Question: Question 1 (1 point) A student is pushing toward the left on a heavy box that is resting on a rough surface. The box is

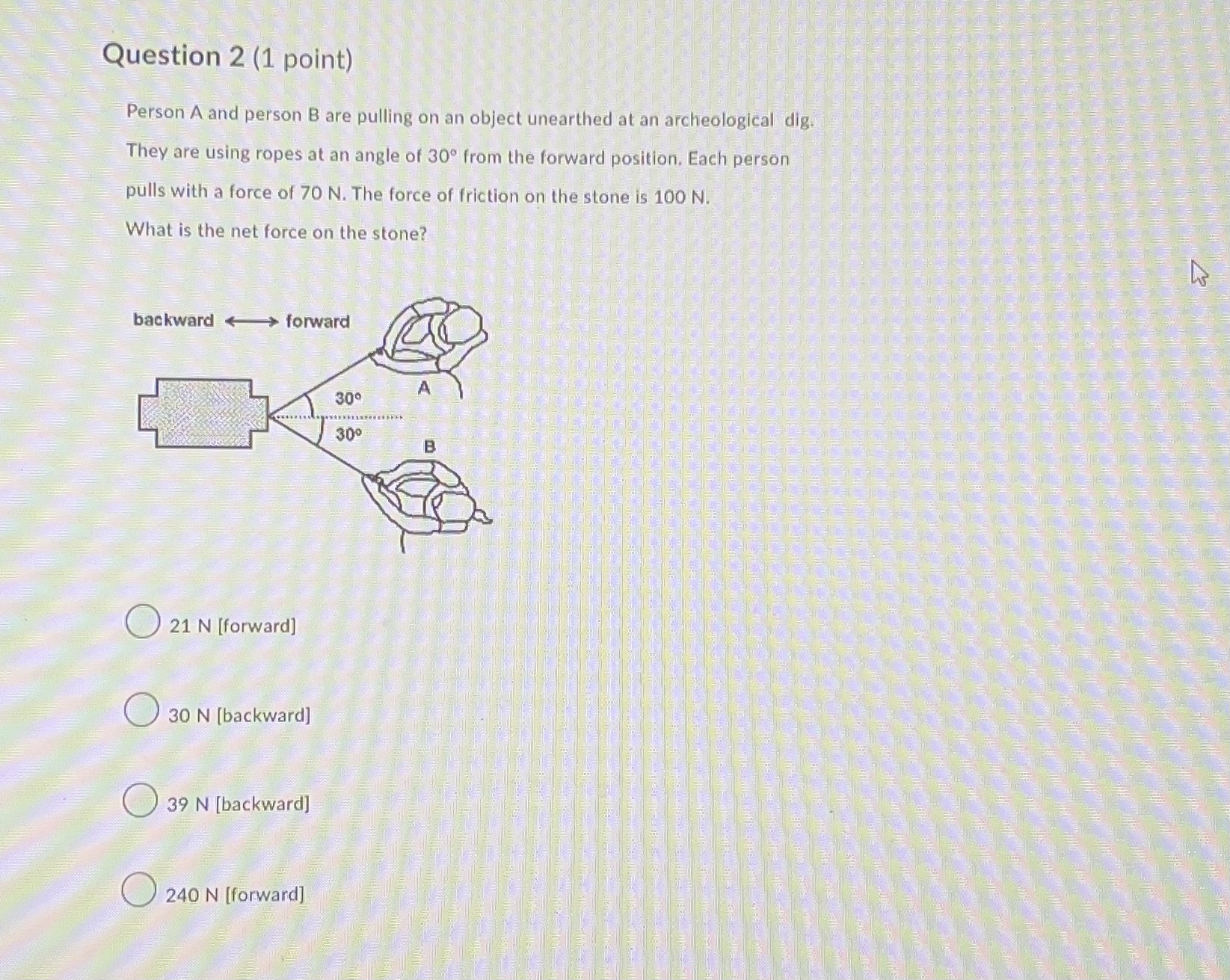
![which directions? force of gravity [down] and applied force [left ] 2](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/07/668973f960438_153668973f93ecac.jpg)
![force of gravity [down], normal force [up], and applied force [left] force](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/07/668973f9b7307_153668973f996faa.jpg)
![of gravity [down], normal force [up], force of friction [left], and applied](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/07/668973fa27967_154668973fa063bf.jpg)
![force [left] 5 force of gravity [down], normal force [up], force of](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/07/668973fac4fe9_154668973fa6cb93.jpg)
![friction [right], and applied force [left]Question 2 (1 point) Person A and](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/07/668973fb33e55_155668973fb0fef0.jpg)
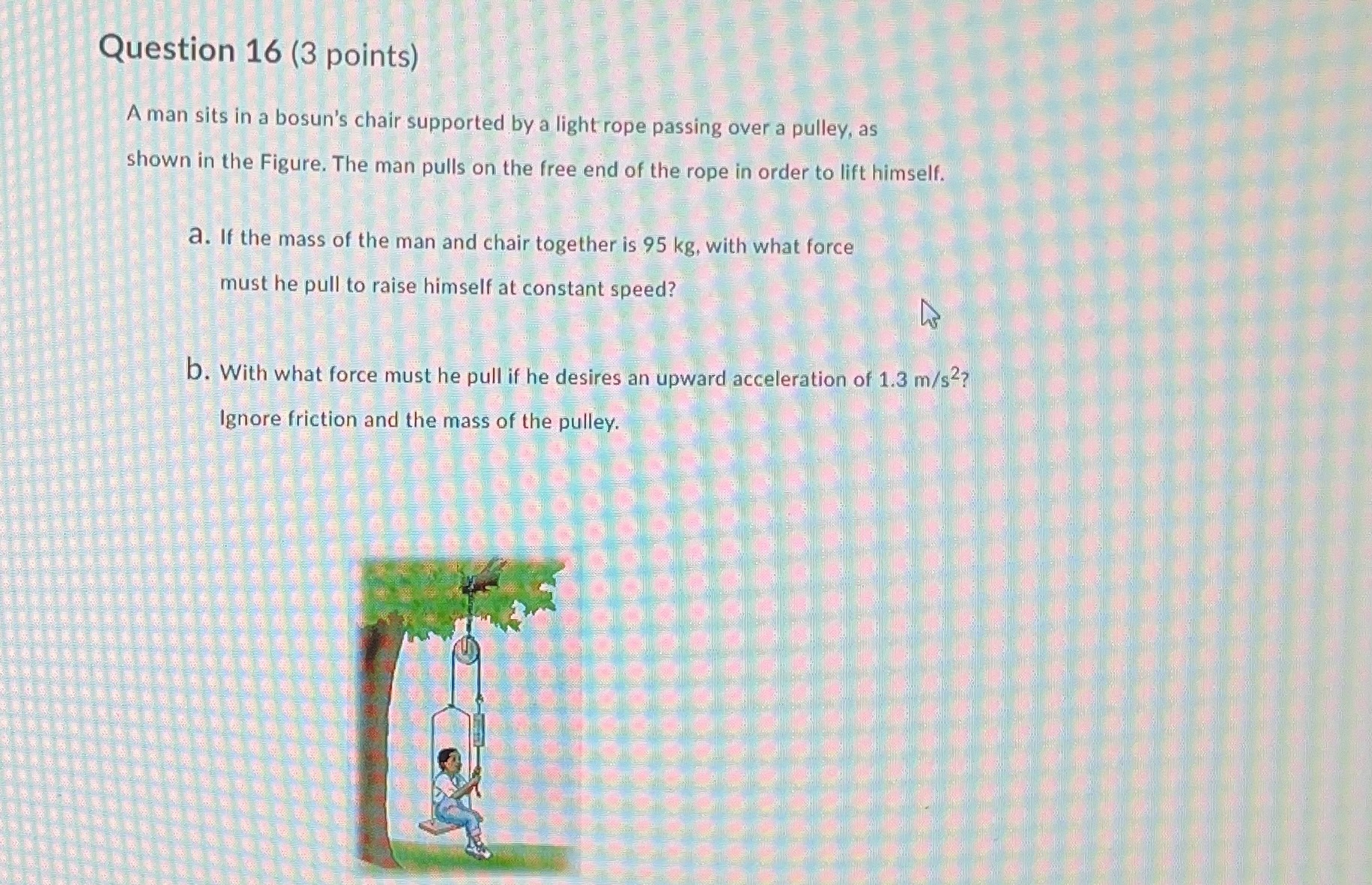

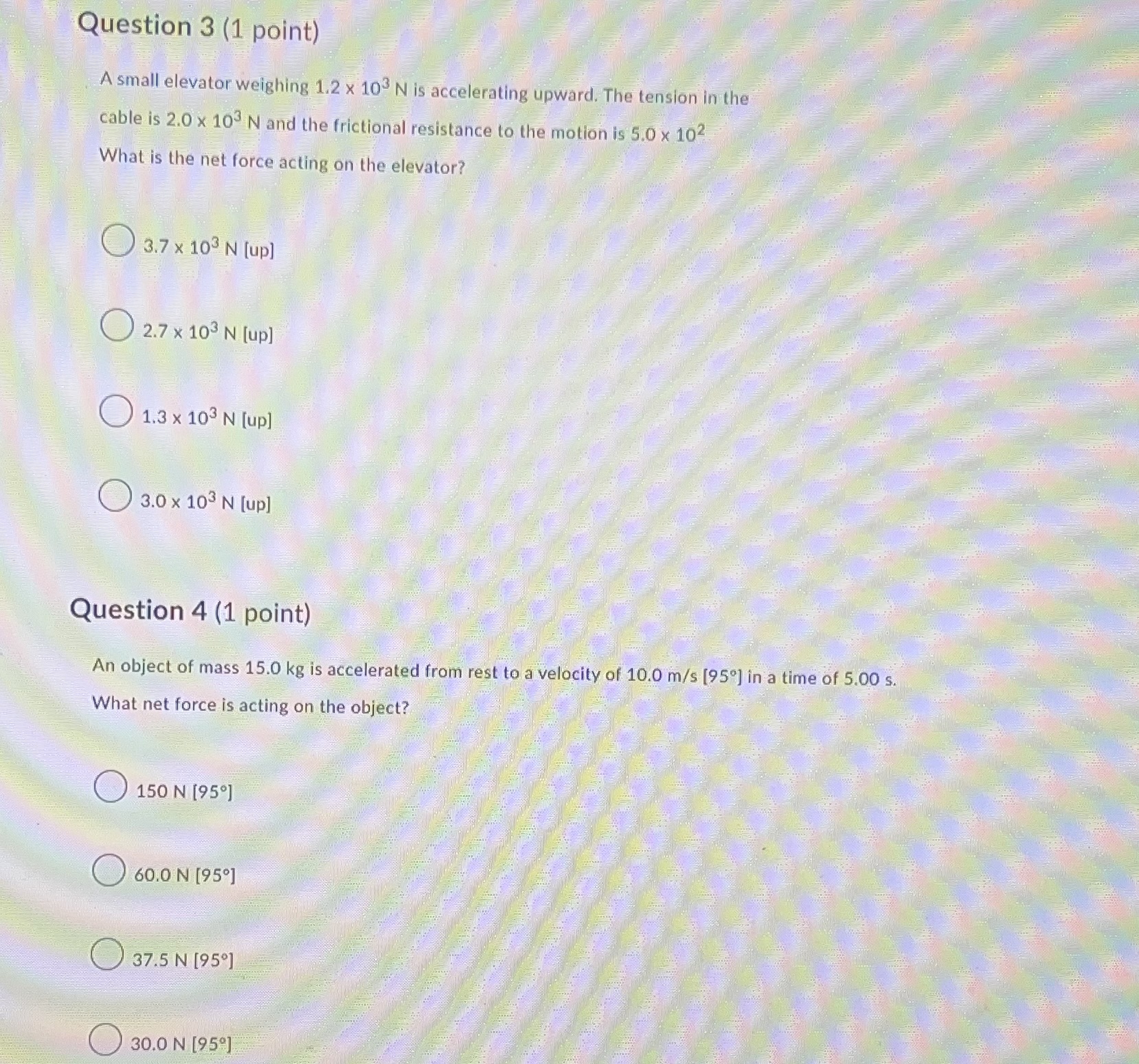
Question 1 (1 point) A student is pushing toward the left on a heavy box that is resting on a rough surface. The box is not What forces are acting on the box and in which directions? force of gravity [down] and applied force [left ] 2 force of gravity [down], normal force [up], and applied force [left] force of gravity [down], normal force [up], force of friction [left], and applied force [left] 5 force of gravity [down], normal force [up], force of friction [right], and applied force [left]Question 2 (1 point) Person A and person B are pulling on an object unearthed at an archeological dig. They are using ropes at an angle of 30 from the forward position. Each person pulls with a force of 