Question: QUESTION 1 3.33343 points save Answ Conditions for a binomial experiment is that it has only two possible outcomes and the probability of success on


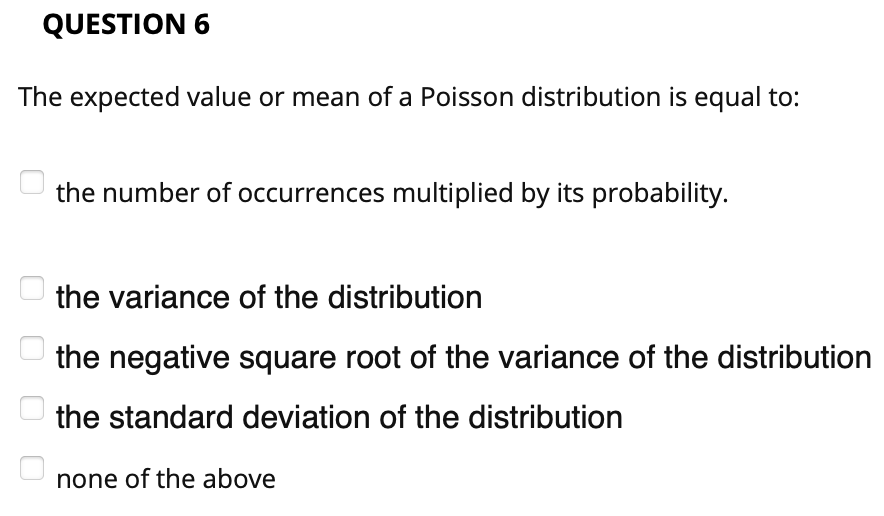




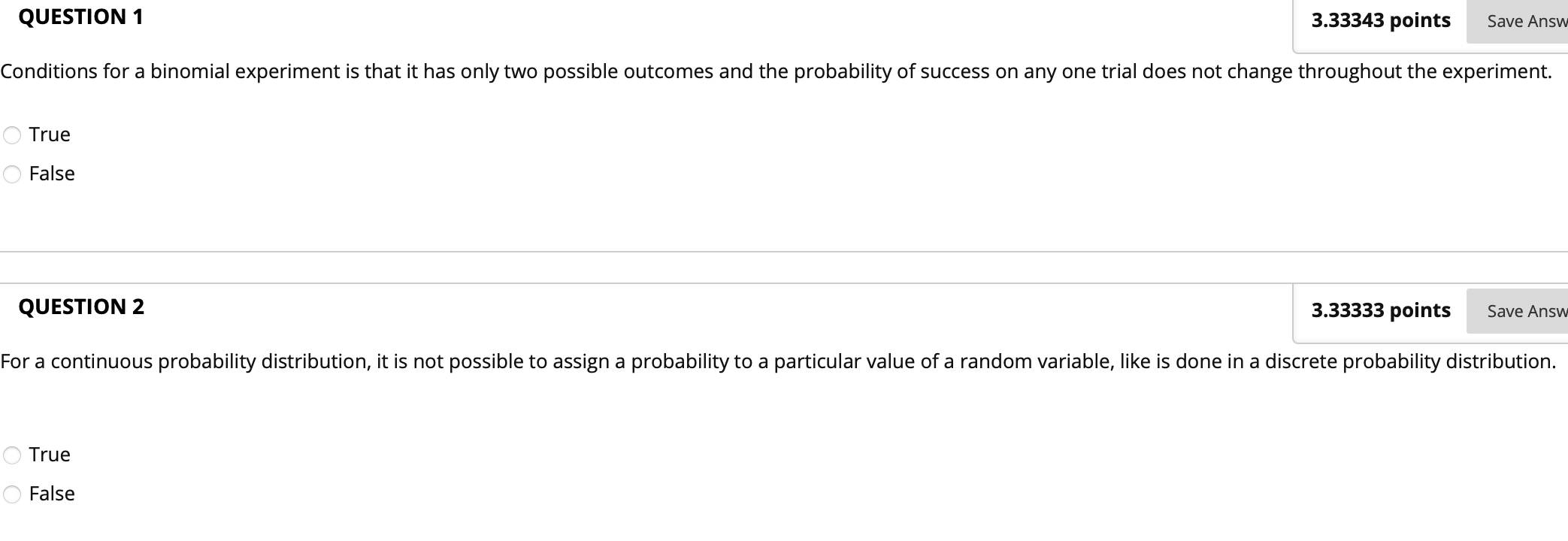



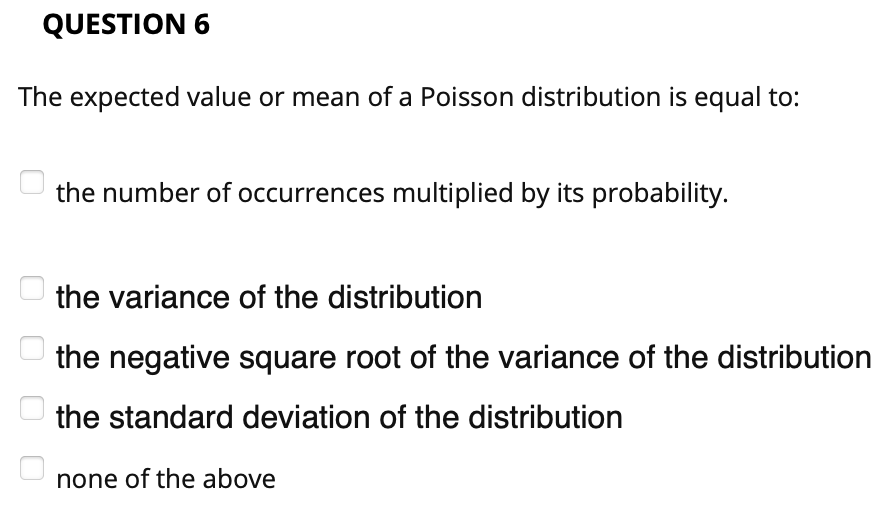




QUESTION 1 3.33343 points save Answ Conditions for a binomial experiment is that it has only two possible outcomes and the probability of success on any one trial does not change throughout the experiment. True False QUESTION 2 3.33333 points save Answ For a continuous probability distribution, it is not possible to assign a probability to a particular value of a random variable, like is done in a discrete probability distribution. True False QUESTION 3 An experiment consists of four outcomes with P(E1} = 0.25, P(E2) = 0.45, and P(E3) = 0.20. The probability of P(E4) is: none of the above _ 0.90 0.10 _ 0.50 7 0.02 QUESTION 4 3.33333 points Save Answel The method enables us to count the number of experimental outcomes when x objects are to be selected from a set of n objects, where the order of selection is not important. . probability tree multiplication method 7 permutation combination 7 joint probability table QUESTION 5 Which of the following is NOT one of the steps involved in building a discrete probability distribution? defining the random variable identifying the values for the random variable C identifying the values for the random variable O building a bar chart of the distribution O none of the aboveQUESTION 6 The expected value or mean ofa Poisson distribution is equal to: the number of occurrences multiplied by its probability. _ the variance of the distribution _ the negative square root of the variance of the distribution _ the standard deviation of the distribution none of the above QUESTION 7 Approximately what percentage of the values in a normal distribution will be within two standard deviations of the distribution mean. _ 100% _ 99.7% 7 95.5% 7 68.3% 50% QUESTION 8 Which of the following can use the exponential distribution to calculate the probability of occurring? number of hits in baseball game none of the above elapsed time between train arrivals all of the above drawing 2 aces in a row QUESTION 9 The time it takes the 50,000 runners to complete the New York City Marathon is an example of: either a continuous or a discrete random variable, depending on how they place I none ofthe above a discrete random variable ' a continuous random variable either a continuous or a discrete random variable, depending on the number of runners QUESTION 10 If weather forecast calls for 30 percent chances of rain tomorrow, what are the chances that it will not rain? .20 .70 .45 .50 .80
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


