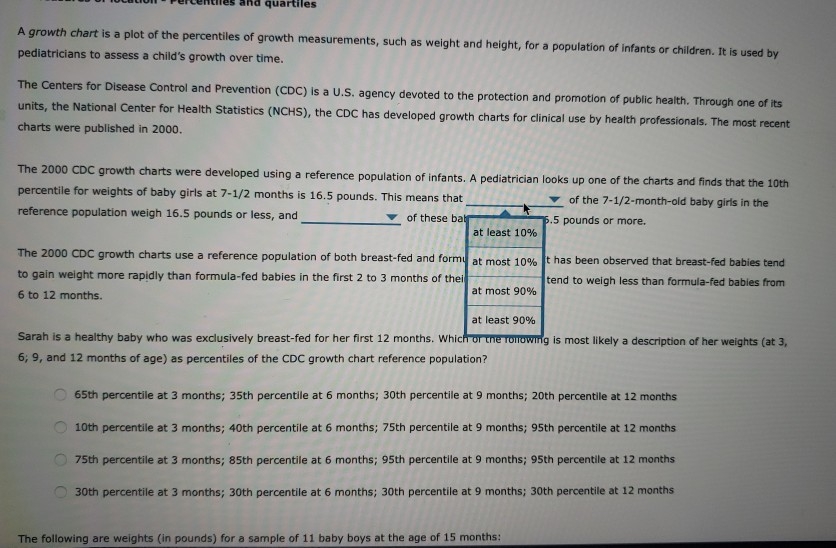
Question: quartiles A growth chart is a plot of the percentiles of growth measurements, such as weight and height, for a population of infants or children.
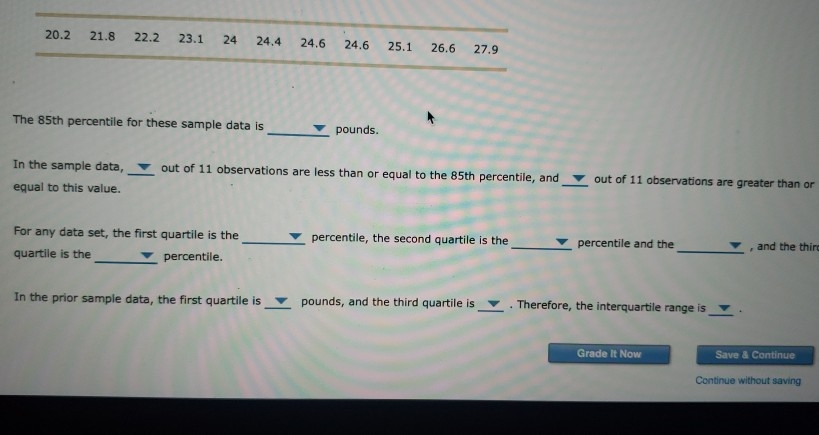
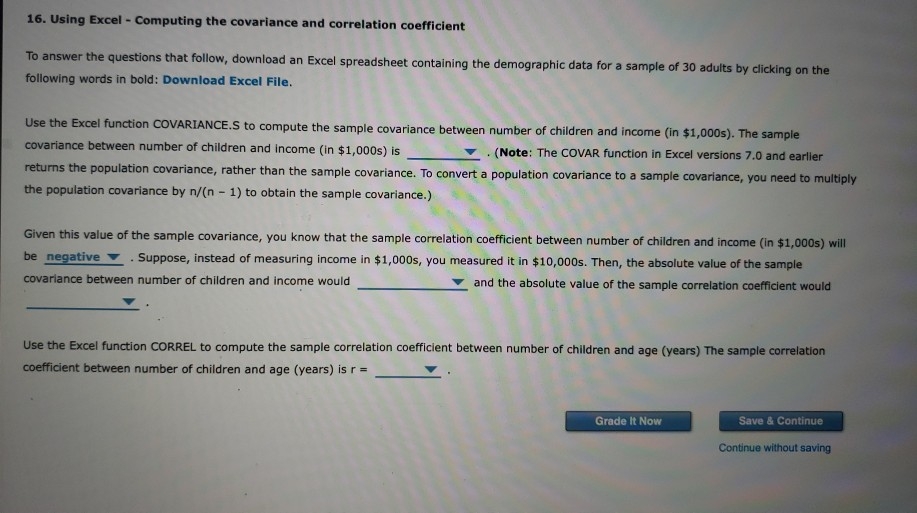
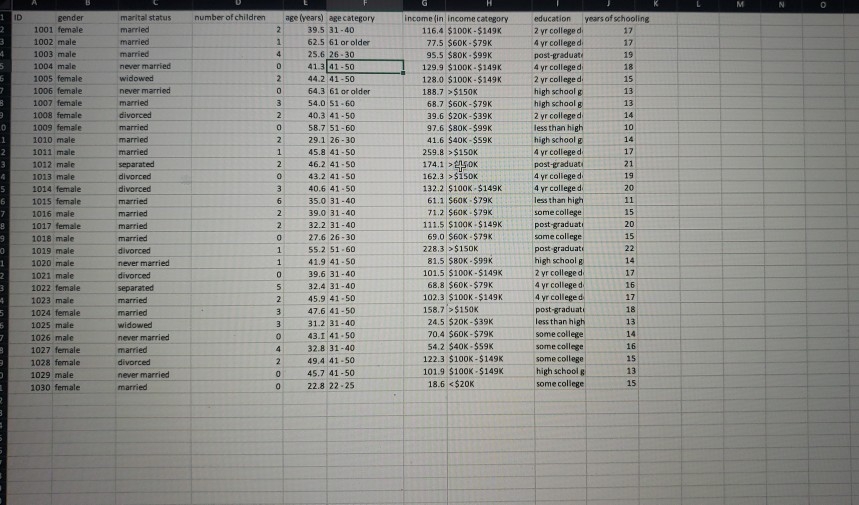
quartiles A growth chart is a plot of the percentiles of growth measurements, such as weight and height, for a population of infants or children. It is used by pediatricians to assess a child's growth over time. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is a U.S. agency devoted to the protection and promotion of public health. Through one of its units, the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS), the CDC has developed growth charts for clinical use by health professionals. The most recent charts were published in 2000. The 2000 CDC growth charts were developed using a reference population of infants. A pediatrician looks up one of the charts and finds that the 10th percentile for weights of baby girls at 7-1/2 months is 16.5 pounds. This means that of the 7-1/2-month-old baby girls in the reference population weigh 16.5 pounds or less, and of these bab .5 pounds or more. at least 10% The 2000 CDC growth charts use a reference population of both breast-fed and formy at most 10% It has been observed that breast-fed babies tend to gain weight more rapidly than formula-fed babies in the first 2 to 3 months of thei tend to weigh less than formula-fed babies from 6 to 12 months. at most 90% at least 90% Sarah is a healthy baby who was exclusively breast-fed for her first 12 months. Which of the following is most likely a description of her weights (at 3, 6; 9, and 12 months of age) as percentiles of the CDC growth chart reference population? ) 65th percentile at 3 months; 35th percentile at 6 months; 30th percentile at 9 months; 20th percentile at 12 months 10th percentile at 3 months; 40th percentile at 6 months; 75th percentile at 9 months; 95th percentile at 12 months 75th percentile at 3 months; 85th percentile at 6 months; 95th percentile at 9 months; 95th percentile