Question: Question 1 Perceptron Table 1 depicts eight training examples (instances) with two attributes (attr1 and attr2) each. The last column gives the class value of
Question 1
Perceptron Table 1 depicts eight training examples (instances) with two attributes (attr1 and attr2) each. The last column gives the class value of either 0 (negative) or 1 (positive).
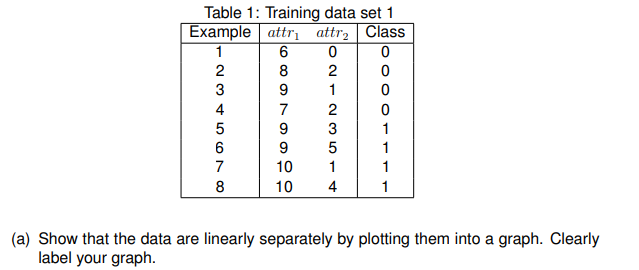

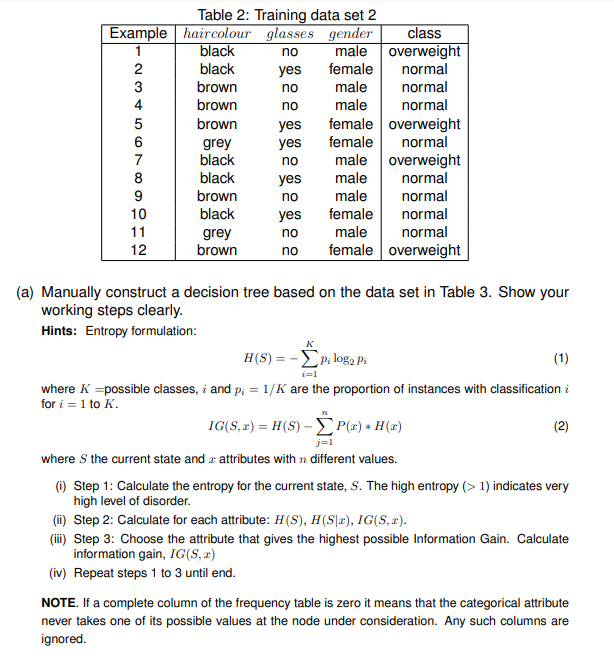

Table 1: Training data eel 1 1 B D {l (a) Show that the data are linearly separately by pletting them into a graph. Clearly label your graph. (b) Beginning with the following arbitrary parameters: . weights w = (wo, w1, w2) = (1, 1, 1) . learning rate n = 1 . attro = 1 of a perceptron, manually calculate the weights w, and w2 change for THREE (3) epoch. Show your steps clearly.Table 2: Training data set 2 Example haircolour glasses gender class black no male overweight SOONOUAWN black yes female normal brown no male normal brown no male normal brown yes female overweight grey yes female normal black no male overweight black yes male normal brown no male normal black yes female normal 11 grey no male normal 12 brown no female overweight (a) Manually construct a decision tree based on the data set in Table 3. Show your working steps clearly. Hints: Entropy formulation: H(S) = -> p; log2 Pi (1) i=1 where k =possible classes, i and p; = 1/k are the proportion of instances with classification for i = 1 to K. IG(5, x) = H(S) - P(x) * H(x) (2) where S the current state and z attributes with n different values. (i) Step 1: Calculate the entropy for the current state, S. The high entropy (> 1) indicates very high level of disorder. (ii) Step 2: Calculate for each attribute: H(S), H(S|x), IG(5, x). (ii) Step 3: Choose the attribute that gives the highest possible Information Gain. Calculate information gain, IG(S, x) (iv) Repeat steps 1 to 3 until end. NOTE. If a complete column of the frequency table is zero it means that the categorical attribute never takes one of its possible values at the node under consideration. Any such columns are ignored.(b) Based on the decision tree constructed in (a), predict the class given an unseen example: (brown, yes, male, ?)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


