Question: Question 1 3 pts We will eventually see using the theory of Taylor series that In (2) can be computed using an infinite series: In
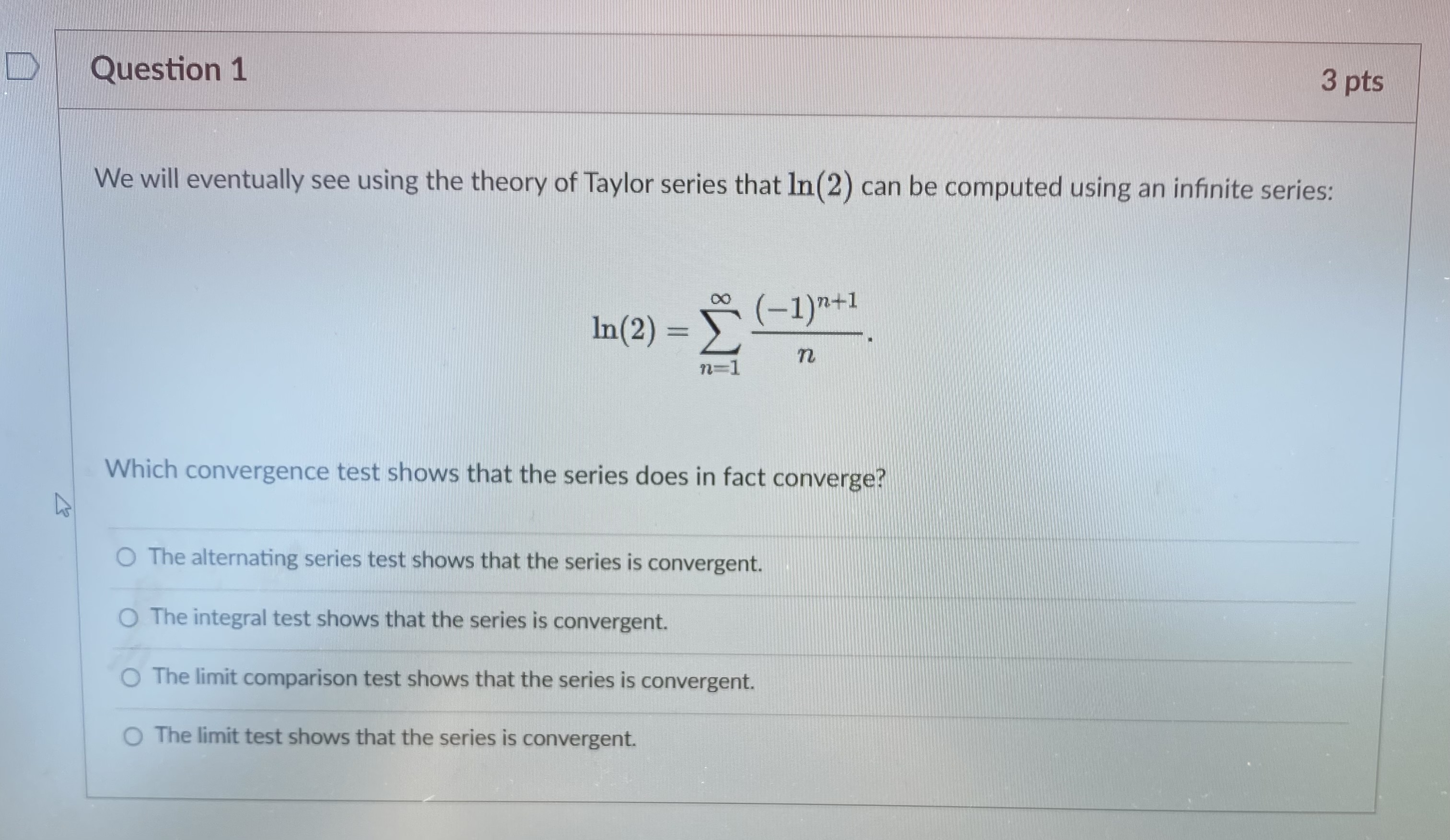
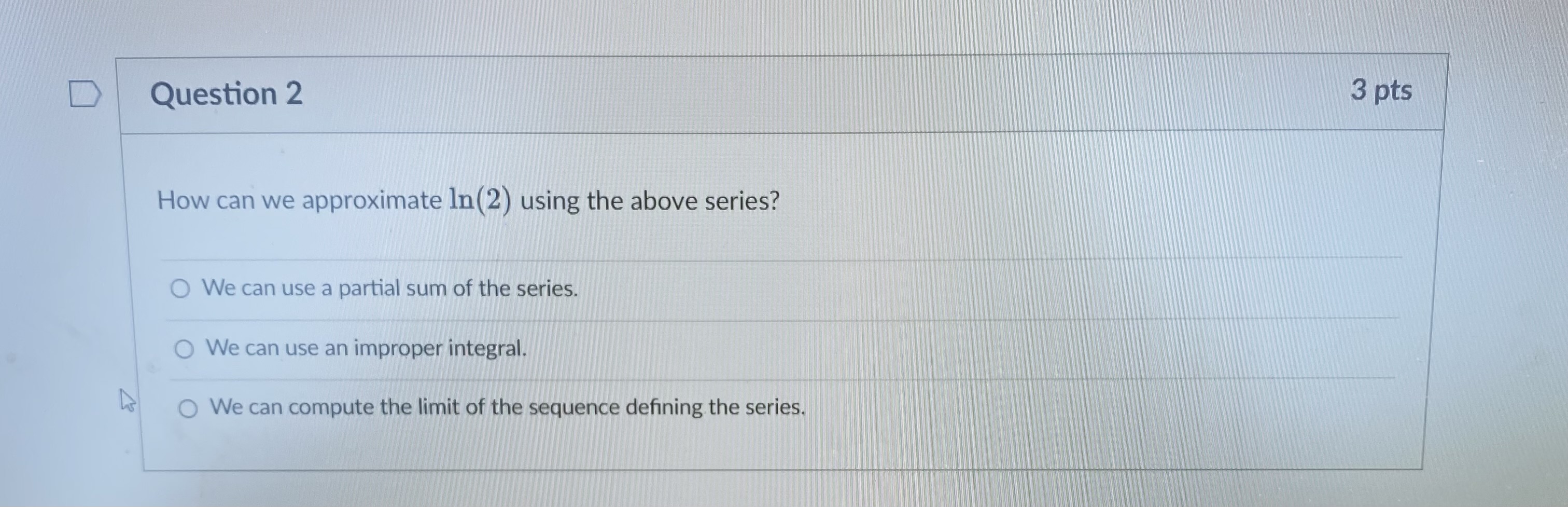