70 N. The force of friction on the stone is 100 N. What is the net force on the stone? backward forward 309 300 21 N [ forward] 30 N [backward] 39 N [backward] 240 N [forward]Question 3 (1 point) A small elevator weighing 1.2 x 10 N is accelerating upward. The tension in the cable is 2.0 x 105 N and the frictional resistance to the motion is 5.0 x 102 What is the net force acting on the elevator? 3.7 x 103 N [up] 2.7 x 103 N [up] 1.3 x 103 N [up] 3.0 x 103 N [up] Question 4 (1 point) An object of mass 15.0 kg is accelerated from rest to a velocity of 10.0 m/s [950] in a time of 5.00 s. What net force is acting on the object? 150 N [95) 60.0 N [95] 37.5 N [95] O 30.0 N [95]Question 5 (1 point) A car of mass 1500 kg and travelling at 5.0 m/s [east] accelerates for 10 s to a velocity of 24 m/s [east]. What is the net force on the car? 7.5 x 102 N [east] 2.9 x 103 N [east ] 3.6 x 103 N [east] 4.4 x 103 N [east] Question 6 (1 point) It takes a force of 64 N to start a 8.0 kg copper block sliding on a dry horizontal copper rail . What is the coefficient of static friction for these copper surfaces? 0.61 0.75 0.82 1Question 7 (1 point) Consider the coefficients of static friction, My, and of kinetic friction, Ak, for a wood block on a rough, horizontal surface made of the same kind of wood. Which of the following statements is correct for most surfaces for these coefficients of friction? OH, = HK HS > HK OH , HK Question 8 (1 point) A light rope is used to lift a 10-kg mass and give it an acceleration of 2.0 m/s2 [up] (g = 9.81 m/s2 [down]). What is the force used? 10 N [up] 20 N [up] 1.0 x 102 N [up] 1.2 x 102 N [up]Question 9 (1 point) A car has a mass of 1500 kg. What net force is needed to accelerate the car from 5.00 m/s [40] to 25.0 m/s [40] in 10.0 s? 7.50 x 102 N [40 ] 