Question: Quantitative Risk Assessment Single loss expectancy (SLE): Total loss expected from a single incident Exposure Factor (EF): the subjective, potential percentage of loss to a
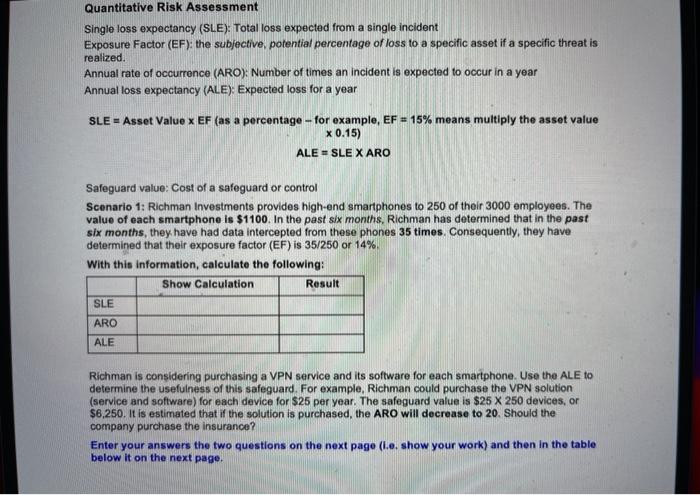
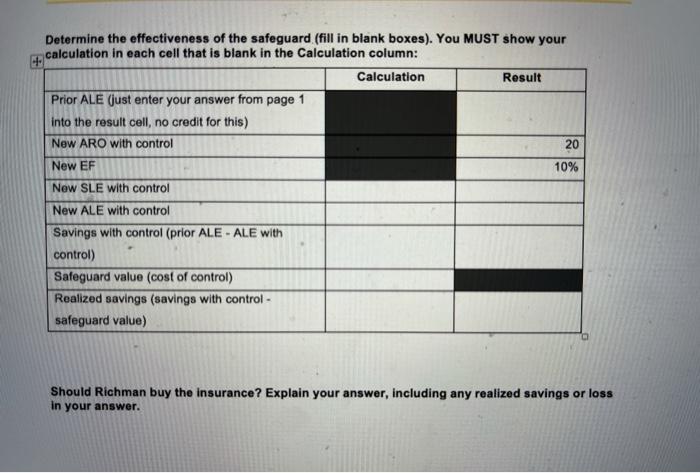
Quantitative Risk Assessment Single loss expectancy (SLE): Total loss expected from a single incident Exposure Factor (EF): the subjective, potential percentage of loss to a specific asset if a specific threat is realized. Annual rate of occurrence (ARO): Number of times an incident is expected to occur in a year Annual loss expectancy (ALE): Expected loss for a year SLE = Asset Value x EF (as a percentage - for example, EF = 15% means multiply the asset value x 0.15) ALE = SLEX ARO Safeguard value: Cost of a safeguard or control Scenario 1: Richman Investments provides high-end smartphones to 250 of their 3000 employees. The value of each smartphone is $1100. In the past six months, Richman has determined that in the past six months, they have had data intercepted from these phones 35 times. Consequently, they have determined that their exposure factor (EF) is 35/250 or 14% With this information, calculate the following: Show Calculation Result SLE ARO ALE Richman is considering purchasing a VPN service and its software for each smartphone. Use the ALE to determine the usefulness of this safeguard. For example, Richman could purchase the VPN solution (service and software) for each device for $25 per year. The safeguard value is $25 X 250 devices, or $6,250. It is estimated that if the solution is purchased, the ARO will decrease to 20. Should the company purchase the insurance? Enter your answers the two questions on the next page (i.e. show your work) and then in the table below it on the next page. Determine the effectiveness of the safeguard (fill in blank boxes). You MUST show your calculation in each cell that is blank in the Calculation column: Calculation Result Prior ALE (just enter your answer from page 1 into the result cell, no credit for this) New ARO with control 20 New EF 10% New SLE with control New ALE with control Savings with control (prior ALE - ALE with control) Safeguard value (cost of control) Realized savings (savings with control - safeguard value) Should Richman buy the insurance? Explain your answer, including any realized savings or loss in your answer. Quantitative Risk Assessment Single loss expectancy (SLE): Total loss expected from a single incident Exposure Factor (EF): the subjective, potential percentage of loss to a specific asset if a specific threat is realized. Annual rate of occurrence (ARO): Number of times an incident is expected to occur in a year Annual loss expectancy (ALE): Expected loss for a year SLE = Asset Value x EF (as a percentage - for example, EF = 15% means multiply the asset value x 0.15) ALE = SLEX ARO Safeguard value: Cost of a safeguard or control Scenario 1: Richman Investments provides high-end smartphones to 250 of their 3000 employees. The value of each smartphone is $1100. In the past six months, Richman has determined that in the past six months, they have had data intercepted from these phones 35 times. Consequently, they have determined that their exposure factor (EF) is 35/250 or 14% With this information, calculate the following: Show Calculation Result SLE ARO ALE Richman is considering purchasing a VPN service and its software for each smartphone. Use the ALE to determine the usefulness of this safeguard. For example, Richman could purchase the VPN solution (service and software) for each device for $25 per year. The safeguard value is $25 X 250 devices, or $6,250. It is estimated that if the solution is purchased, the ARO will decrease to 20. Should the company purchase the insurance? Enter your answers the two questions on the next page (i.e. show your work) and then in the table below it on the next page. Determine the effectiveness of the safeguard (fill in blank boxes). You MUST show your calculation in each cell that is blank in the Calculation column: Calculation Result Prior ALE (just enter your answer from page 1 into the result cell, no credit for this) New ARO with control 20 New EF 10% New SLE with control New ALE with control Savings with control (prior ALE - ALE with control) Safeguard value (cost of control) Realized savings (savings with control - safeguard value) Should Richman buy the insurance? Explain your answer, including any realized savings or loss in your
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


