Question: Question 1 Preamble First let's review Maximum Likelihood Theory. To this we first need to define the probability density function (pdi) for probability mass function


![mass function (pmf) for the discrete case], the likelihood principle and the](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f2e57228eda_48166f2e571a25ac.jpg)
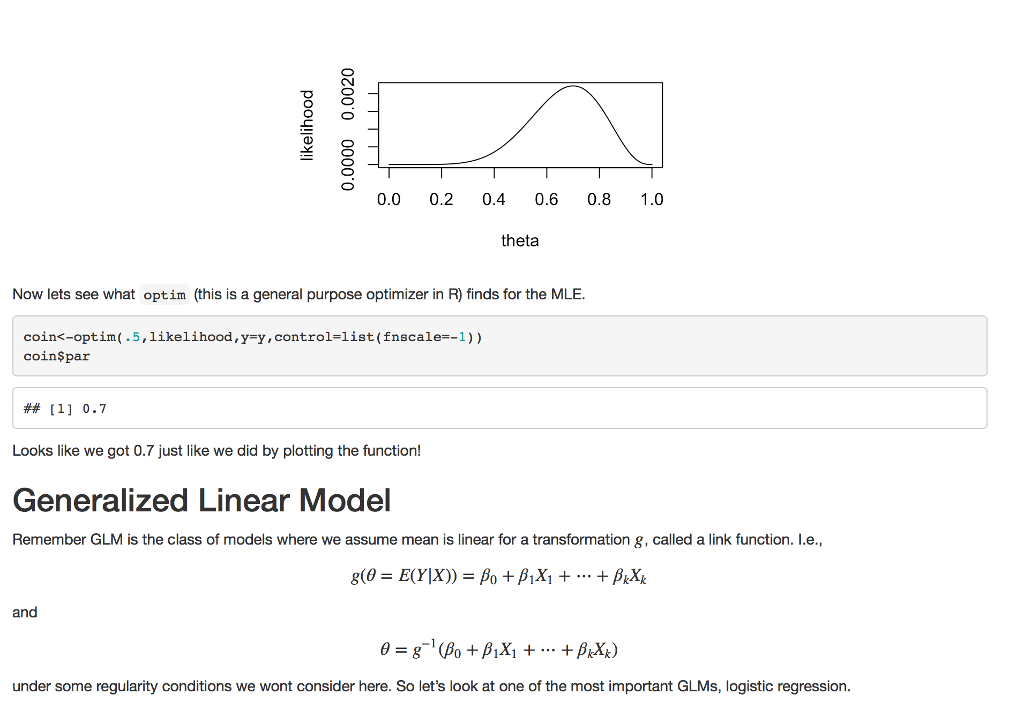
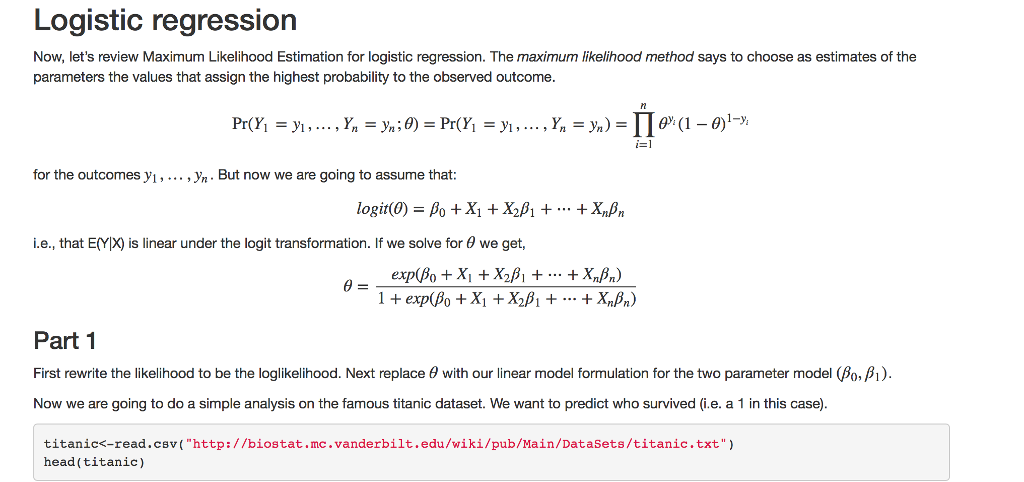
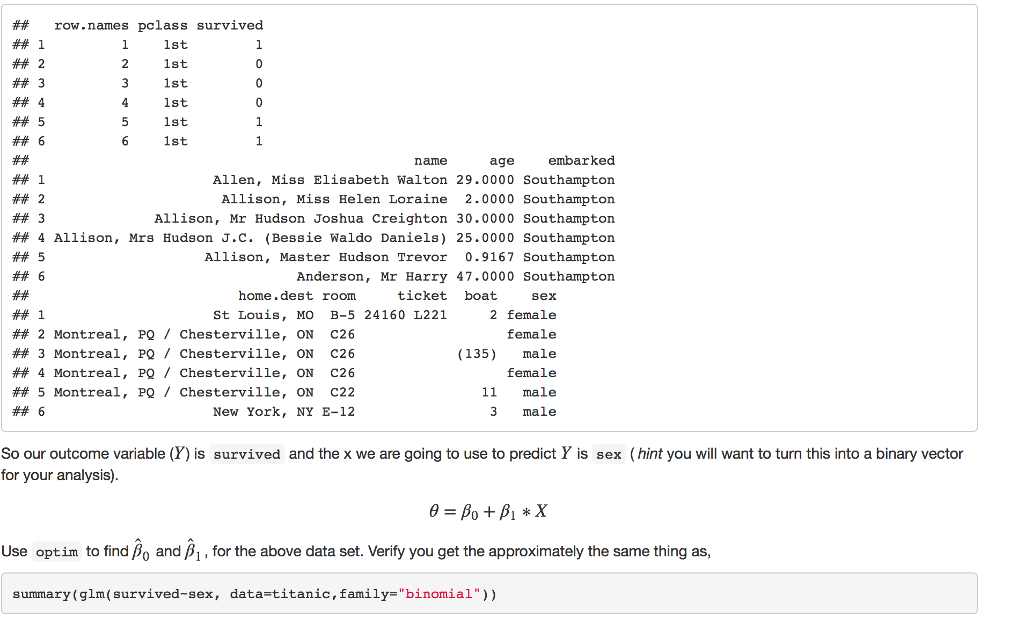
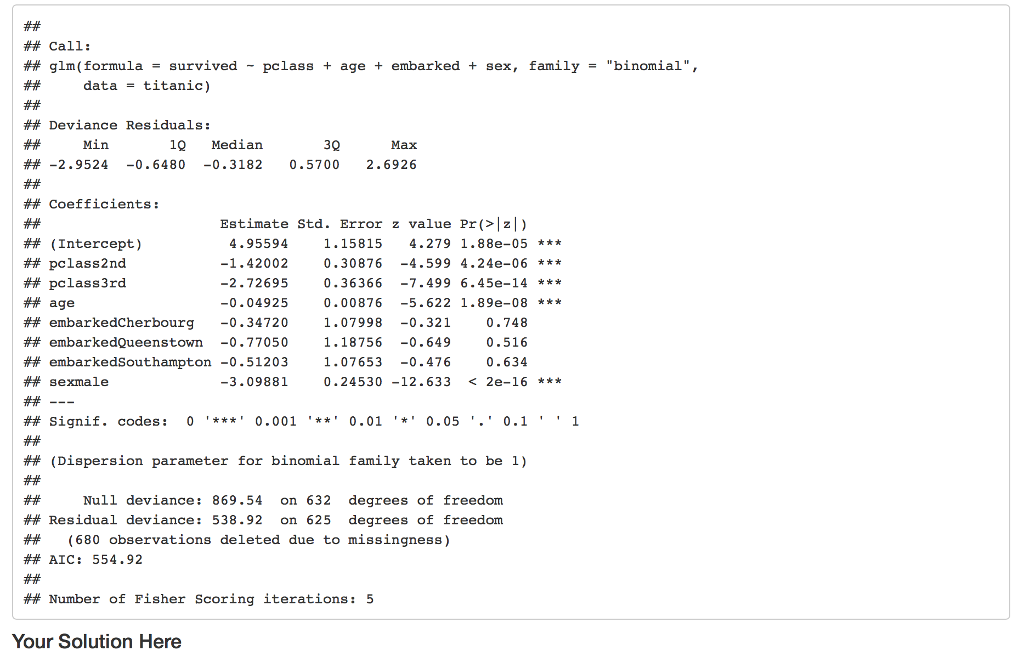
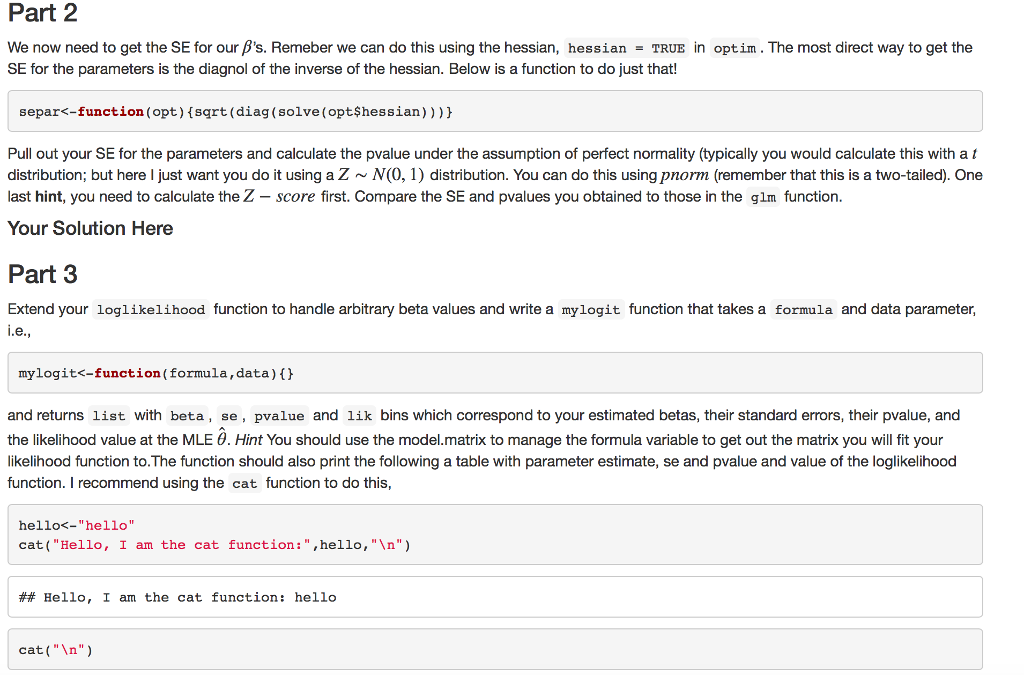
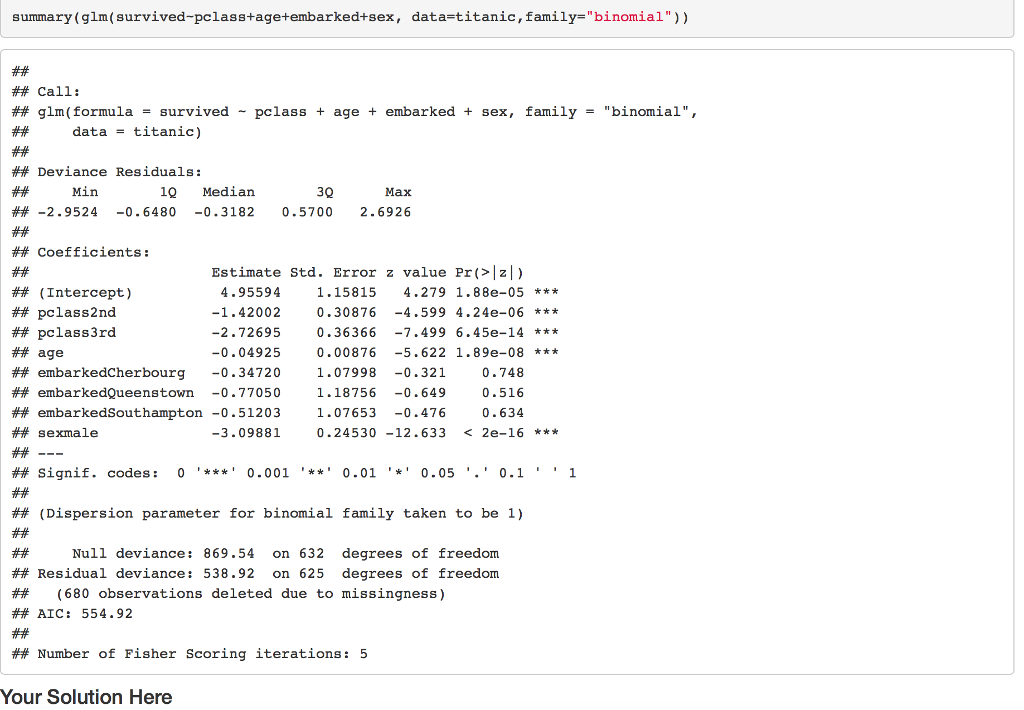
Question 1 Preamble First let's review Maximum Likelihood Theory. To this we first need to define the probability density function (pdi) for probability mass function (pmf) for the discrete case], the