Question: Q2a: Table 1 provides a matrix for dimensionless numbers based on momentum/force, just as we have seen in class and in the tutorial for mass
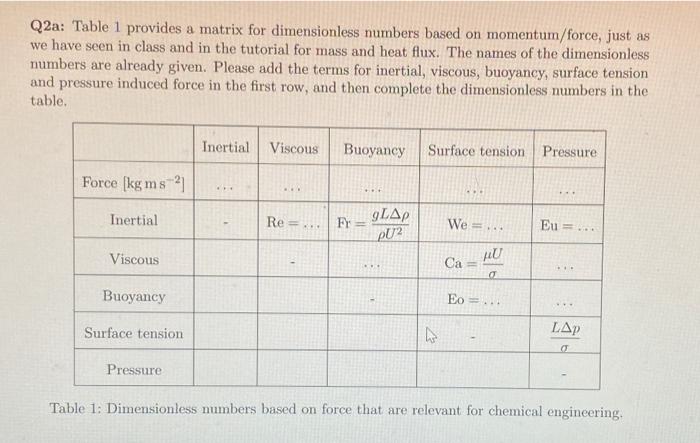

Q2a: Table 1 provides a matrix for dimensionless numbers based on momentum/force, just as we have seen in class and in the tutorial for mass and heat flux. The names of the dimensionless numbers are already given. Please add the terms for inertial, viscous, buoyancy, surface tension and pressure induced force in the first row, and then complete the dimensionless numbers in the table. Inertial Viscous Buoyancy Surface tension Pressure Force [kg ms? Inertial Re = GLAP Fr= pU? We = Eu = Viscous Ca AU 0 Buoyancy Eo =... Surface tension LAP o Pressure Table 1: Dimensionless numbers based on force that are relevant for chemical engineering, Q2b: In a horizontal pipe and under turbulent flow, the head loss over the length of the pipe relates to the pressure drop, Ap. The head loss happens as a result of energy dissipation along the pipe as the pipe wall is never completely smooth: there will be friction along the wall. The head loss depends on the pipe diameter d[m, the viscosity [kg m-s-'), liquid density p[kg m-3), the velocity of the flow v ms'], the length of the pipe ! (m) and the surface roughness 11-1, which is a measure of the height of the roughness respective to the pipe diameter. Using the Buckingham Pi theorem, formulate a model for the dimensionless head loss as a function of other dimensionless groups (Hint: used, w and p as recurring variables). [18 marks
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


