Question: QUESTION 1 A sorting algorithm is gemeral purpose ifit makes no assumptions about the data except that a comparison operator (such as en) is defined.
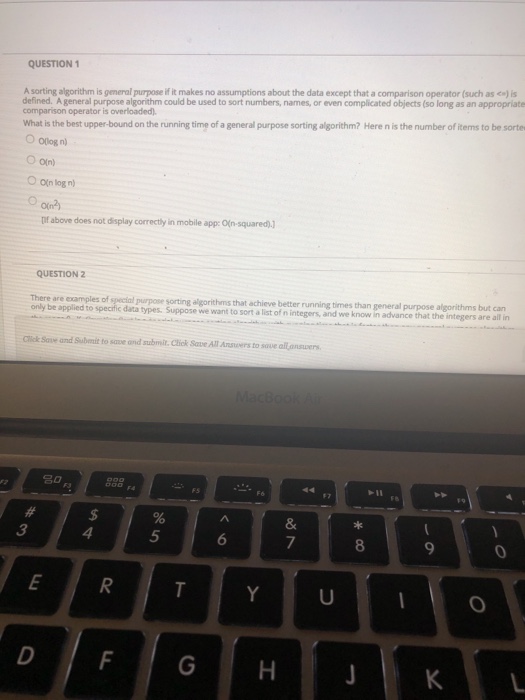
QUESTION 1 A sorting algorithm is gemeral purpose ifit makes no assumptions about the data except that a comparison operator (such as en) is defined. A general purpose algorithm could be used to sort numbers, names, or even complicated objects (so long as an appropriate comparison operator is overloaded What is the best upper-bound on the running time of a general purpose sorting algorithm? Here n is the number of items to be sorte OOllogn) O on) O oin log n) [if above does not display correctly in mobile app: O(n-squared) QUESTION 2 There are examples of special purpose sorting algorithms that achieve better running times than general purpose algorithms but can only be applied to specific data types, Suppose we want to sort a list of n integers, and we know in advance that the integers are all in ick Save and Submit to save and submit. Click Save All Answers to sove allanswers 3 5 9
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


