Question: Q1. Diamond Structure The diamond structure shown below is NOT a Bravais lattice. It can be viewed as two inter- penetrating FCC lattices: Points
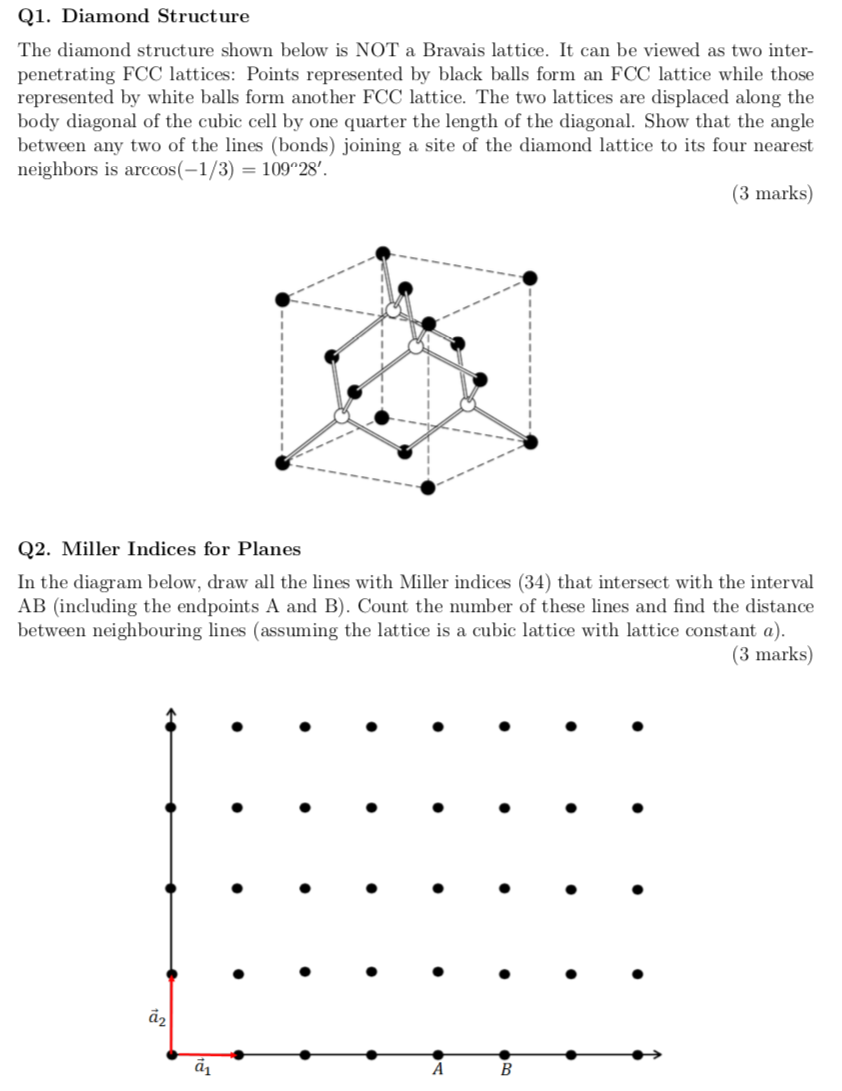

Q1. Diamond Structure The diamond structure shown below is NOT a Bravais lattice. It can be viewed as two inter- penetrating FCC lattices: Points represented by black balls form an FCC lattice while those represented by white balls form another FCC lattice. The two lattices are displaced along the body diagonal of the cubic cell by one quarter the length of the diagonal. Show that the angle between any two of the lines (bonds) joining a site of the diamond lattice to its four nearest neighbors is arccos(-1/3) = 10928. (3 marks) Q2. Miller Indices for Planes In the diagram below, draw all the lines with Miller indices (34) that intersect with the interval AB (including the endpoints A and B). Count the number of these lines and find the distance between neighbouring lines (assuming the lattice is a cubic lattice with lattice constant a). (3 marks) a a A B Q3. Relation Between [hkl] and (hkl) (a) In a simple cubic Bravais lattice, a set of primitive lattice vectors are given by a = a, a = a and a3 = a. Is the direction with Miller indices [hkl] always perpendicular to the lattice planes with Miller indices (hkl) for any possible values of h, k and l? Show details of your reasoning. (2 marks) (b) Answer the same question if the lattice is BCC and the set of primitive lattice vectors are given by a = (- + + ), = ( + 2) and 3 = (2+ 2). Show details of your reasoning. (2 marks)
Step by Step Solution
3.42 Rating (158 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Question 1 Question 2 Miller indices are used to specify directions and planes in lattices and cryst... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