3.00 x 103 N [40] 3.75 x 103 N [409] 4.50 x 103 N [40] Question 10 (1 point) Which best explains why we are able to accelerate forward when starting to run? The striking foot pushes backward against the ground. The friction with the ground provides an equal and opposite force forward. As one leg moves backward, it provides an equal and opposite force for the other foot to move forward. The runner's upper body quickly leans forward, causing the entire body to begin accelerating forward. The foot not touching the ground propels the entire body as it swings forward.Question 11 (1 point) All of the following situations can be explained using Newton's 3d law, except for one of them. Which situation can NOT be explained using 3'd law ideas? An inflated balloon is not tied, and is let go. It moves forward as it pushes air backward out of the hole. The gravitational interaction between Earth and the Moon affects both objects, with Earth's tides mostly due to the Moon's gravitational pull. A projectile's horizontal velocity remains constant, because gravity is a vertical force and no horizontal force acts on the projectile. A propeller airplane would not work in outer space, because propellers work by pushing air backward to move the airplane forward.Question 12 (1 point) A girl holds an orange at rest in her hand. One force in an section/reaction pair is the force of earth's gravity pulling down on the orange. What is the other force in action/reaction pair of forces? O The force of the hand pushing up on the orange. The force of the earth pushing up on the girl's foot. The force of the orange pushing down on the girl's hand. O The force of the orange pulling up on the earth. Question 13 (1 point) Which of these laws is not one of Newton's laws? Action is reaction. ma All objects