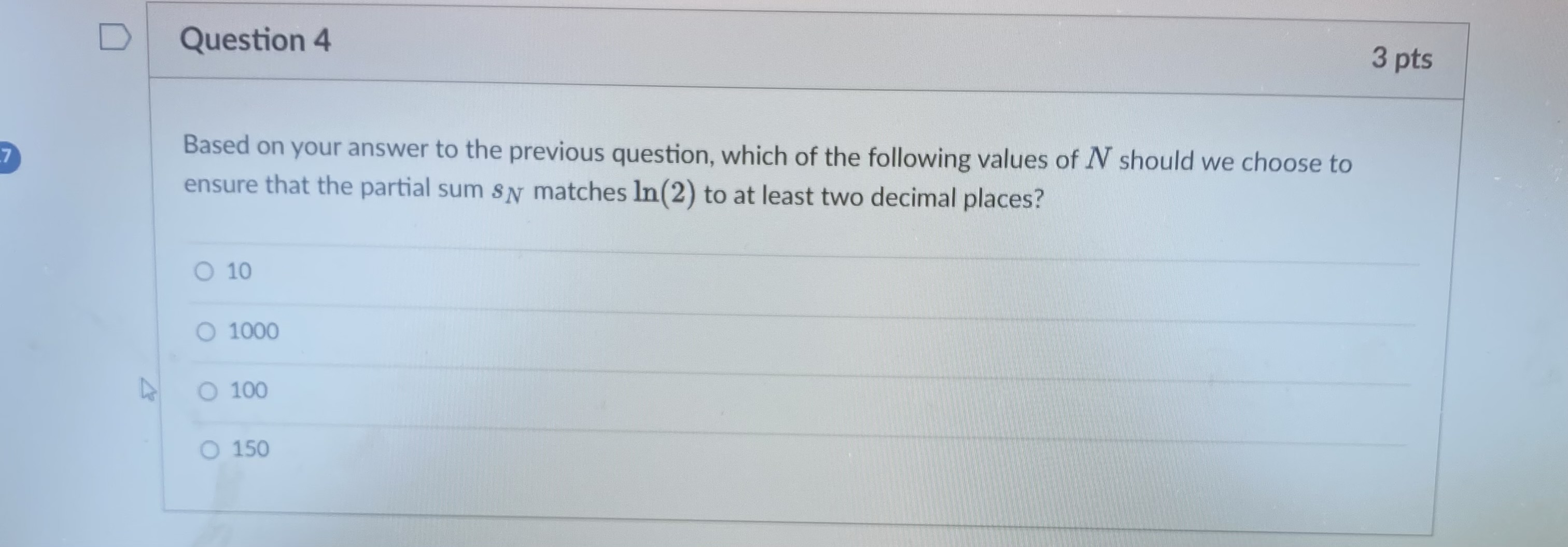
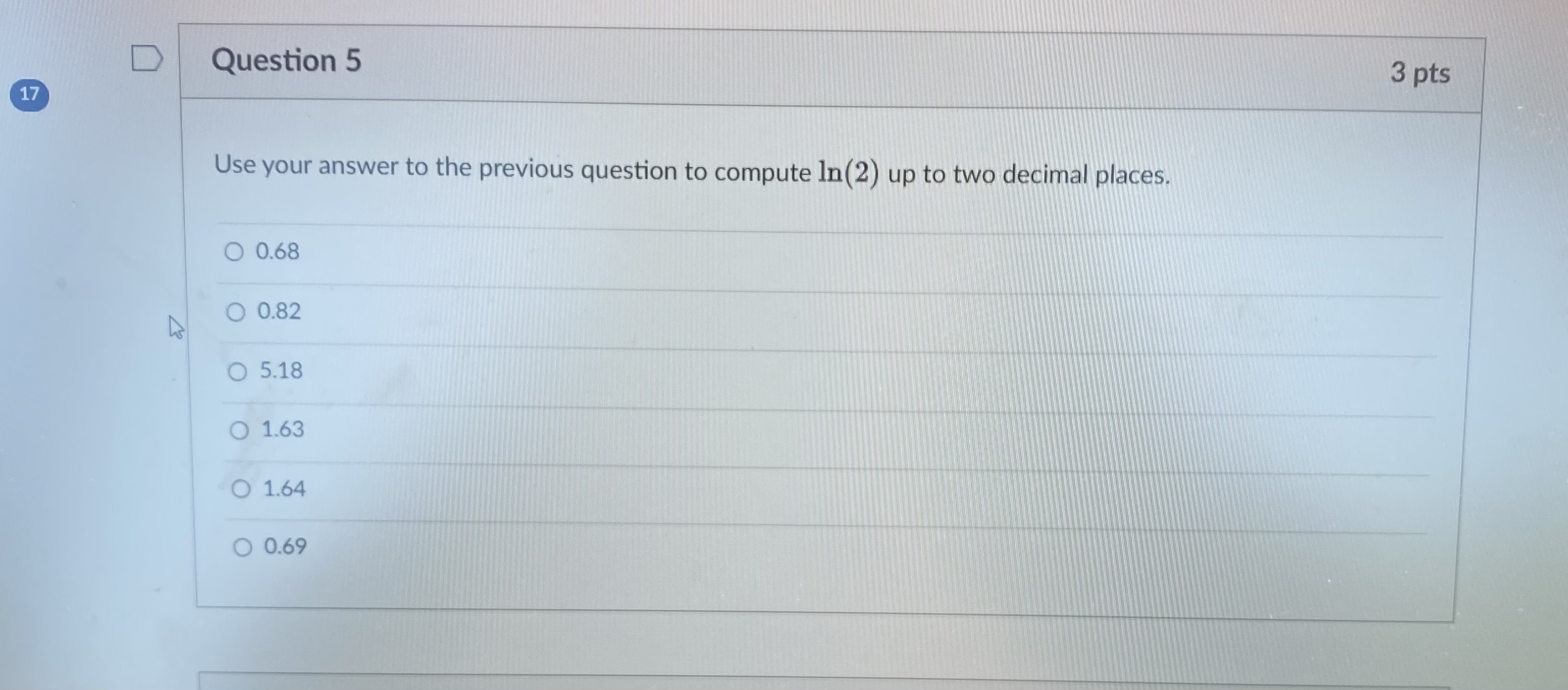
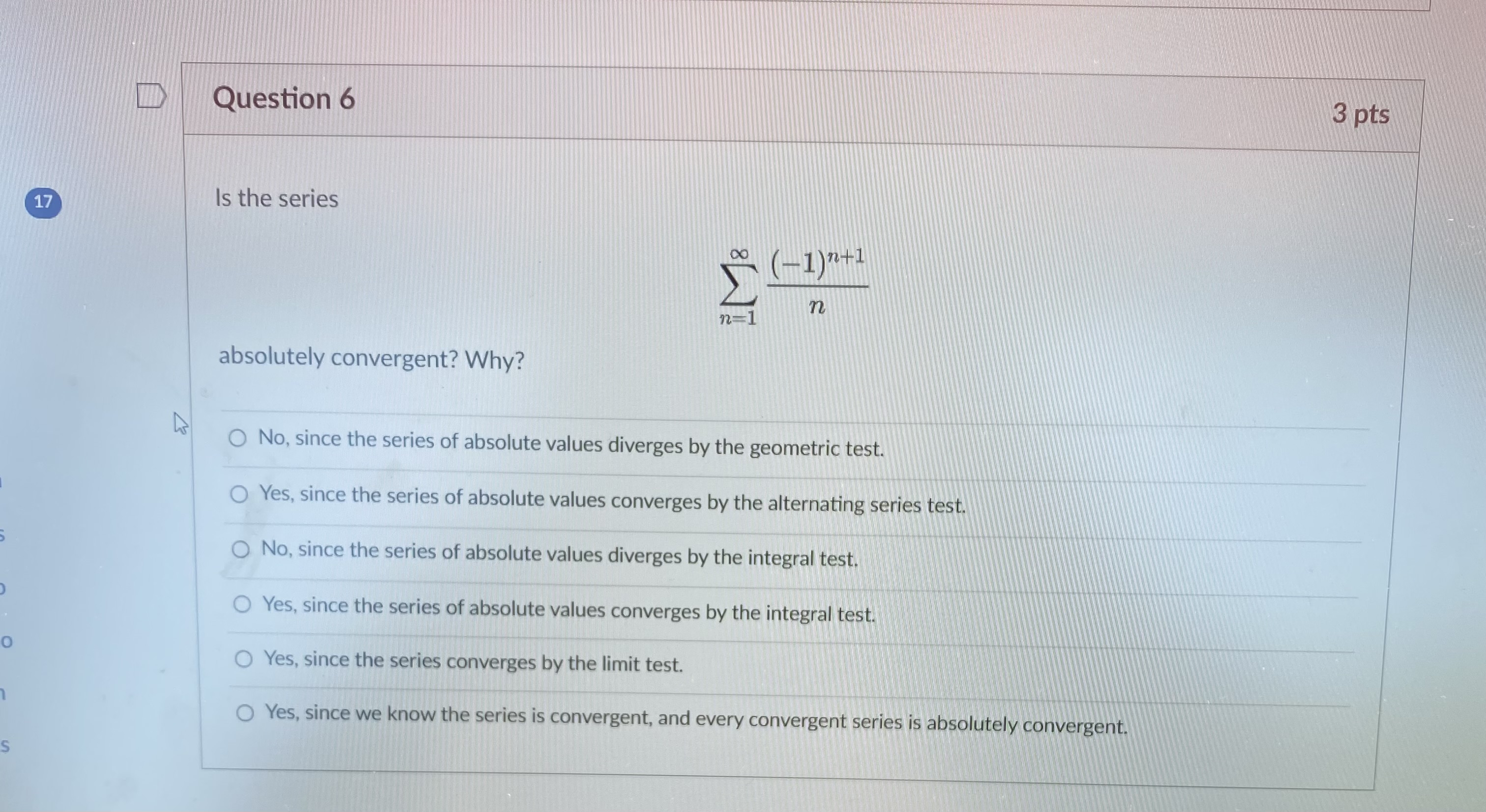
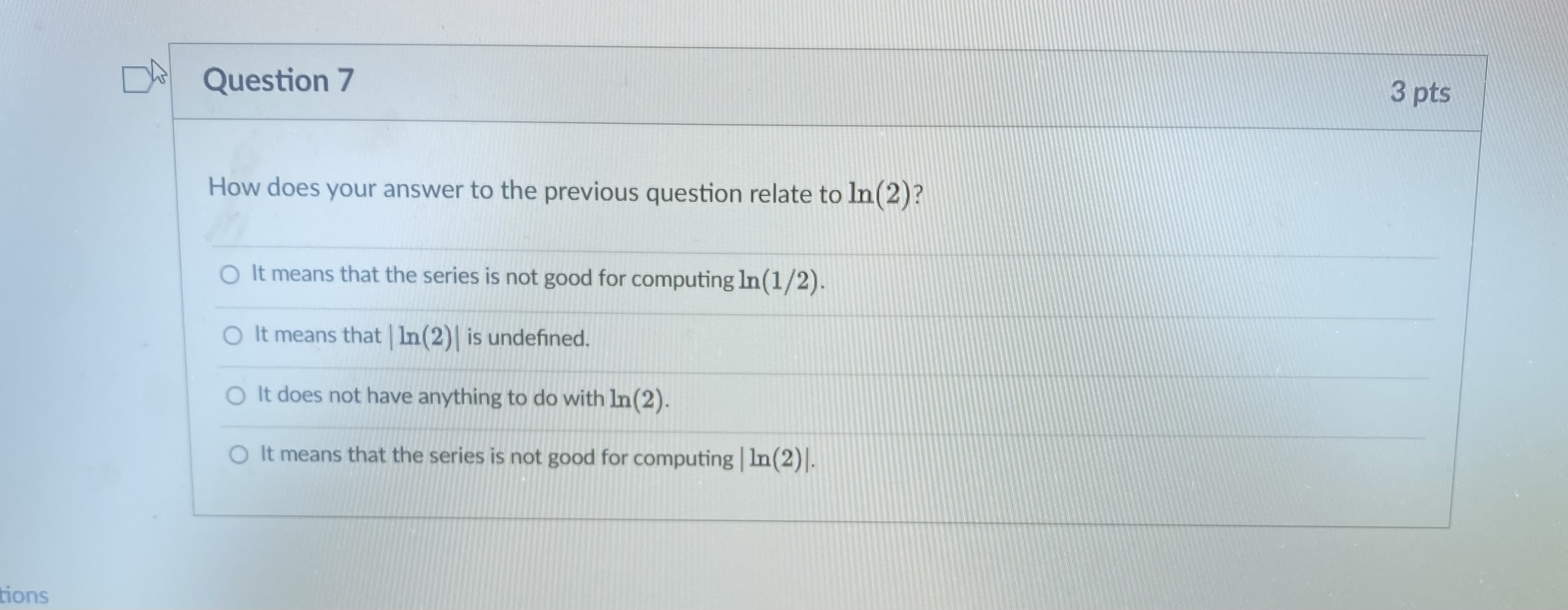
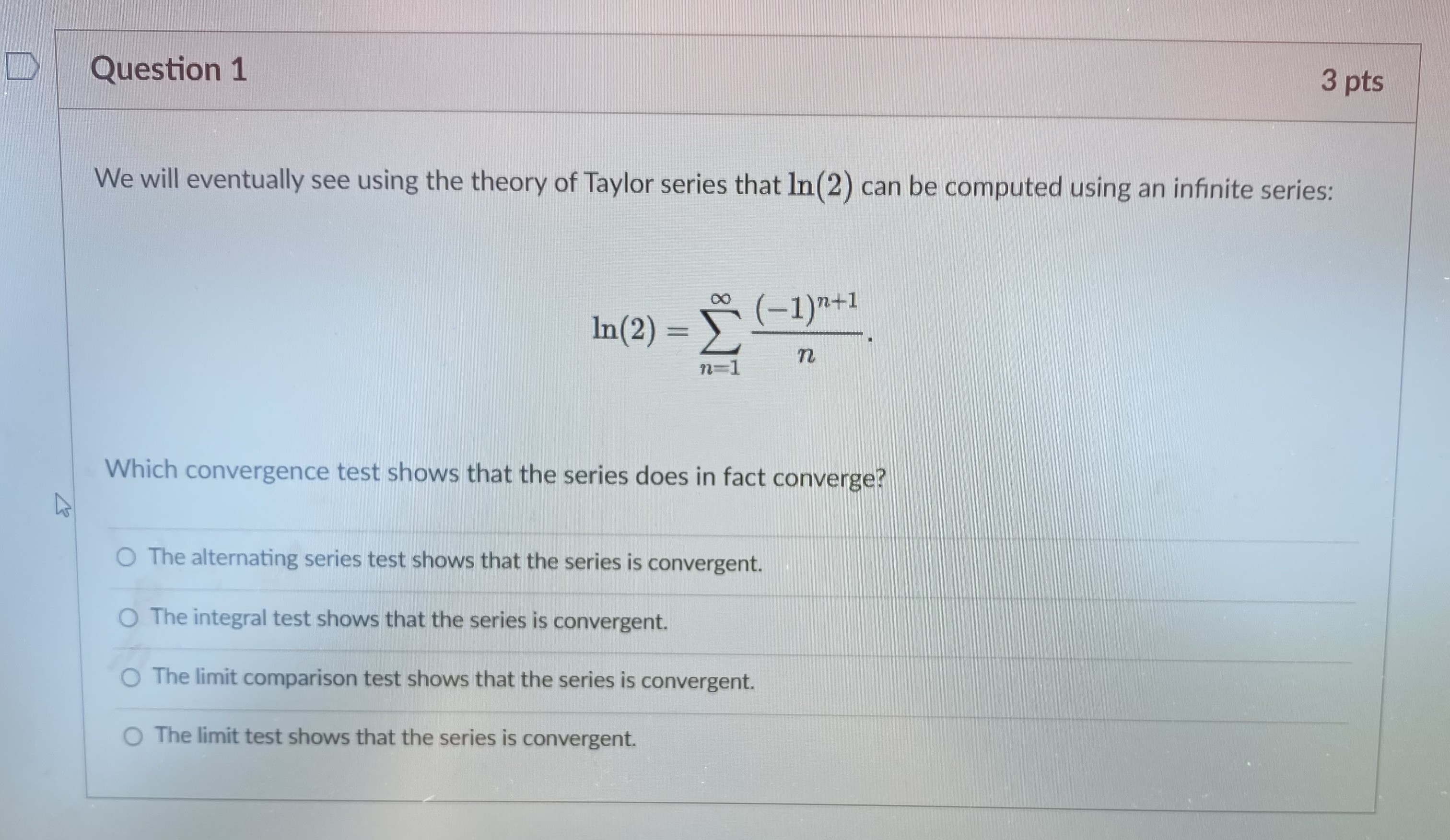
