Question: Question 1 a) Suppose that two attributes, w and y, both measures of salt content, have been recorded in two different samples. For each, we
Question 1
a)
Suppose that two attributes, w and y, both measures of "salt content", have been recorded in two different samples. For each, we wish to perform inference to their respective target populations. Assume the populations are very large, that our samples were realized by a method of random selection, and that for both, the normal model is appropriate: (pick one multiple choice)
Everything else equal, if the sample size of w is larger than that of y, then:
none of these selections are correct
Our calculated CI for w will be the same as that for y
Our calculated CI for w will be wider than that for y
Our calculated CI for w will be narrower than that for y
Everything else equal, if the variance of w is 9 times larger than that of y, then:
Our calculated CI for w will be 2 times wider than that for y
none of these selections are correct
Our calculated CI for w will be 5 times narrower than that for y
Our calculated CI for w will be 3 times wider than that for y
Our calculated CI for w will be 2 times narrower than that for y
Our calculated CI for w will be 10 times narrower than that for y
b)
Suppose that two attributes, y and w, both measures of "income", have been recorded in two different samples. For each, we wish to perform inference to their respective target populations. Assume the populations are very large, that our samples were realized by a method of random selection, and that for both, the normal model is appropriate:
Everything else equal, if the sample size of y is smaller than that of w, then:
none of these selections are correct
Our calculated CI for y will be narrower than that for w
Our calculated CI for y will be the same as that for w
Our calculated CI for y will be wider than that for w
Everything else equal, if the sample size of y is 100 times larger than that of w, then:
Our calculated CI for y will be 5 times wider than that for w
Our calculated CI for y will be 2 times wider than that for w
Our calculated CI for y will be 3 times wider than that for w
none of these selections are correct
Our calculated CI for y will be 2 times narrower than that for w
Our calculated CI for y will be 10 times narrower than that for w
c)
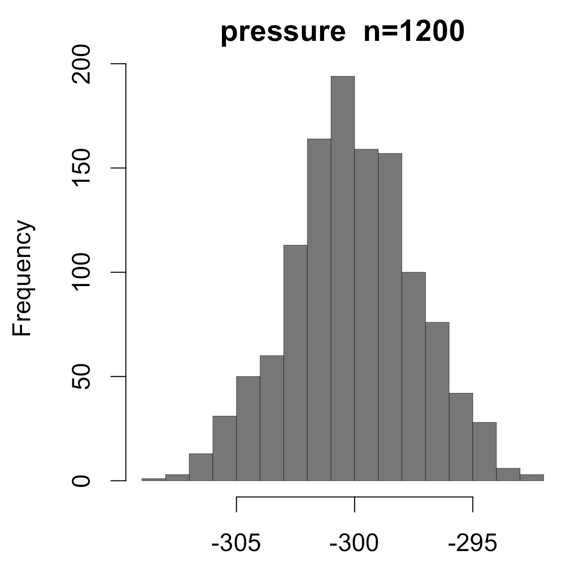
The mean (arithmetic average) of these data is closest to:
-1000.085
-700.09
-300.09
-500.09
-100.09
99.915
-200.09
The sample standard deviation is closest to:
225.14
912.98
20.42
13.69
2.764
5.036
0.6816
We can be 50 percent confident that the actual population average of pressure is (closest to):
Between -100.48 and -99.688
Between -300.14 and -300.03
Between 82.138 and 117.69
Between -204.47 and -195.7
Between -500.18 and -499.99
Between -700.1 and -700.07
Between -1000.352 and -999.82
We can be 70 percent confident that the actual population average of pressure is (closest to):
Between -300.15 and -300.02
Between -300.19 and -299.98
Between -300.17 and -300
Between -300.22 and -299.95
Between -300.29 and -299.88
Between -300.24 and -299.93
\f
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