at 12 months 30th percentile at 3 months; 30th percentile at 6 months; 30th percentile at 9 months; 30th percentile at 12 months The following are weights (in pounds) for a sample of 11 baby boys at the age of 15 months:20.2 21.8 22.2 23.1 24 24.4 24.6 24.6 25.1 26.6 27.9 The 85th percentile for these sample data is pounds. In the sample data, out of 11 observations are less than or equal to the 85th percentile, and * out of 11 observations are greater than or equal to this value. For any data set, the first quartile is the percentile, the second quartile is the percentile and the and the thir quartile is the percentile. In the prior sample data, the first quartile is pounds, and the third quartile is . Therefore, the interquartile range is Grade It Now Save & Continue Continue without saving16. Using Excel - Computing the covariance and correlation coefficient To answer the questions that follow, download an Excel spreadsheet containing the demographic data for a sample of 30 adults by clicking on the following words in bold: Download Excel File. Use the Excel function COVARIANCE.S to compute the sample covariance between number of children and income (in $1,000s). The sample covariance between number of children and income (in $1,000s) is . (Note: The COVAR function in Excel versions 7.0 and earlier returns the population covariance, rather than the sample covariance. To convert a population covariance to a sample covariance, you need to multiply the population covariance by n/(n - 1) to obtain the sample covariance.) Given this value of the sample covariance, you know that the sample correlation coefficient between number of children and income (in $1,000s) will be negative . Suppose, instead of measuring income in $1,000s, you measured it in $10,000s. Then, the absolute value of the sample covariance between number of children and income would and the absolute value of the sample correlation coefficient would Use the Excel function CORREL to compute the sample correlation coefficient between number of children and age (years) The sample correlation coefficient between number of children and age (years) is