Question: Question 1: Given that a city has 120 commuters. Given inverse demand function for commuting on highway: D(T) = 120 ? T. This function means
Question 1:
Given that a city has 120 commuters. Given inverse demand function for commuting on highway: D(T) = 120 ? T. This function means the marginal benefit (in dollars) of adding another car to the road when there are T cars on the road. If T people are using highway, travel times (in minutes) are M(T) = T. Everyone values their time at 2 dollars per minute.
a) Why might the marginal benefit of using the road differ across people?
b) Derive the social marginal cost curve. Please give steps in details.
c) When there is no toll, what are the equilibrium quantity of highway users, equilibrium quantity of alternative-route users, equilibrium total cost of commuting for highway users, equilibrium total cost of commuting for alternative-route users, equilibrium total cost of commuting? Show every step for computing all these quantities and show all these quantities' curves on a graph.
d) When the toll is set to maximize social welfare, what are the equilibrium quantity of highway users, equilibrium quantity of alternative-route users, equilibrium total cost of commuting for highway users, equilibrium total cost of commuting for alternative-route users, equilibrium total cost of commuting, toll and toll revenue? Show every step for computing all these quantities and show all these quantities' curves on a graph.
e) For each person, how much better or worse off they are after the introduction of the toll? Is there enough toll revenue to compensate for their loss in welfare?
Question 2:
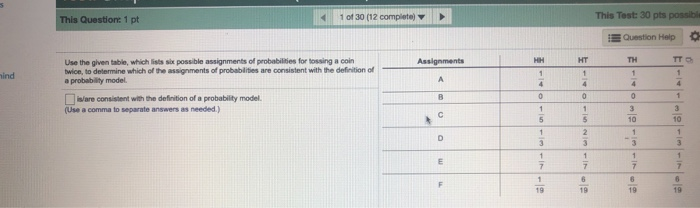


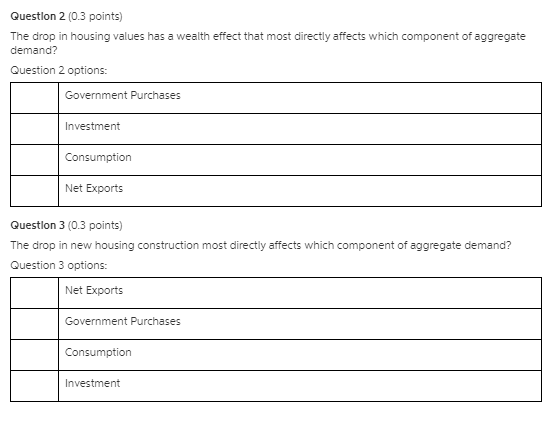
This Question: 1 pt 1 of 30 (12 complete) + This Test: 30 pts possibl Question Help Use the given table, which lists six possible assignments of probabilities for tossing a coin Assignments HH HT TH TT twice, to determine which of the assignments of probabilities are consistent with the definition of probability model. A Ware consistent with the definition of a probability model. 1 (Uve a comma to separate answers as needed.) 10 10 D - 4- F 19Question #1: Let M be a module over a ring R. Suppose w1, ..., W/ E M are linear combinations of [v1, ..., Vx]. Prove that any linear combination of [w1, ..., w/] is also a linear combination of [v1,..., Vx]. Use only the properties M1)-M8) in the definition of a module, and the properties of a ring. Keep track of each time you use a property and which one you use (one step at a time!).E. One month Question 5: An increase in real wealth in India will . Select all that apply. Choose one or more: A. increase Indian aggregate demand B. decrease Indian aggregate demand C. increase U.S. aggregate demand D. decrease U.S. aggregate demand Question 6: Choose the right answer: Net exports will increase/decrease/stay the same when the value of the dollar result, the aggregate demand curve will shift left/increase. ECON 1204-001 Principles of Macro Spring 2019 Question 7:Duestlon 2 [I13 points] The drop in housing values has a wealth effect that most directly affects which component of aggregate deman d\"? Question 2 options: - Government Purchases - Investment _ I w Duestlon 3 {I13 points] The drop in nevir housing construction most directly.r affects which component of aggregate demand? Question 3 options: - Government Purchases
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


