Question: Quantitative Methods for Finance Practice Questions for Lectures 1 and 2 1. The prices of a stock are given in the table on the right.
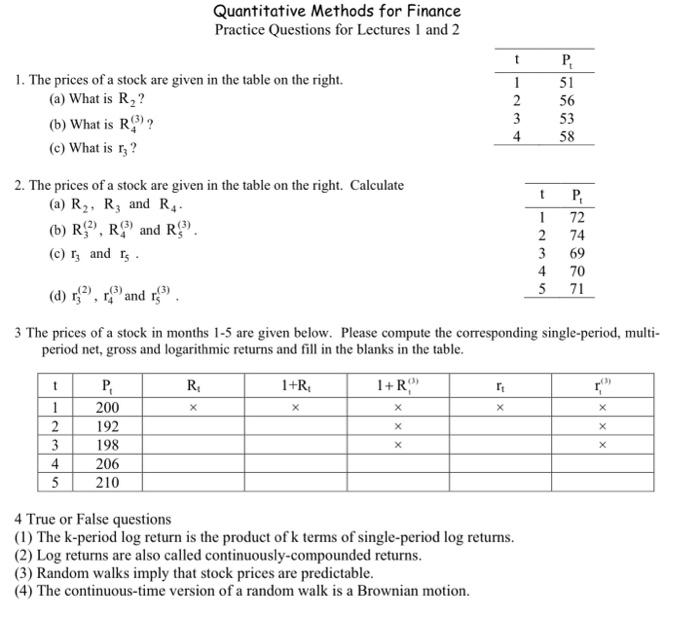
Quantitative Methods for Finance Practice Questions for Lectures 1 and 2 1. The prices of a stock are given in the table on the right. (a) What is R2 ? (b) What is R4(3) ? (c) What is r3 ? 2. The prices of a stock are given in the table on the right. Calculate (a) R2,R3 and R4. (b) R3(2),R4(3) and R5(3). (c) r3 and r5. (d) r3(2),r4(3) and r5(3). 3 The prices of a stock in months 1-5 are given below. Please compute the corresponding single-period, multiperiod net, gross and logarithmic returns and fill in the blanks in the table. 4 True or False questions (1) The k-period log return is the product of k terms of single-period log returns. (2) Log returns are also called continuously-compounded returns. (3) Random walks imply that stock prices are predictable. (4) The continuous-time version of a random walk is a Brownian motion. Quantitative Methods for Finance Practice Questions for Lectures 1 and 2 1. The prices of a stock are given in the table on the right. (a) What is R2 ? (b) What is R4(3) ? (c) What is r3 ? 2. The prices of a stock are given in the table on the right. Calculate (a) R2,R3 and R4. (b) R3(2),R4(3) and R5(3). (c) r3 and r5. (d) r3(2),r4(3) and r5(3). 3 The prices of a stock in months 1-5 are given below. Please compute the corresponding single-period, multiperiod net, gross and logarithmic returns and fill in the blanks in the table. 4 True or False questions (1) The k-period log return is the product of k terms of single-period log returns. (2) Log returns are also called continuously-compounded returns. (3) Random walks imply that stock prices are predictable. (4) The continuous-time version of a random walk is a Brownian motion
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


