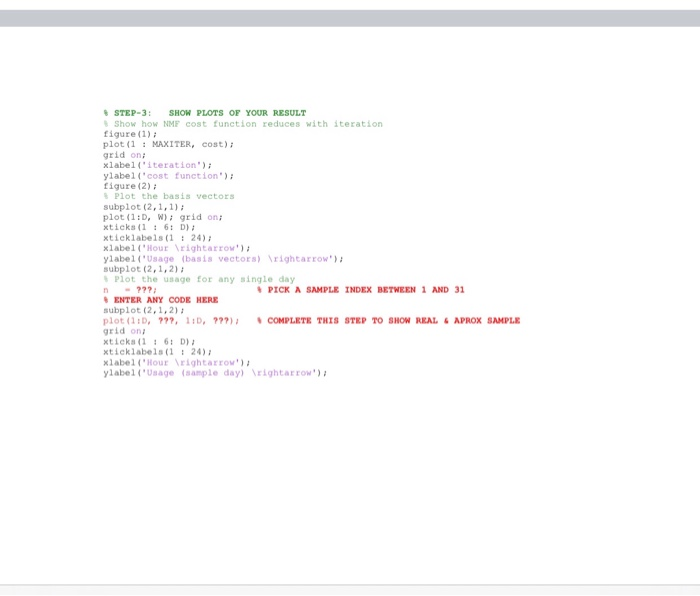
Question: Q1. Non-Negative Matrix Factorization (MATLAB). 40 points. The following program contains partially written MATLAB code for non-negative matrix factorization of a sample matrix X of
Q1. Non-Negative Matrix Factorization (MATLAB). 40 points. The following program contains partially written MATLAB code for non-negative matrix factorization of a sample matrix X of daily energy consumption for a certain household sampled at regular intervals. Each column of the matrix is a sample day and there is a total of 31 weekdays, so that the samples can be denoted as x(n), n = 1,2,...31. Let (n) = Wh, be the reconstruction of sample x(n) from the M = 4 basis vectors in W, so that x(n) *(n). The complete MATLAB program will implement the multiplicative algorithm for NMF to minimize ||X-WH || %. It will produce two figures. Figure 1 will plot ||X - W H , vs. iteration k. Figure 2 will plot the M = 4 basis vectors (top) and a sample x(n) and its reconstruction (n) (bottom). Warning: Do not make changes to the MATLAB code except wherever indicated (in red below). ( Add MATLAB code to perform multiplicative updates of the matrix H so that X WH (W, H > 0). (in Pick any sample index n (of your choice). Add MATLAB code to obtain (n) and produce a figure similar to that shown below. Provide the following: (a) The completed MATLAB code. (one page) (b) Figure 1 produced by the code. (half page) (c) Figure 2 produced by the code with your choice of n. (half page) M och This is how Figure 2 will look like. - 4; Number of basis vectors MAXITER - 100; Number OE NMF iterations Ing (1) seed random number generator STEP-1: LOAD SAMPLE MATRIX 'X' (SIZE: DxN) load Data; (D, N) -size (X); Datamatrix dimensions STEP-2: APPLY NON-NEGATIVE MATRIX FACTORIZATION - 0.1rand ( D M ); Initialize W -0.1rand ( M N); Initialize H cost - zeros (MAXITER, 1); for k-1 MAXITER cost (k)-norm (X - WH'fro") Frobenius norm of difference -W . (x )/( W H ), Multiplicative update of W - 72; COMPLETE THIS STEP FOR MULTIPLICATIVE UPDATE OF H end STEP-3: SHOW PLOTS OF YOUR RESULT Show how NMF cost function reduces with iteration figure (1); plot (1 : MAXITER, cost); grid on xlabel('iteration'); ylabel('cost function'); figure (2) Plot the basis vectors subplot (2,1,1) plot (1:0, Wigrid on: xtiek ( 1 61D) xticklabels ( 1 24); xlabelHour rightarrow'); vlabel('Usage basis vectors) Wrightarrow) subplot (2,1,2); Plot the stage for any single day - ??? PICK A SAMPLE INDEX BETWEEN 1 AND 31 ENTER ANY CODE HERE subplot (2,1,2): plot (1:0, ???, 1:0, ???) COMPLETE THIS STEP TO SHOW REAL & APROX SAMPLE grid on xtieks ( 1 6 : D) xtiek labels ( 1 24) xlabel('Rour rightarrow') ylabel (Usage Sample day) rightarrow'); Q1. Non-Negative Matrix Factorization (MATLAB). 40 points. The following program contains partially written MATLAB code for non-negative matrix factorization of a sample matrix X of daily energy consumption for a certain household sampled at regular intervals. Each column of the matrix is a sample day and there is a total of 31 weekdays, so that the samples can be denoted as x(n), n = 1,2,...31. Let (n) = Wh, be the reconstruction of sample x(n) from the M = 4 basis vectors in W, so that x(n) *(n). The complete MATLAB program will implement the multiplicative algorithm for NMF to minimize ||X-WH || %. It will produce two figures. Figure 1 will plot ||X - W H , vs. iteration k. Figure 2 will plot the M = 4 basis vectors (top) and a sample x(n) and its reconstruction (n) (bottom). Warning: Do not make changes to the MATLAB code except wherever indicated (in red below). ( Add MATLAB code to perform multiplicative updates of the matrix H so that X WH (W, H > 0). (in Pick any sample index n (of your choice). Add MATLAB code to obtain (n) and produce a figure similar to that shown below. Provide the following: (a) The completed MATLAB code. (one page) (b) Figure 1 produced by the code. (half page) (c) Figure 2 produced by the code with your choice of n. (half page) M och This is how Figure 2 will look like. - 4; Number of basis vectors MAXITER - 100; Number OE NMF iterations Ing (1) seed random number generator STEP-1: LOAD SAMPLE MATRIX 'X' (SIZE: DxN) load Data; (D, N) -size (X); Datamatrix dimensions STEP-2: APPLY NON-NEGATIVE MATRIX FACTORIZATION - 0.1rand ( D M ); Initialize W -0.1rand ( M N); Initialize H cost - zeros (MAXITER, 1); for k-1 MAXITER cost (k)-norm (X - WH'fro") Frobenius norm of difference -W . (x )/( W H ), Multiplicative update of W - 72; COMPLETE THIS STEP FOR MULTIPLICATIVE UPDATE OF H end STEP-3: SHOW PLOTS OF YOUR RESULT Show how NMF cost function reduces with iteration figure (1); plot (1 : MAXITER, cost); grid on xlabel('iteration'); ylabel('cost function'); figure (2) Plot the basis vectors subplot (2,1,1) plot (1:0, Wigrid on: xtiek ( 1 61D) xticklabels ( 1 24); xlabelHour rightarrow'); vlabel('Usage basis vectors) Wrightarrow) subplot (2,1,2); Plot the stage for any single day - ??? PICK A SAMPLE INDEX BETWEEN 1 AND 31 ENTER ANY CODE HERE subplot (2,1,2): plot (1:0, ???, 1:0, ???) COMPLETE THIS STEP TO SHOW REAL & APROX SAMPLE grid on xtieks ( 1 6 : D) xtiek labels ( 1 24) xlabel('Rour rightarrow') ylabel (Usage Sample day) rightarrow')