Question: Question 1 0.0m) point {graded} What does the hypothesis test below test? 1 N HD:E;Y(1}Y[O}=O 1 N HE:F;Y(1)Y[D)a0 The null hypothesis that there is no
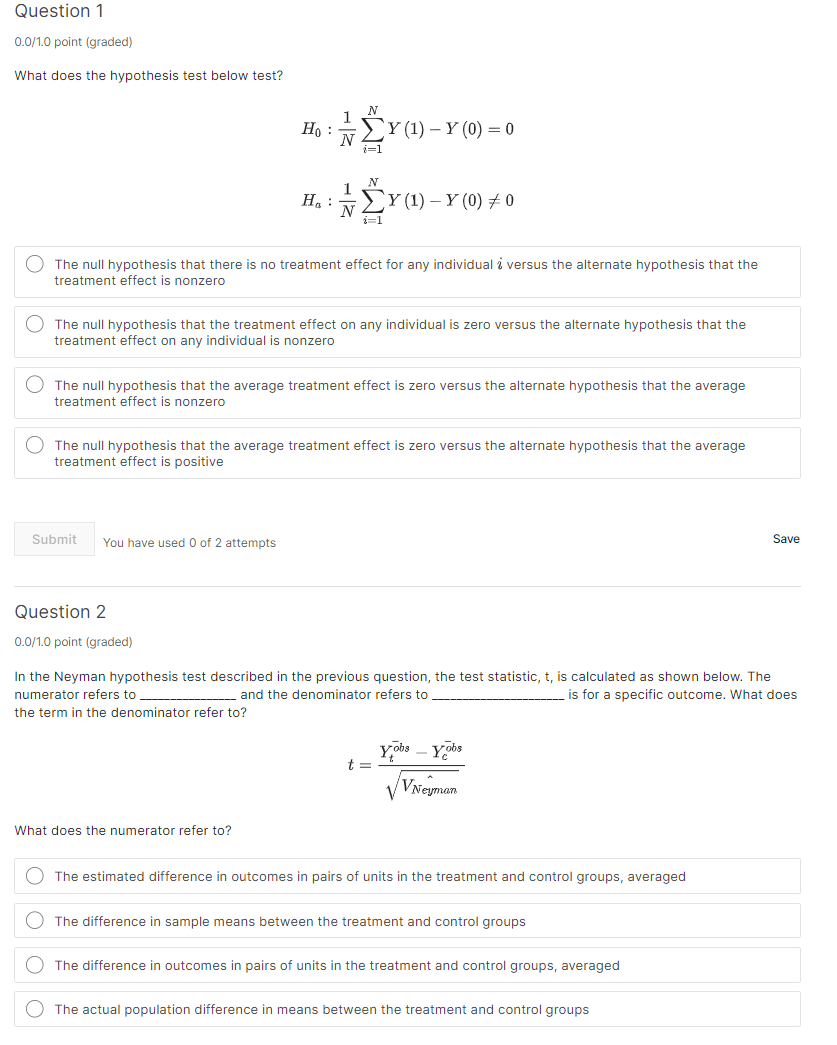
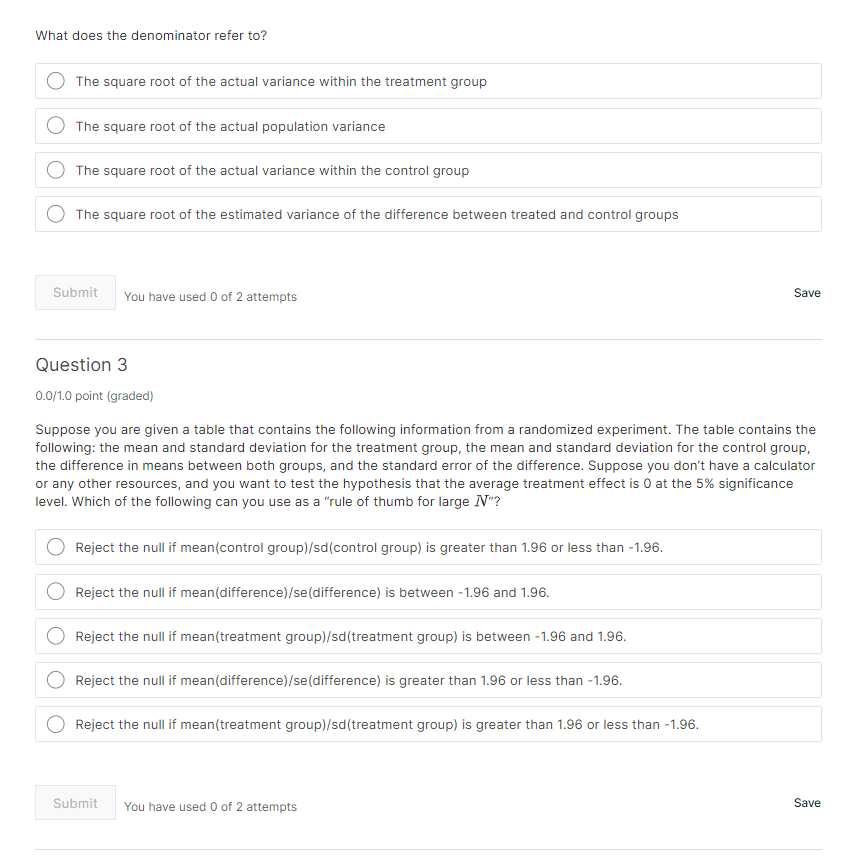
Question 1 0.0m) point {graded} What does the hypothesis test below test? 1 N HD:E;Y(1}Y[O}=O 1 N HE:F;Y(1)Y[D)a0 The null hypothesis that there is no treatment effect for any individual '3: versus the alternate hypothesis that the treatment effect is nonzero The null hypothesis that the treatment effect on any individual is zero versus the alternate hypothesis that the treatment effect on any individual is nonzero The null hypothesis that the average treatment effect is zero versus the alternate hypothesis that the average treatment effect is nonzero 0000 The null hypothesis that the average treatment effect is zero versus the alternate hypothesis that the average treatment effect is positive Submit You have used 0 of 2 attempts Save Question 2 0.0m) point {graded} In the Neyman hypothesis test described in the previous question, the test statistic, t, is calculated as shown below. The numerator refers to and the denominator refers to is for a specific outcome; What does the term in the denominator refer to? What does the numerator refer to? O The estimated difference in outcomes in pairs of units in the treatment and control groups, averaged O The difference in sample means between the treatment and control groups 0 The difference in outcomes in pairs of units in the treatment and control groups, averaged O The actual population difference in means between the treatment and control groups What does the denominator reter to? O The square root of the actual variance within the treatment group O The square root of the actual population variance 0 The square root of the actual variance within the control group O The square root of the estimated variance of the difference between treated and control groups Submit You have used 0 of 2 attempts Save Question 3 some point [graded] Suppose you are given a table that contains the following information from a randomized experiment. The table contains the following: the mean and standard deviation for the treatment group, the mean and standard deviation tor the control groupr the difference in means between both groups] and the standard error of the difterence. Suppose you don't have a calculator or anyr other resources, and you want to test the hypothesis that the average treatment effect is 6 at the 5% significance level. Which of the following can you use as a "rule of thumb for large N"? O Reject the null if meanicontrol grouplfsdjcontrol group) is greater than 1.96 or less than -1.96. Reject the null if mean[differencejfseidifference] is between -1.96 and 1.96. Reject the null if meanitreatment groupjfsdjtreatment group) is between -'l.96 and 1.96. Reject the null if mean[differencejfseidifference] is greater than 1.96 or less than -1.96. 0000 Reject the null if meanitreatment groupjfsdjtreatment group) is greater than 1.96 or less than -1.96. Submit You have used 0 of 2 attempts Save
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


