Question: q1 ANS def forward_elim(D,g): #this is for solving forward linear eq A=np.array((D),dtype=float) f=np.array((g),dtype=float) n = f.size for i in range(0,n-1): # Loop through the columns

q1 ANS
def forward_elim(D,g): #this is for solving forward linear eq
A=np.array((D),dtype=float)
f=np.array((g),dtype=float)
n = f.size
for i in range(0,n-1): # Loop through the columns of the matrix
for j in range(i+1,n): # Loop through rows below diagonal for each column
if A[i,i] == 0:
print("Error: Zero on diagonal!")
print("Need algorithm with pivoting")
break
m = A[j,i]/A[i,i]
A[j,:] = A[j,:] - m*A[i,:]
f[j] = f[j] - m*f[i]
return A,f
def Backward_Subs(A,f): #backward substitution
n = f.size
x = np.zeros(n) # Initialize the solution vector, x, to zero
x[n-1] = f[n-1]/A[n-1,n-1] # Solve for last entry first
for i in range(n-2,-1,-1): # Loop from the end to the beginning
sum_ = 0
for j in range(i+1,n): # For known x values, sum and move to rhs
sum_ = sum_ + A[i,j]*x[j]
x[i] = (f[i] - sum_)/A[i,i]
return x
def gaussian_elim(A,f): #driver code doesn't ned to be defined like a function but as mentioned in question so here it is
A = np.array([[2,1,-2],[1,-1,-1],[1,1,3]])
f = np.array([3,0,12])
B,g = forward_elim(A,f)
x= Backward_Subs(B,g)
print(x)
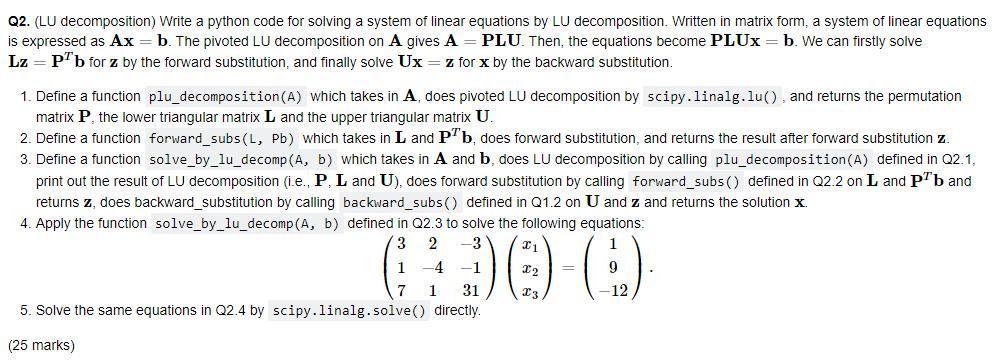
Q1. (Gaussian elimination) Write a python code for solving a system of linear equations by Gaussian elimination. Written in matrix form, a system of linear equations is expressed as Ax=b. 1. Define a function forward_elim(A, b) which takes in A and b, does forward elimination, and returns the new A and b after foward elimination. 2. Define a function backward_subs(A, b) which takes in the A and b obtained by foward elimination, does backward substitution, and returns the solution x. 3. Define a function gaussian_elim(a, b) which takes in the initial A and b and returns the solution x. In this function, we need to call the two functions defined in Q1.1 and 21.2. 4. Apply the function gaussian_elim(A, b) defined in Q1.3 to solve the following equations: 2 2 (3 1) ) -(0) (25 marks) Q2. (LU decomposition) Write a python code for solving a system of linear equations by LU decomposition. Written in matrix form, a system of linear equations is expressed as Ax = b. The pivoted LU decomposition on A gives A PLU. Then, the equations become PLUx=b. We can firstly solve Lz = PTb for z by the forward substitution, and finally solve Ux = z for x by the backward substitution. 1. Define a function plu_decomposition(A) which takes in A, does pivoted LU decomposition by scipy.linalg.lu), and returns the permutation matrix P. the lower triangular matrix L and the upper triangular matrix U. 2. Define a function forward_subs(L, Pb) which takes in L and PTb, does forward substitution, and returns the result after forward substitution z. 3. Define a function solve_by_lu_decomp (A, b) which takes in A and b, does LU decomposition by calling plu_decomposition(A) defined in 22.1, print out the result of LU decomposition (i.e., P. L and U), does forward substitution by calling forward_subs() defined in Q2.2 on L and Pb and returns z, does backward_substitution by calling backward_subs() defined in Q1.2 on U and z and returns the solution x 4. Apply the function solve_by_lu_decomp (A, b) defined in Q2.3 to solve the following equations: 3 2 -3 21 1-4 -1 22 9 1 31 C3 12 5. Solve the same equations in Q2.4 by scipy.linalg.solve directly. (25 marks) Q1. (Gaussian elimination) Write a python code for solving a system of linear equations by Gaussian elimination. Written in matrix form, a system of linear equations is expressed as Ax=b. 1. Define a function forward_elim(A, b) which takes in A and b, does forward elimination, and returns the new A and b after foward elimination. 2. Define a function backward_subs(A, b) which takes in the A and b obtained by foward elimination, does backward substitution, and returns the solution x. 3. Define a function gaussian_elim(a, b) which takes in the initial A and b and returns the solution x. In this function, we need to call the two functions defined in Q1.1 and 21.2. 4. Apply the function gaussian_elim(A, b) defined in Q1.3 to solve the following equations: 2 2 (3 1) ) -(0) (25 marks) Q2. (LU decomposition) Write a python code for solving a system of linear equations by LU decomposition. Written in matrix form, a system of linear equations is expressed as Ax = b. The pivoted LU decomposition on A gives A PLU. Then, the equations become PLUx=b. We can firstly solve Lz = PTb for z by the forward substitution, and finally solve Ux = z for x by the backward substitution. 1. Define a function plu_decomposition(A) which takes in A, does pivoted LU decomposition by scipy.linalg.lu), and returns the permutation matrix P. the lower triangular matrix L and the upper triangular matrix U. 2. Define a function forward_subs(L, Pb) which takes in L and PTb, does forward substitution, and returns the result after forward substitution z. 3. Define a function solve_by_lu_decomp (A, b) which takes in A and b, does LU decomposition by calling plu_decomposition(A) defined in 22.1, print out the result of LU decomposition (i.e., P. L and U), does forward substitution by calling forward_subs() defined in Q2.2 on L and Pb and returns z, does backward_substitution by calling backward_subs() defined in Q1.2 on U and z and returns the solution x 4. Apply the function solve_by_lu_decomp (A, b) defined in Q2.3 to solve the following equations: 3 2 -3 21 1-4 -1 22 9 1 31 C3 12 5. Solve the same equations in Q2.4 by scipy.linalg.solve directly. (25 marks)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


