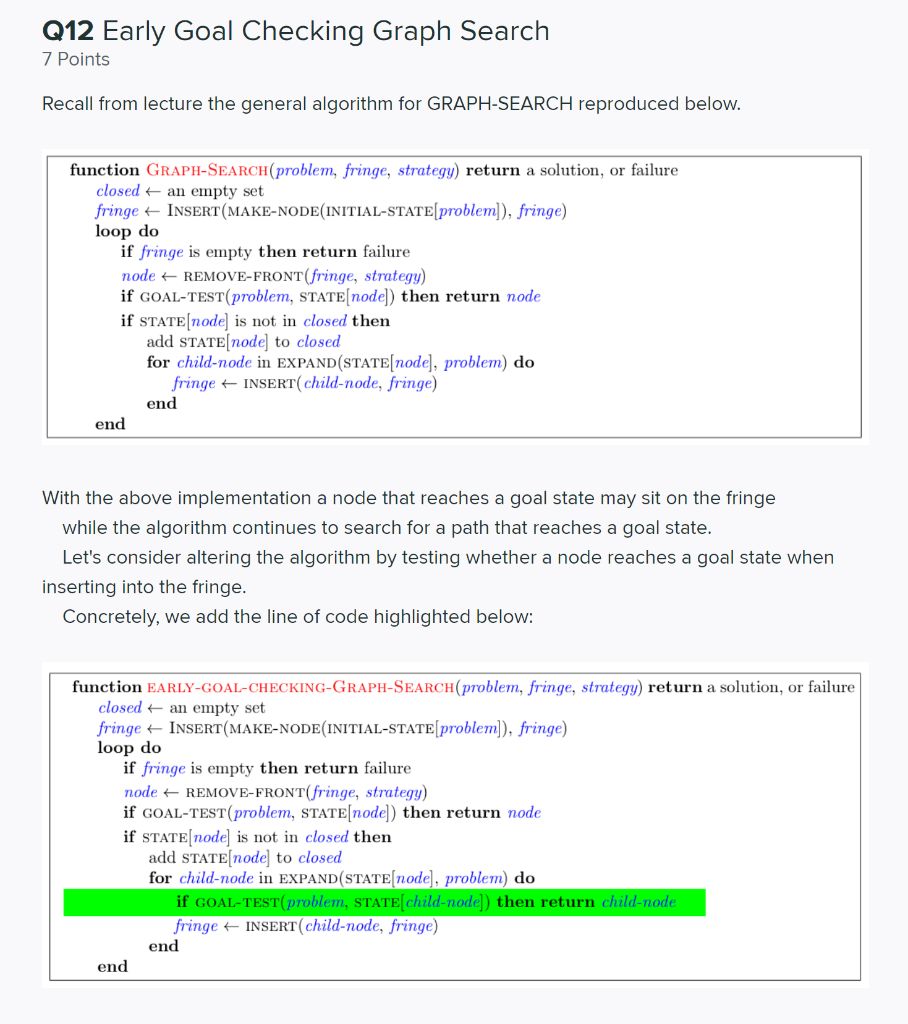
Question: Q12 Early Goal Checking Graph Search 7 Points Recall from lecture the general algorithm for GRAPH-SEARCH reproduced below. function GRAPH-SEARCH(problem, fringe, strategy) return a solution,
![a solution, or failure closed an empty set fringe + INSERT (MAKE-NODE(INITIAL-STATE[problem]),](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f4f2c569cc2_96466f4f2c4d7859.jpg)
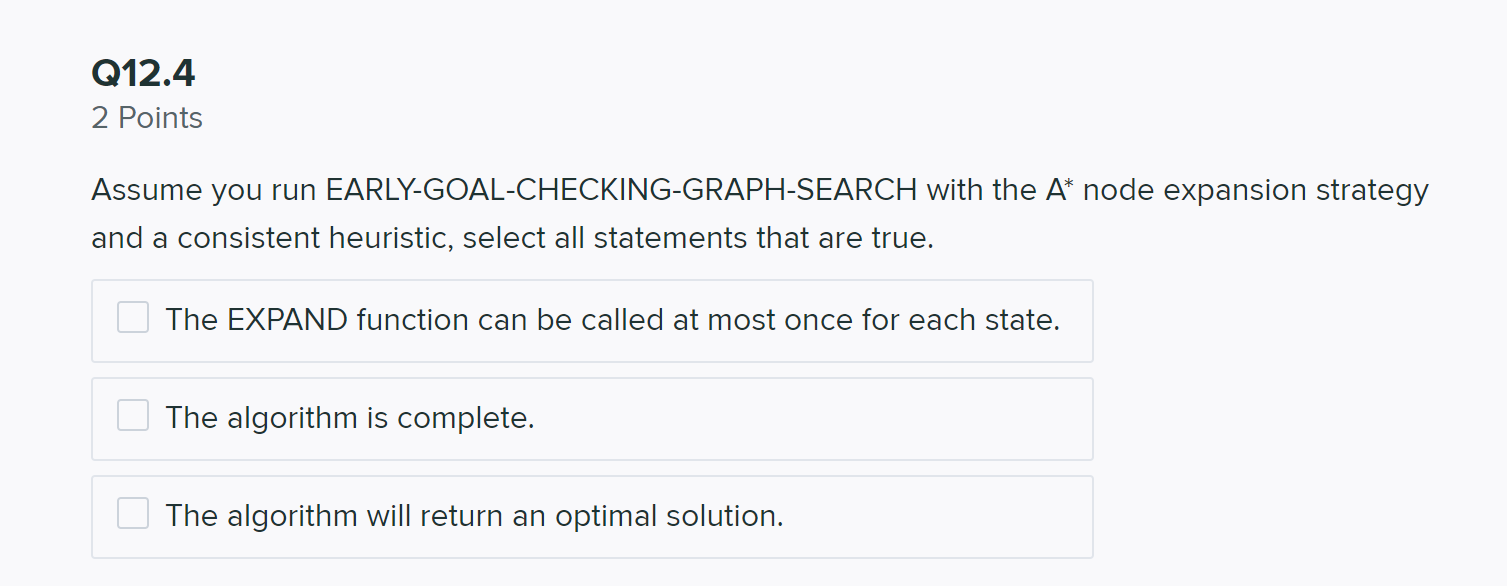
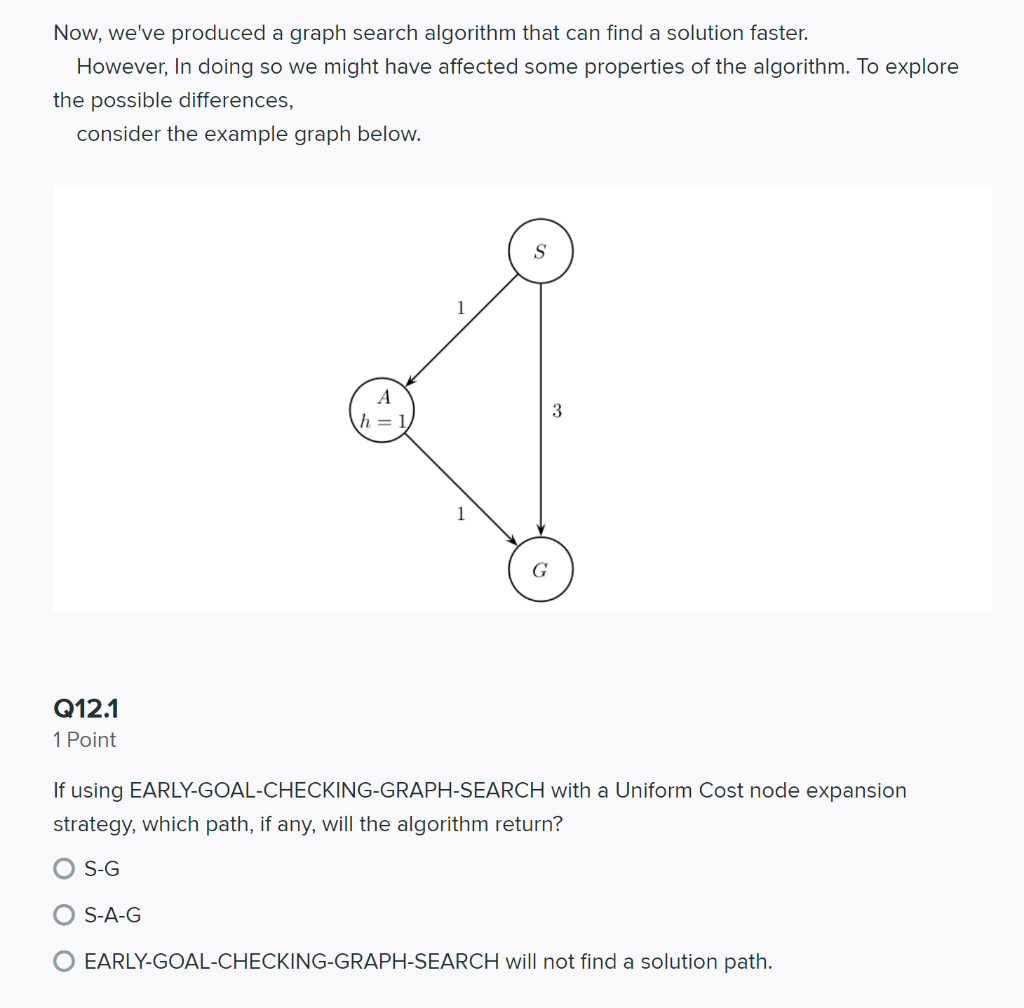
Q12 Early Goal Checking Graph Search 7 Points Recall from lecture the general algorithm for GRAPH-SEARCH reproduced below. function GRAPH-SEARCH(problem, fringe, strategy) return a solution, or failure closed an empty set fringe + INSERT (MAKE-NODE(INITIAL-STATE[problem]), fringe) loop do if fringe is empty then return failure node + REMOVE-FRONT(fringe, strategy) if GOAL-TEST(problem, STATE[node]) then return node if STATE[node] is not in closed then add STATE[node] to closed for child-node in EXPAND(STATE[node), problem) do fringe + INSERT(child-node, fringe) end end With the