Question: Question 1; Apply a second derivative to identify a critical points as a local maximum, local minimum or saddle point for a function. Find and

Question 1;

![5y). Local minimums: Saddle points: [ ] For each classification, enter a](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/6678aaa0918ce_0326678aaa077daa.jpg)

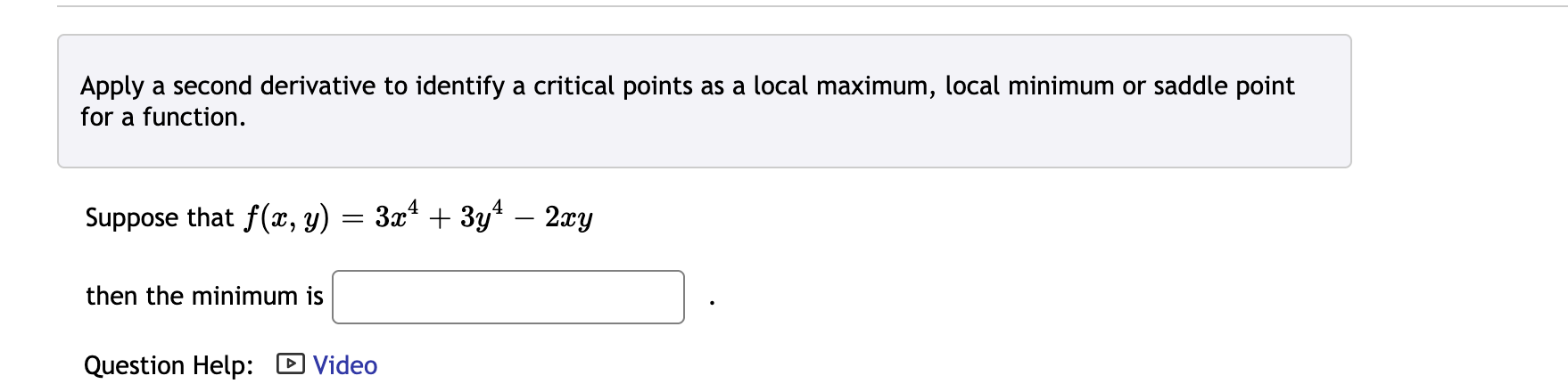
Apply a second derivative to identify a critical points as a local maximum, local minimum or saddle point for a function. Find and classify the critical points of z = (m2 3:13) (312 5y). Local minimums: Saddle points: [ ] For each classification, enter a list of ordered pairs (x, y) where the max/ min/ saddle occurs. Enter DNE if there are no points for a classification. Apply a second derivative to identify a critical points as a local maximum, local minimum or saddle point for a function. Suppose that f(9:, y) = 3n:4 + 33,:4 2933; then the minimum is Question Help: El Video Apply a second derivative to identify a critical points as a local maximum, local minimum or saddle point for a function. Suppose that f(a:, y) = $2 + y2 at which 0 S m, y and 29: + 83; S 8. 1. Absolute minimum of f(m, y) is 2. Absolute maximum of f(a:, y) is
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


