Question: Q1: Question 5 Select all statements that are true. (Note: Parfiai credit is avaiiabie for this question.) [:1 A Bayesian-Nash Equilibrium of a Bayesian game


Q1:
![game. C] The Revenue Equivalence Theorem implies that every bidder's expected payoff](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/6674fc4873c5d_7926674fc4854e2c.jpg)

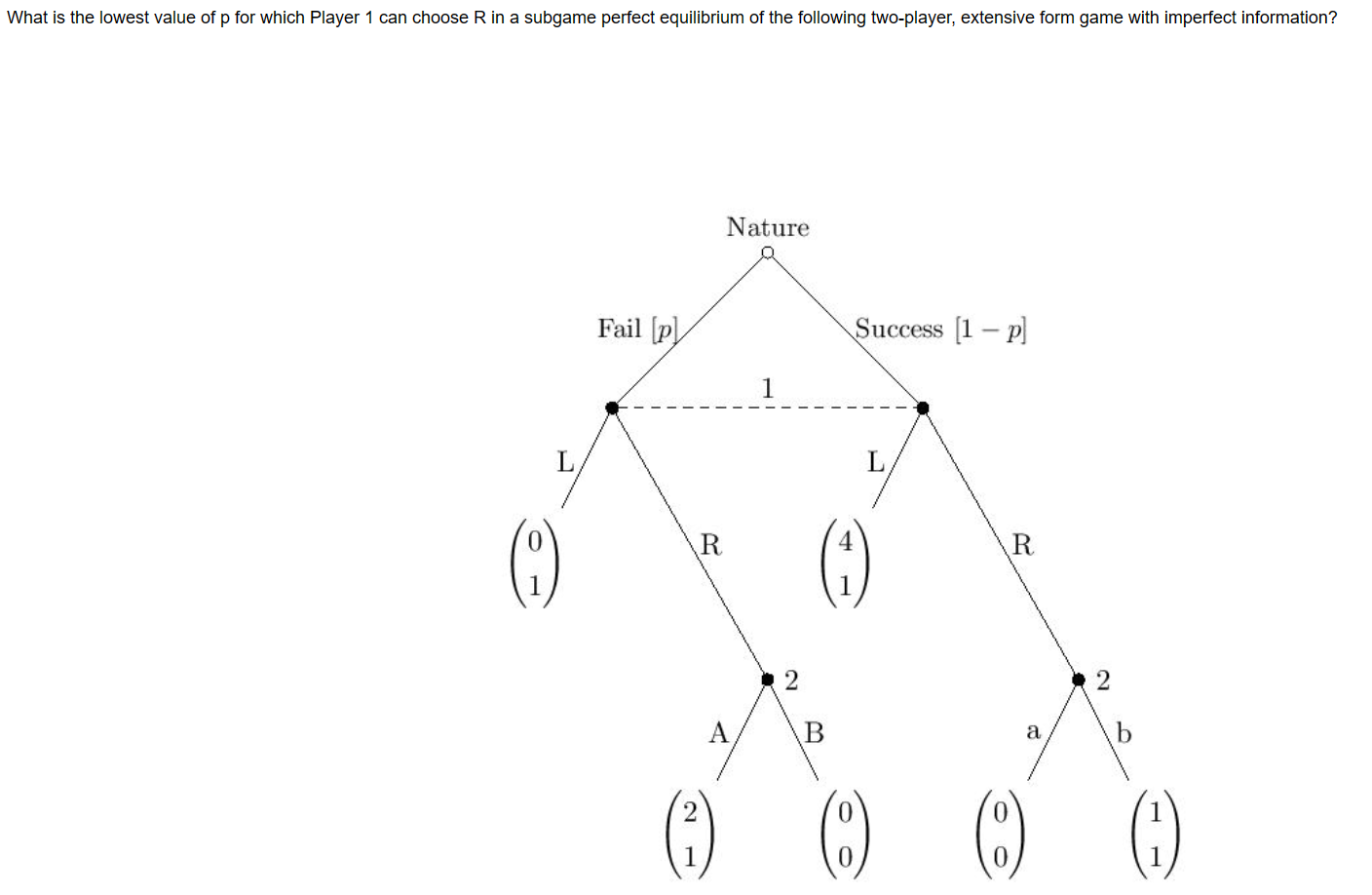
Question 5 Select all statements that are true. (Note: Parfiai credit is avaiiabie for this question.) [:1 A Bayesian-Nash Equilibrium of a Bayesian game is a Nash equilibrium of its associated ex-ante normal form game. C] The Revenue Equivalence Theorem implies that every bidder's expected payoff is the same in the all-pay, first-price and second-price auctions. [:1 A subgame in an extensive form game with imperfect information cannot split up or "break" any information set. [:1 A simultaneous game with perfect information cannot be depicted as an extensive form game with imperfect information sets Magnus Blahsen and Ian Nomnomitchy sit down to play a game of chess. Select all features from the list below that MOST LIKELY apply to this situation. (Note: partiai credit is possible for this question.) C] The game is simultaneous, not sequential. [j The game is zero-sum. [j The game involves imperfect information. [3 An individual move in chess is an action, not a strategy. What is the lowest value of p for which Player 1 can choose R in a subgame perfect equilibrium of the following two-player, extensive form game with imperfect information? Nature Fail [pl Success [1 - p] L L R R N N A B a
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


