Question: Question 1 (1 point) When do we compute a simple main effect test? 0 When there is a main effect. 0 When there is a









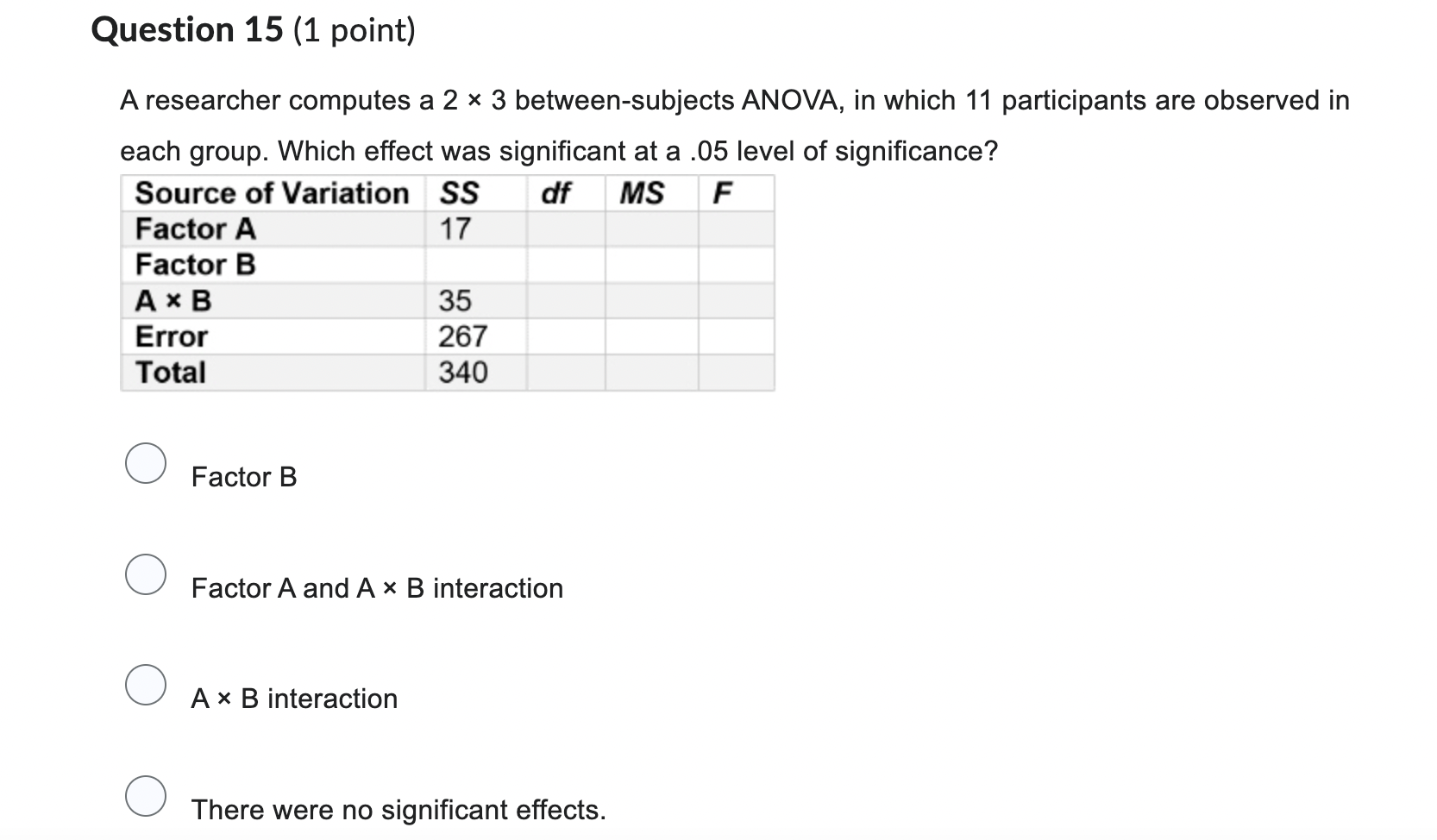
Question 1 (1 point) When do we compute a simple main effect test? 0 When there is a main effect. 0 When there is a significant main effect, where k > 2. Q When there is a significant interaction. 0 none of these Question 2 (1 point) When computing a two-way between-subjects ANOVA, we assume that the data we measure were obtained from a sample that was selected using a random sampling procedure. 0 1) True 0 2) False Question 3 (1 point) When computing a two-way between-subjects ANOVA in SPSS, which rows in the output table provide the necessary information to summarize the results of the test? O the first five rows under the row intercept O the first two rows O the last three rows O the middle three rowsQuestion 5 (1 point) What is the second reason :92 is less biased than n2 when computing a two-way between-subjects ANOVA? Q It corrects for size of error by including MSBG in its formula. 0 It corrects for the number of groups by including the degrees of freedom for the main effect or interaction. 0 It corrects for size of error by including M85 in its formula. 0 It corrects for the number of groups by including the degrees of freedom for the between- groups variation or within-groups variation. Question 6 (1 point) While computing a two-way between-subjects ANOVA, a researcher determines that there is a significant main effect of Factor A and a significant A x B interaction. Which significant effect should the researcher analyze first? O A x B interaction O main effect of Factor B O main effect of Factor A O a post hoc should be computed insteadA researcher computes a 2 x 4 between-subjects ANOVA and determines one signicant main effect and a significant interaction. What is the next step the researcher should take? O compute pairwise comparisons for the interaction 0 compute a simple main effect test for the interaction 0 compute pairwise comparisons for the main effect compute a simple main effect test for the main effect Question 8 (1 point) A between-subjects factorial design is one in which the same participants are observed in each cell or group. Question 9 (1 point) A researcher conducts a 3 x 4 between subjects ANOVA, in which five participants are observed in each group. If the researcher determines that 38.; = 12 and 33.; = 248. what decision will be made for Factor B at a .01 level of signicance? 0 reject the null hypothesis O retain the null hypothesis 0 FactorA showed no significance. 0 There is not enough information to answer this question. Question 10 (1 point) A researcher observes the amount of water (in milliliters) a sample of rats drink from a solution containing sugar and a solution containing saccharine. What type of factorial design should the researcher use for this study? 0 a mixed factorial design 0 a between-subjects factorial design 0 a within-subjects factorial design 0 a 1-between, 1-within factorial design If a researcher finds no significance in either the main effects or interactions, a post hoc test should be performed. ( 1) True ( 2) False Question 12 (1 point) A research assistant computes 3 x 5 ANOVA design. How many groups are in their design? O 8 O 15 O 2 O 3A researcher conducts a 2 x 3 between subjects ANOVA, in which 10 participants are observed in each group. If the researcher determines that SSA = 15 and SSE = 235, what decision will be made for FactorA at a .05 level of significance? 0 reject the null hypothesis 0 retain the null hypothesis O Factor A showed no significance. 0 There is not enough information to answer this question. Question 14 (1 point) When computing a two-way between-subjects ANOVA, we assume that variance in each population is equal to each other. O 1) True 0 2) False Question 15 (1 point) A researcher computes a 2 x 3 between-subjects ANOVA, in which 11 participants are observed in each group. Which effect was significant at a .05 level of significance? Source of Variation SS df MS F Factor A 1? Factor B A x B 35 Error 267 Total 340 0 Factor B 0 Factor A and A x B interaction 0 A x B interaction 0 There were no significant effects
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