r = Grade It Now Save & Continue Continue without savingID gender marital status number of children age (years) age category income (in Income category education years of schooling 1001 female married 39.5 31-40 116,4 $100K - $149K 2 yr college d 17 1002 male married 62.5 61 or older 77.5 $60K - $79K 4 yr college d 17 1003 male married 25.6 26-30 95.5 $8OK - $99K post-graduate 19 1004 male never married 41 3 41-50 129.9 $10OK - $149K 4 yr college d 18 1005 female widowed 44 2 41-50 128.0 $10OK -$149K 2 yr college d 15 1006 female never married 64.3 61 or older 188 7 > $150K high school g 13 1007 female married 3 1008 female divorced 1009 female married 1010 male married 1011 male married NON 54.0 51-60 68 7 $60K -$79K high school g 13 40.3 41-50 39.6 $20K-$39K 2 yr college d 14 58.7 51-60 97_6 $80K-$99K less than high 10 29.1 26-30 41 6 $40K-$59K high school g 14 45.8 41-50 259.8 > $150K 4 yr colleged 17 1012 male separated 46.2 41-50 174.1 > E45OK post-graduate 21 1013 male divorced 43.2 41-50 162.3 > $150K 4 yr colleged 19 1014 female divorced ONNOW 40.6 41 -50 132,2 $10OK - $149K 4 yr college d 20 1015 fernale married 35.0 31-40 61.1 56OK - $79K less than high 11 1016 male married 39.0 31-40 71.2 SEOK - $79K some college 15 1017 female married 32.2 31-40 111.5 $100K - $149K post-graduate 20 1018 male married 27.6 26-30 69.0 560K - $79K some college 15 1019 male divorced 1 55.2 51 -60 228.3 >$150K post graduate 22 1020 male never married 41.9 41-50 81.5 580K - 599K high school g 14 1021 male divorced 39.6 31-40 101.5 $100K - $149K 2 yr colleged 17 1022 female separated 32.4 31-40 68.8 $60K -$79K 4 yr colleged 16 1023 male married 45.9 41-50 102.3 $100K - $149K 4 yr college d 17 1024 female married 47.6 41-50 158.7 > $150K post-graduate 18 1025 male widowed 31.2 31-40 24.5 $20K-$39K less than high 13 1026 male never married 43.1 41-50 70.4 $60K-$79K some college 14 1027 female married DON & 32.8 31-40 54.2 $40K-$59K some college 16 1028 female divorced 49.4 41 -50 122.3 $100K-$149K some college 15 1029 male never married 45.7 41-50 101 9 $100K - $149K high school g 13 1030 female married 22.8 22-25 18.6