,20,1,15]
lst = [] myL2 = myRevOrderedNumberList() myL2.add(15) myL2.add(20) myL2.add(1) myL.add("hello") # Only numbers can be added. print(myL2) # [20, 15, 1] print(myL2.head()) # 20
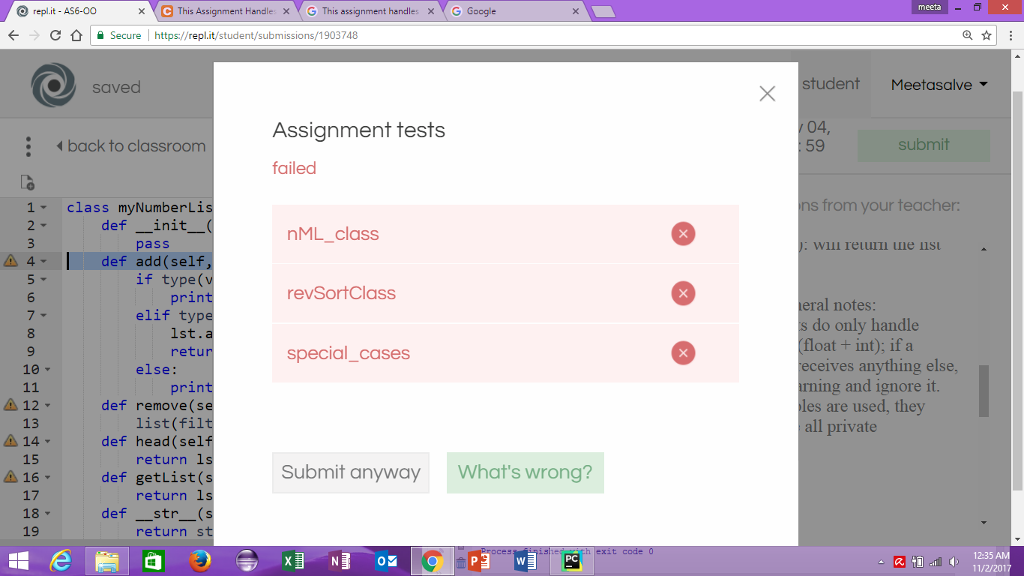
for this solution my tests are failed in repl.it.
i need help with this so that my tests doesnt fail.
meeta e This Assignment Handle x Y G This assignment handle: replit - AS6-00 C G Google Secure | https://repl.it/student/submissions/1903748 student Meetasalve Saved Assignment tests 04 59 back to classroom ubmit failed 1 class myNumberLis s from your teacher def init nML class pass if type(v elif type willl reluini ine iis 4 | def add (self, revSortClass prin ral notes: s do only handle float+ int); if a eceives anything else, lst retur special_cases 10 else: ing and ignore it les are used, they all private prin 12 13 14- 15 16- 17 def remove (se list(filt def head(self return is def getlist(s return 1s def _str_(s Submit anyway What's 18 19 return s R 71.1 ) 12:35AM 11/2/201 0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