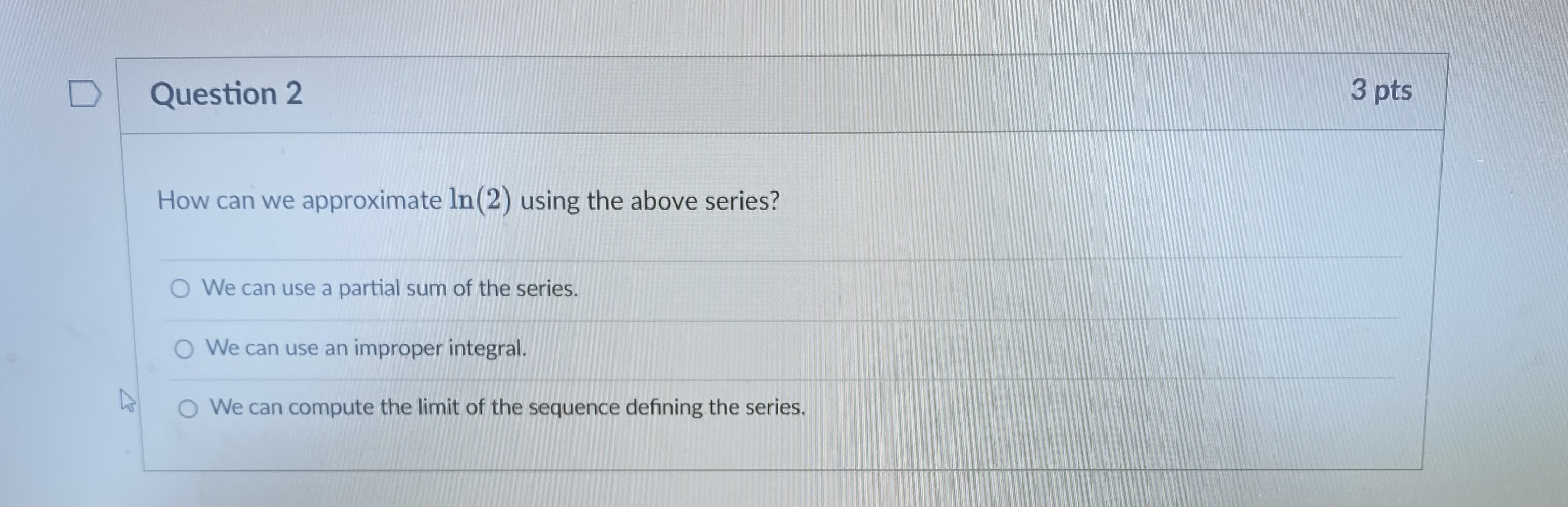


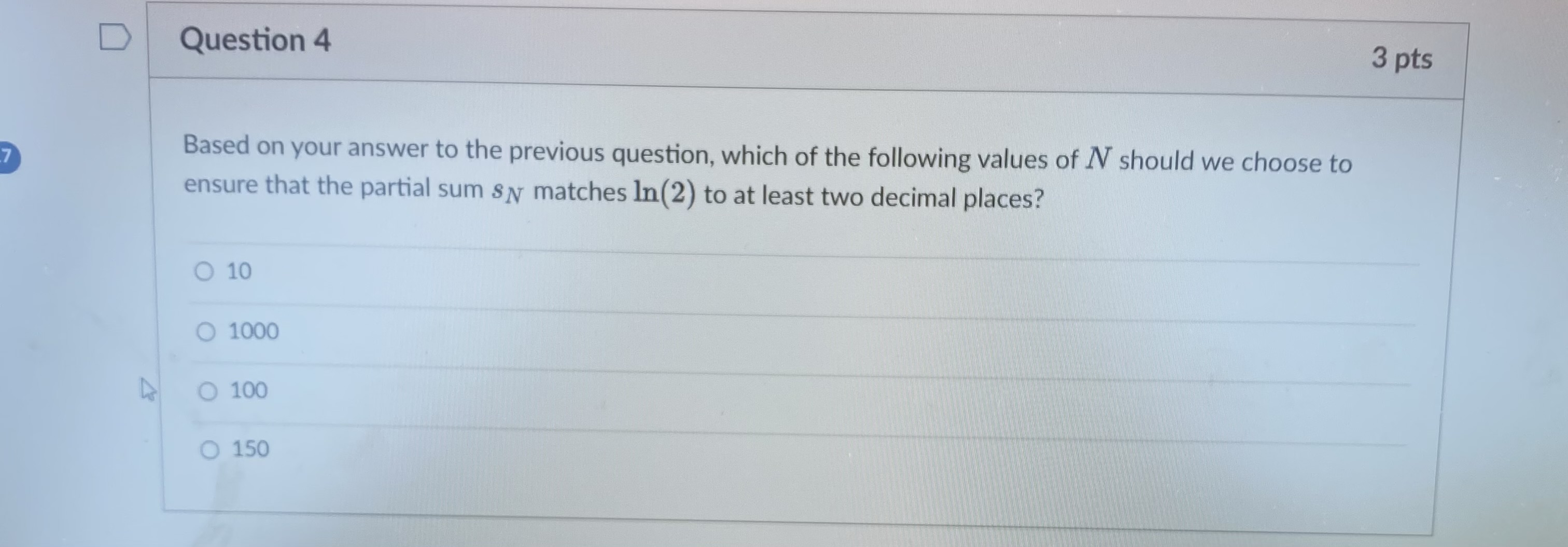
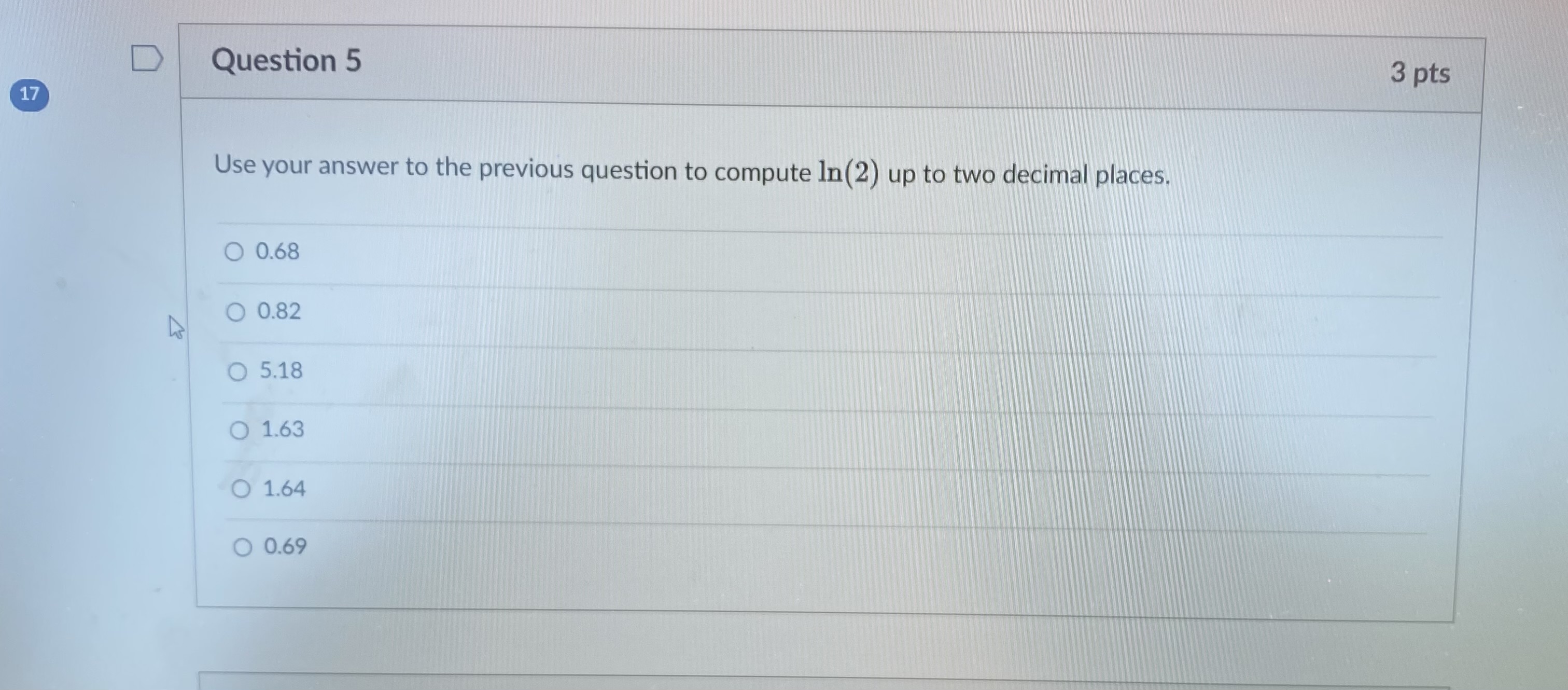
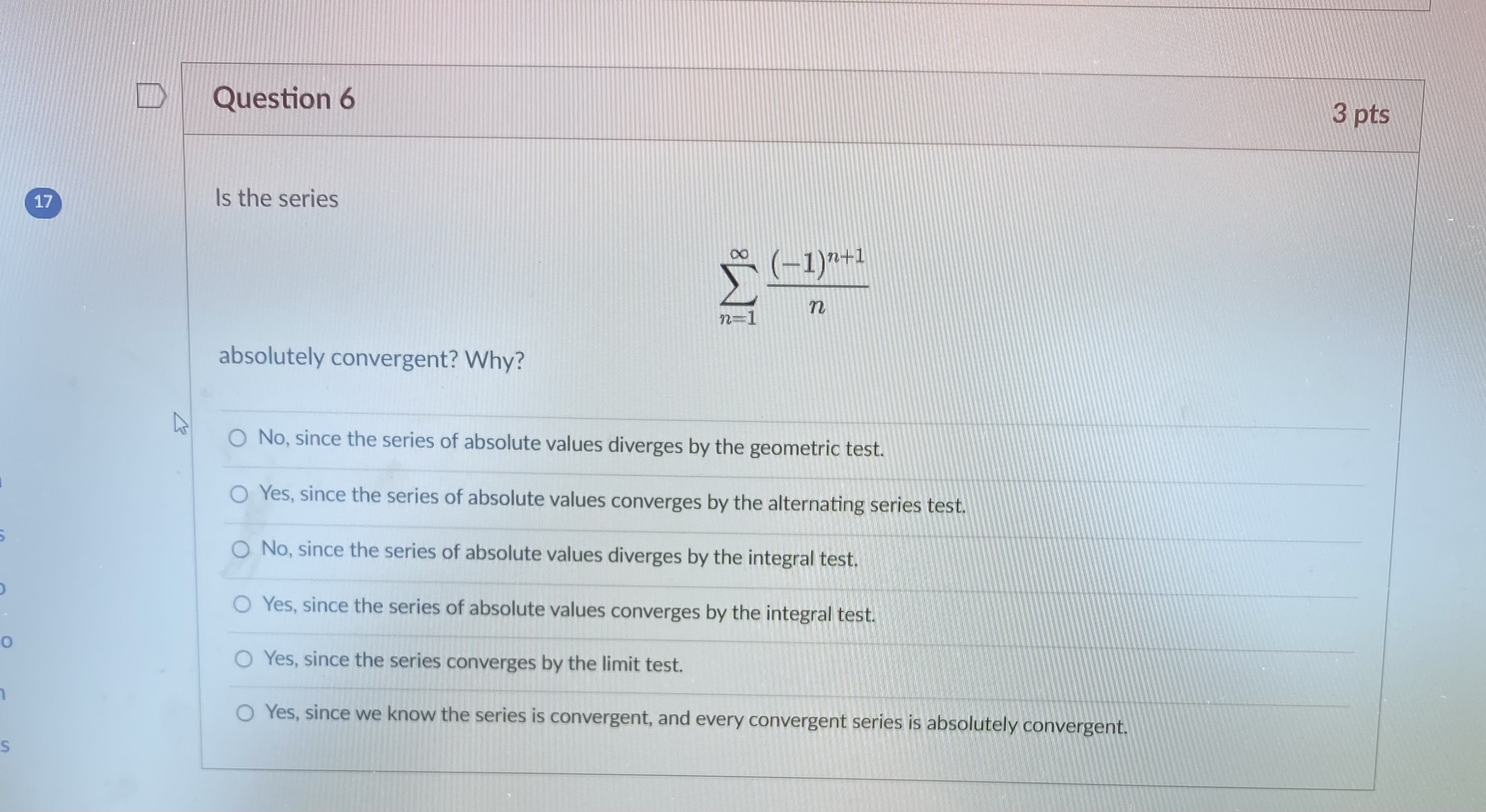
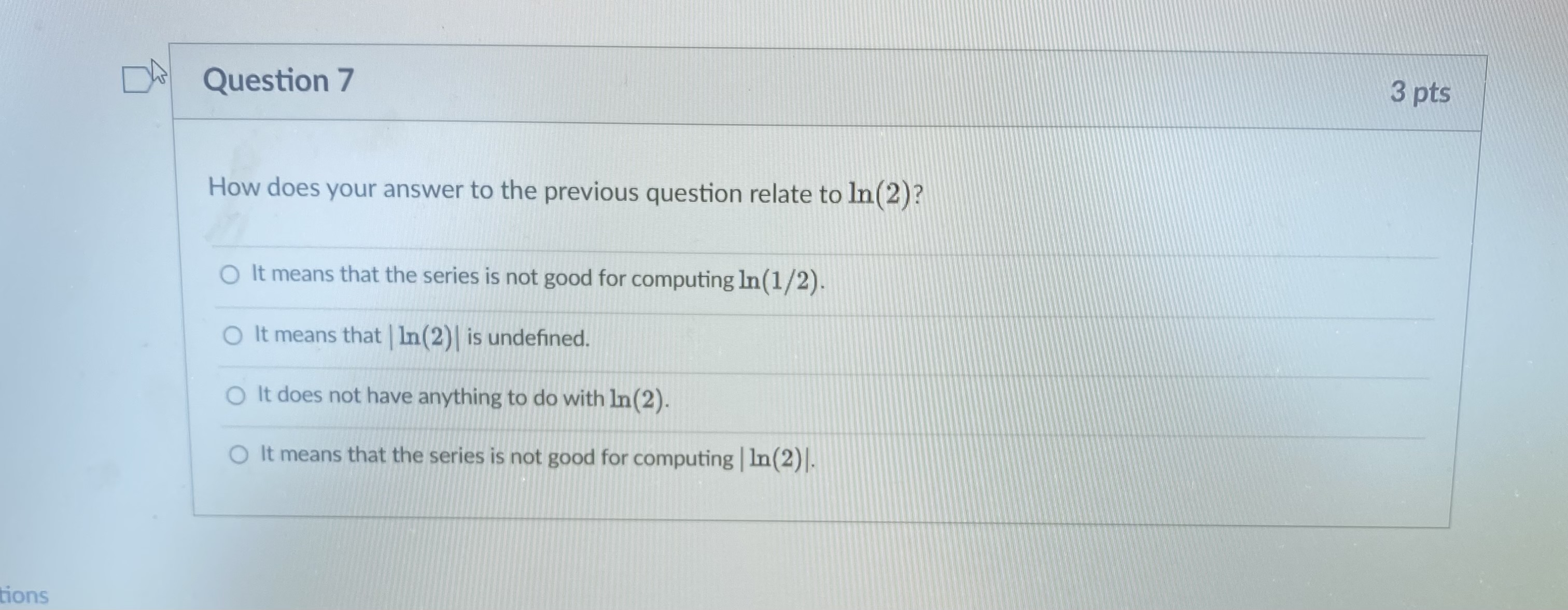
Question 1 3 pts We will eventually see using the theory of Taylor series that In (2) can be computed using an infinite series: In ( 2 ) (-1)n+1 n=1 n Which convergence test shows that the series does in fact converge? O The alternating series test shows that the series is convergent. O The integral test shows that the series is convergent. The limit comparison test shows that the series is convergent. O The limit test shows that the series is convergent.D Question 2 3 pts How can we approximate In(2) using the above series? O We can use a partial sum of the series. O We can use an improper integral. We can compute the limit of the sequence defining the series.D Let's recall the error estimate for the partial sums of an alternating series. Say the series 00 [(-1) 2+1 0n. 17 n=1 satisfies the conditions of the alternating series test. If the sum of the series is s, and the /Vth partial sum of the series is N SN = [(-1) 12 1 bra. then |s - SN|
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