fall with equal acceleration. Objects at rest stay at rest, etc.Question 14 (2 points) A 360 kg box rests on the bed of a truck that is going down a slope on a straight section of road. The truck starts down the slope with a speed of 100 km/h and slows to 60 km/h in 20 s. Assume that the acceleration is constant during this interval and calculate the strength and direction of the resultant force that must act on the box during this period of time. [Click on [..] in your answer box to use more math tools] Paragraph v BIUA Ev EV A v Insert Stuff Question 15 (3 points) Two blocks are in contact on a frictionless table. A horizontal force is applied to one block as shown in Figure. mi a. If m1 = 2.0 kg and m2 = 1.0 kg and F = 3.0 N, find the force of contact between the two blocks. b. If the same force is applied to my rather than to m1, do you think the force of contact is the same value derived in (a)? What is that?Question 16 (3 points) A man sits in a bosun's chair supported by a light rope passing over a pulley, as shown in the Figure. The man pulls on the free end of the rope in order to lift himself. a. If the mass of the man and chair together is 95 kg, with what force must he pull to raise himself at constant speed? b. With what force must he pull if he desires an upward acceleration of 1.3 m/s2? Ignore friction and the mass of the pulley.Question 17 (4 points) A 5.0 kg block is pulled along horizontal frictionless floor by a cord that exerts a force F = 12 N at an angle 0 = 250. a. What is the acceleration of the block? b. If the force F is slowly increases, what is the value of F just before the block is lifted off the floor? C. What is the acceleration of the block just before it is lifted off the floor
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


