Question: Q2 answer is provided q4 please Q4. What difference does it make to your calculations in the previous problem (Q2) if a dividend of $1.50

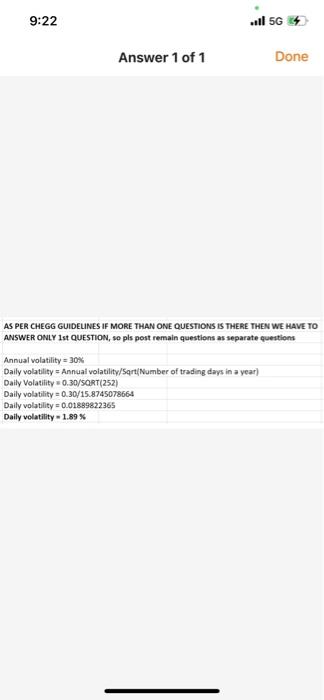

Q4. What difference does it make to your calculations in the previous problem (Q2) if a dividend of $1.50 is expected in two months? 9:22 ... 56 Answer 1 of 1 Done AS PER CHEGG GUIDELINES IF MORE THAN ONE QUESTIONS IS THERE THEN WE HAVE TO ANSWER ONLY 1st QUESTION, so pls post remain questions as separate questions Annual volatility = 30% Daily volatility = Annual volatility/Sqrt(Number of trading days in a year) Daily Volatility 0.30/SORT(252) Daily volatility = 0.30/15.8745078664 Daily volatility -0.01889822365 Daily volatility - 1.89% Q2. The volatility of a stock price is 30% per annum. What is the standard deviation of the percentage price change in one trading day? Q3. Calculate the price of a three-month European put option on a non-dividend-paying stock with a strike price of $50 when the current stock price is $50, the risk-free interest rate is 10% per annum, and the volatility is 30% per annum. Q4. What difference does it make to your calculations in the previous problem (Q2) if a dividend of $1.50 is expected in two months? Q5. What is the price of a European call option on a non- dividend-paying stock when the stock price is $52, the strike price is $50, the risk-free interest rate is 12% per annum, the volatility is 30% per annum, and the time to maturity is three months? At what future stock price will the buyer of the call option breakeven? Q6. What is the price of a European put option on a non- dividend-paying stock when the stock price is $69, the strike price is $70, the risk-free interest rate is 5% per annum, the volatility is 35% per annum, and the time to maturity is six months? At what future stock price will the buyer of the put option breakeven? Q4. What difference does it make to your calculations in the previous problem (Q2) if a dividend of $1.50 is expected in two months? 9:22 ... 56 Answer 1 of 1 Done AS PER CHEGG GUIDELINES IF MORE THAN ONE QUESTIONS IS THERE THEN WE HAVE TO ANSWER ONLY 1st QUESTION, so pls post remain questions as separate questions Annual volatility = 30% Daily volatility = Annual volatility/Sqrt(Number of trading days in a year) Daily Volatility 0.30/SORT(252) Daily volatility = 0.30/15.8745078664 Daily volatility -0.01889822365 Daily volatility - 1.89% Q2. The volatility of a stock price is 30% per annum. What is the standard deviation of the percentage price change in one trading day? Q3. Calculate the price of a three-month European put option on a non-dividend-paying stock with a strike price of $50 when the current stock price is $50, the risk-free interest rate is 10% per annum, and the volatility is 30% per annum. Q4. What difference does it make to your calculations in the previous problem (Q2) if a dividend of $1.50 is expected in two months? Q5. What is the price of a European call option on a non- dividend-paying stock when the stock price is $52, the strike price is $50, the risk-free interest rate is 12% per annum, the volatility is 30% per annum, and the time to maturity is three months? At what future stock price will the buyer of the call option breakeven? Q6. What is the price of a European put option on a non- dividend-paying stock when the stock price is $69, the strike price is $70, the risk-free interest rate is 5% per annum, the volatility is 35% per annum, and the time to maturity is six months? At what future stock price will the buyer of the put option breakeven
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


