Question: Quantitative Problem 1: Beasley Industries' sales are expected to increase from $4 million in 2017 to $5 million in 2018 , or by 25%. Its
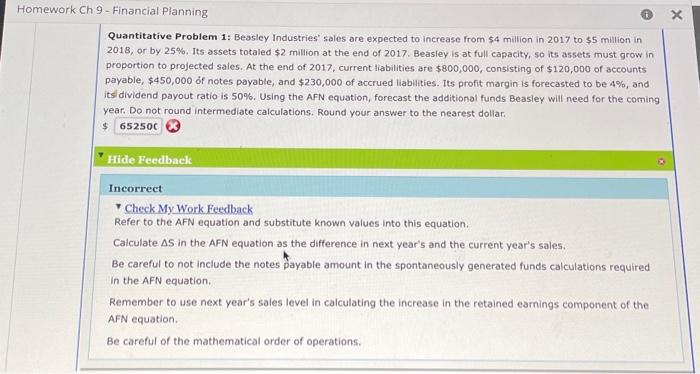

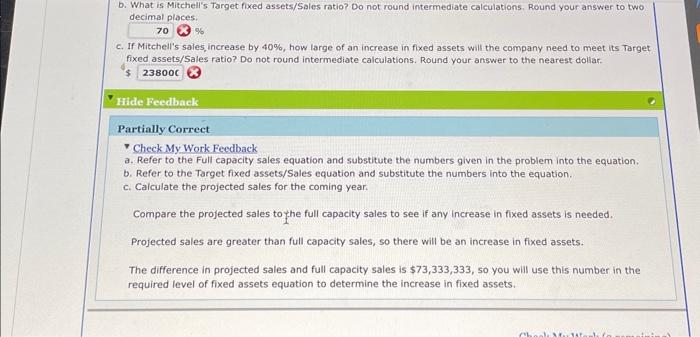
Quantitative Problem 1: Beasley Industries' sales are expected to increase from $4 million in 2017 to $5 million in 2018 , or by 25%. Its assets totaled $2 million at the end of 2017 . Beasley is at full capacity, so its assets must grow in proportion to projected sales. At the end of 2017 , current liabilities are $800,000, consisting of $120,000 of accounts payable, $450,000 of notes payable, and $230,000 of accrued liabilities. Its profit margin is forecasted to be 4%, and its dividend payout ratio is 50%. Using the AFN equation, forecast the additional funds Beasley will need for the coming year. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to the nearest dollar. $ Hide Feedback Incorrect Check My Work Feedback Refer to the AFN equation and substitute known values into this equation. Calculate S in the AFN equation as the difference in next year's and the current year's sales. Be careful to not include the notes payable amount in the spontaneously generated funds calculations required in the AFN equation. Remember to use next year's sales level in calculating the increase in the retained earnings component of the AFN equation. Be careful of the mathematical order of operations. The AFN equation assumes that ratios remain constant. However, firms are not always operating at full capacity so adjustments need to be made to the existing asset forecast. Excess capacity adjustments are changes made to the existing asset forecast because the firm is not operating at full capacity. For example, a firm may not be at full capacity with respect to its fixed assets. First, the firm's management must find out the firm's full copacity sales as follows: Fullcapacitysales=PereentageofcapacityatwhichfixedautswreeoperatedActualwale Next, management would calculate the firm's target fixed assets ratio as follows: Finally, management would use the target fixed assets ratio with the projected sales to caiculate the firm's required level of fixed assets as follows: Required level of fixed assets = (Target fixed assets / Sales) (Projected sales) Quantitative Problem 2: Mitchell Majufacturing Company has $1,100,000,000 in sales and $220,000,000 in fixed assets. Currently, the company's fixed assets are operating at 75% of capacity. a. What level of sales could Mitchell have obtained if it had been operating at full capacity? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to the nearest dollar. $ b. What is Mitchell's Target fixed assets/Sales ratio? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimal places. % b. What is Mitchell's Target fixed assets/Sales ratio? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to two decimat places: % c. If Mitchell's sales, increase by 40%, how large of an increase in fixed assets will the company need to meet its Target fixed assets/Sales ratio? Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to the nearest dollar. $ Hide Feedback Partially Correct - Check My Work Feedback a. Refer to the Full capacity sales equation and substitute the numbers given in the problem into the equation. b. Refer to the Target fixed assets/Sales equation and substitute the numbers into the equation. c. Calculate the projected sales for the coming year. Compare the projected sales to fhe full capacity sales to see if any increase in fixed assets is needed. Projected sales are greater than full capacity sales, so there will be an increase in fixed assets. The difference in projected sales and full capacity sales is $73,333,333, so you will use this number in the required level of fixed assets equation to determine the increase in fixed assets
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