above implementation a node that reaches a goal state may sit on the fringe while the algorithm continues to search for a path that reaches a goal state. Let's consider altering the algorithm by testing whether a node reaches a goal state when inserting into the fringe. Concretely, we add the line of code highlighted below: function EARLY-GOAL-CHECKING-GRAPH-SEARCH(problem, fringe, strategy) return a solution, or failure closed an empty set fringe + INSERT MAKE-NODE(INITIAL-STATE[problem]), fringe) loop do if fringe is empty then return failure node + REMOVE-FRONT(fringe, strategy) if GOAL-TEST(problem, STATE[node]) then return node if STATE[node] is not in closed then add STATE[node] to closed for child-node in EXPAND(STATE(node), problem) do if GOAL-TEST(problem, STATE[child-node]) then return child-node fringe + INSERT (child-node, fringe) end end Now, we've produced a graph search algorithm that can find a solution faster. However, In doing so we might have affected some properties of the algorithm. To explore the possible differences, consider the example graph below. h=1 3 1 G Q12.1 1 Point If using EARLY-GOAL-CHECKING-GRAPH-SEARCH with a Uniform Cost node expansion strategy, which path, if any, will the algorithm return? S-G O S-A-G O EARLY-GOAL-CHECKING-GRAPH-SEARCH will not find a solution path. Q12.2 2 Points If using EARLY-GOAL-CHECKING-GRAPH-SEARCH with an A* node expansion strategy, which path, if any, will the algorithm return? OS-G O S-A-G O EARLY-GOAL-CHECKING-GRAPH-SEARCH will not find a solution path. Save Answer Q12.3 2 Points Assume you run EARLY-GOAL-CHECKING-GRAPH-SEARCH with the Uniform Cost node expansion strategy, select all statements that are true. The EXPAND function can be called at most once for each state. The algorithm is complete. The algorithm will return an optimal solution. Q12.4 2 Points Assume you run EARLY-GOAL-CHECKING-GRAPH-SEARCH with the A* node expansion strategy and a consistent heuristic, select all statements that are true. The EXPAND function can be called at most once for each state. The algorithm is complete. The algorithm will return an optimal solution
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


