Question: Question 1 ( 1 point ) Saved Figure 1 showing the Stauffer canopy and Figure 2 showing the simplified model Cables support the entrance roof
Question point
Saved
Figure showing the Stauffer canopy and Figure showing the simplified model
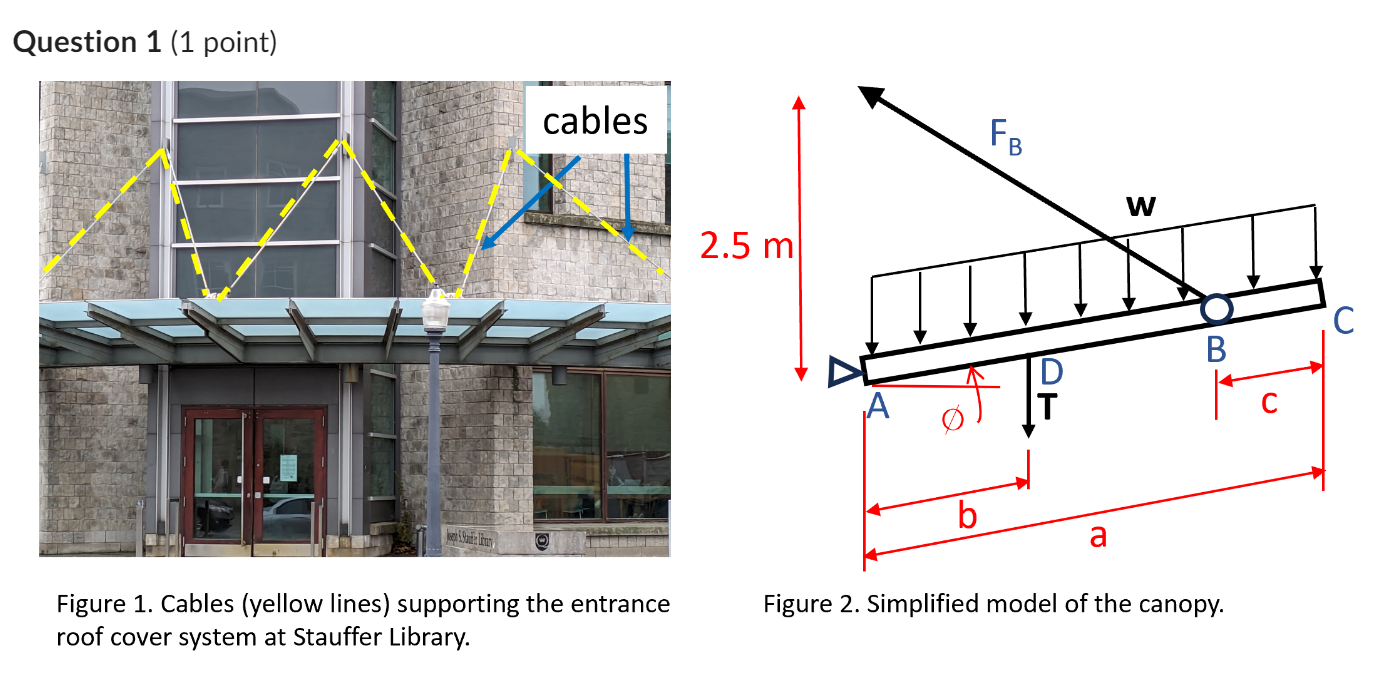
Cables support the entrance roof at Stauffer Library as shown in Figure A simplified model of the canopy is given in Figure where the cable has been replaced with a force, FB that acts through a point m above the canopy. The canopy can be at any angle,
The analysis below is to be completed using the simplified model in Figure For simplicity assume that the roof is pinned at point A see Figure Figure also shows additional dimensions of the roof. The roof is m in length between points A and C labelled as length a The cable force, FB acts at point B which is located at distance c from point C
The roof has a load from the selfweight of the structure, T that acts at point D which is located at distance b from point A Snow can accumulate on the roof to a thickness of m resulting in a uniformly distributed load UDL w applied between points A and C The snow has a density of kgm
Note: mass of snow density of snow thickness of snow width of roof section
In your tutorial group complete the following and have the TA mark your work during the tutorial and record your work on onQ. Apply a sign convention that forces acting up and to the right are positive and clockwise moments are positive. Complete your calculations for a m width section of the roof.
Calculate the UDL, w with units of kNm and enter it in the space below. Use significant figures.
Draw the free body diagram for the structure.
Develop equations for the reactions at A and the force in the cable, FB that work for any value of w T and angle,
Get the TA to check your work.
Complete the remaining tutorial questions on your own, enter your answers into onQ, and upload your calculations. For the remaining questions assume the canopy angle,
is zero degrees and the distance b is m
Your Answer:
Question options:
Answer
Question point
Saved
Note that each question will have different values of the force, T the density of snow, the thickness of snow, and the distance, c
For T of kN density of snow of kgm thickness of snow of m and distance c of m calculate the vertical reaction at A
Your Answer:
Question options:
Answer
Question point
Saved
Note that each question will have different values of the force, T the density of snow, and the distance, c
For a force in the cable FB of kN and distance c of m calculate the horizontal reaction at A
Your Answer:
Question options:
Answer
Add attachments to support your work
Question point
Note that each question will have different values of the force, T the density of snow, the thickness of snow, and the distance, c
For T of kN density of snow of kgm thickness of snow of m and distance c of m calculate the vertical component of the force in the cable, FB
Your Answer:
Question point
Figure Cables yellow lines supporting the entrance
Figure Simplified model of the canopy. roof cover system at Stauffer Library.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


