Question: Q1). SOL (1). Calculate the arithmetic mean diameter (DN) for the 4 to 10 mesh fractions of the material analysed in the following table. How
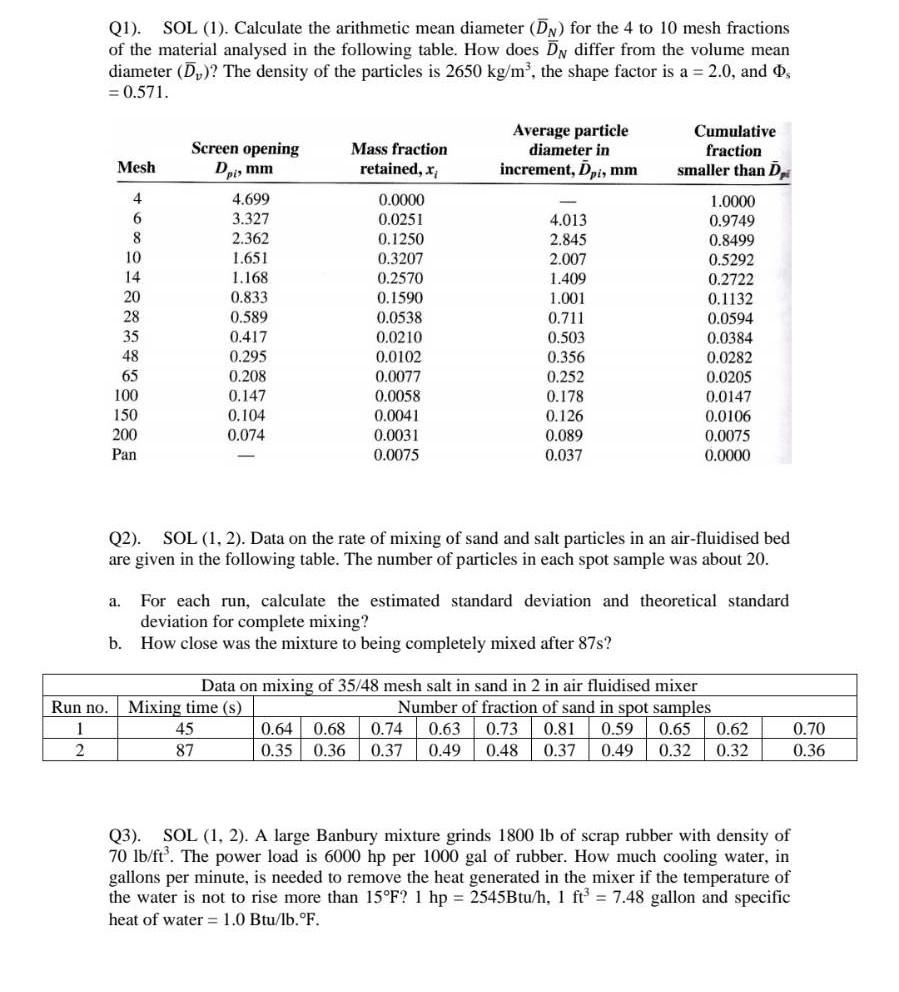
Q1). SOL (1). Calculate the arithmetic mean diameter (DN) for the 4 to 10 mesh fractions of the material analysed in the following table. How does DN differ from the volume mean diameter (Dv) ? The density of the particles is 2650kg/m3, the shape factor is a =2.0, and s =0.571. Q2). SOL (1,2). Data on the rate of mixing of sand and salt particles in an air-fluidised bed are given in the following table. The number of particles in each spot sample was about 20. a. For each run, calculate the estimated standard deviation and theoretical standard deviation for complete mixing? b. How close was the mixture to being completely mixed after 87 s? Q3). SOL (1,2). A large Banbury mixture grinds 1800lb of scrap rubber with density of 70lb/ft3. The power load is 6000hp per 1000 gal of rubber. How much cooling water, in gallons per minute, is needed to remove the heat generated in the mixer if the temperature of the water is not to rise more than 15F?1hp=2545Btu/h,1ft3=7.48 gallon and specific heat of water =1.0Btu/lb.F
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


