Question: Q2: Modify the above BNF, EBNF and syntax diagrams by adding the integer remainder and power operations to the simple integer arithmetic expressions. Use %
Q2: Modify the above BNF, EBNF and syntax diagrams by adding the integer remainder and power operations to the simple integer arithmetic expressions. Use % for the remainder operation and for the power operation.
Hint: Note that the remainder operation is left-associative and has the same precedence as multiplication, but that power is right-associative (and has greater precedence than multiplication, so 2 2 3 = 256, not 64).
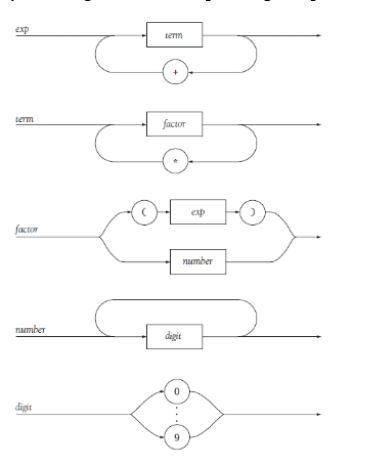
BNF rules for simple integer arithmetic expressions: expr expr + term | term term term * factor | factor factor ( expr ) | number number number digit | digit digit 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 EBNF rules for simple integer arithmetic expressions: expr term { + term } term factor { * factor } factor ( expr ) | number number digit { digit } digit 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 Syntax diagrams for a simple integer expression grammar:
Ten factor F0 facto number number 0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


