Question: question 1 and 2 1. Explain why a capital budget is necessary. 2. Describe the different types of capital expenditures and how they affect the



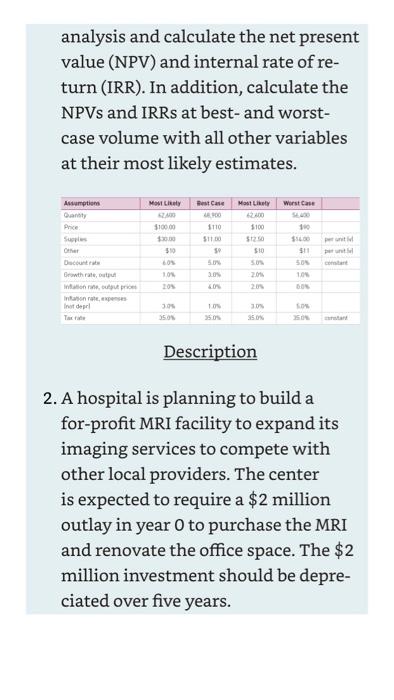
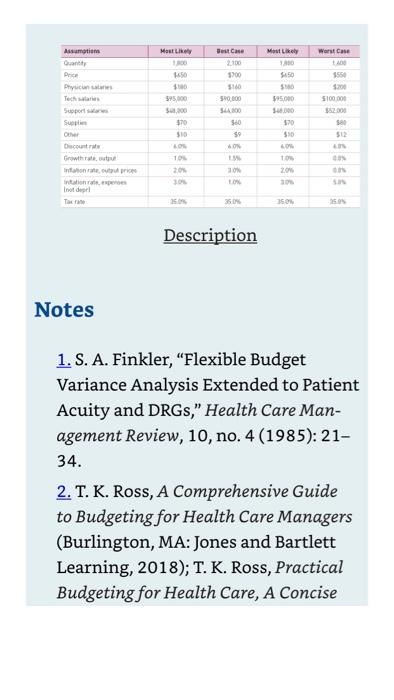
1. Explain why a capital budget is necessary. 2. Describe the different types of capital expenditures and how they affect the capital expenditure analysis. 3. Describe the differences between payback period, net present value, and internal rate of return. 4. Explain the three factors that affect capital budget decisions. 5. Explain the effect of limited funds (i.e., capital rationing) on the capital budgeting process. Problems 1. A hospital is planning to build a nonprofit urgent care center next to its emergency department (ED) to siphon off nonemergent cases. The ED frequently operates beyond its designed capacity, creating patient and employee dissatisfaction. It is expected that the ED will not lose any patients if the center is built due to patients leaving before treatment is rendered and a growing demand for ED services. The center is expected to require a $4 million outlay in year 0 . No depreciation expense is needed since the center is nonprofit and reaps no tax benefit. The following table provides the best-case, most likely, and worstcase estimates for patient quantity, reimbursement, supply and other expenses per encounter, and growth rates for patient quantity, reimbursement, and expenses beginning in year 1. The ED and finance departments have estimated that the center will need five physicians earning an average of $240,000 in salaries and benefits, twelve nurses at $84,000 each, and nine other staff at \$48,000 each. Create a five-year capital budget The following table provides the best-case, most likely, and worstcase estimates for patient quantity, reimbursement, supply and other expenses per encounter, and growth rates for patient quantity, reimbursement, and expenses beginning in year 1. Physician salaries are $180 per image for reading and interpretation of images. The technician and other salaries are annual salaries and benefits. Create a five-year capital budget analysis and calculate the net present value (NPV) and internal rate of return (IRR). In addition, calculate the NPVs and IRRs at best- and worstcase volume with all other variables at their most likely estimates. analysis and calculate the net present value (NPV) and internal rate of return (IRR). In addition, calculate the NPVs and IRRs at best- and worstcase volume with all other variables at their most likely estimates. Description 2. A hospital is planning to build a for-profit MRI facility to expand its imaging services to compete with other local providers. The center is expected to require a $2 million outlay in year 0 to purchase the MRI and renovate the office space. The $2 million investment should be depreciated over five years. Description Notes 1. S. A. Finkler, "Flexible Budget Variance Analysis Extended to Patient Acuity and DRGs," Health Care Management Review, 10, no. 4 (1985): 2134. 2. T. K. Ross, A Comprehensive Guide to Budgeting for Health Care Managers (Burlington, MA: Jones and Bartlett Learning, 2018); T. K. Ross, Practical Budgeting for Health Care, A Concise
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