likelihood principle and the Law of Likelihood. Definition The probability density function (pdf) of a continuous random variable X with support S is an integrable function (x) satisfying the following: 1. f(x) is positive everywhere in the support S, that is,)>0, for all x in S 2. The area under the curve$ f(x)$ in the support S is 1, that is: 3. Iff(x) is the pdf of x, then the probability that x belongs to A, where A is some interval, is given by the integral of f(x) over that interval, that is: The Likelihood Principle "[Gjiven a statistical model, all the evidence in a sample relevant to model parameters is contained in the likelihood function." Wikipedia The Law of Likelihood "[The notion that the extent to which the evidence supports one parameter value or hypothesis against another is equal to the ratio of their likelihoods." Wikipedia If we accept the basis of the The Likelihood Principie and The Law of Likelihood then best way maximize our probability model is to maximize the likelihood function. Likelihood methods can done on non-independ data, but we will not consider that case here. Given x,2,.. ,xn simple random sample of observations from unknown p then We define the likelihood as, Question 1 Preamble First let's review Maximum Likelihood Theory. To this we first need to define the probability density function (pdi) for probability mass function (pmf) for the discrete case], the likelihood principle and the Law of Likelihood. Definition The probability density function (pdf) of a continuous random variable X with support S is an integrable function (x) satisfying the following: 1. f(x) is positive everywhere in the support S, that is,)>0, for all x in S 2. The area under the curve$ f(x)$ in the support S is 1, that is: 3. Iff(x) is the pdf of x, then the probability that x belongs to A, where A is some interval, is given by the integral of f(x) over that interval, that is: The Likelihood Principle "[Gjiven a statistical model, all the evidence in a sample relevant to model parameters is contained in the likelihood function." Wikipedia The Law of Likelihood "[The notion that the extent to which the evidence supports one parameter value or hypothesis against another is equal to the ratio of their likelihoods." Wikipedia If we accept the basis of the The Likelihood Principie and The Law of Likelihood then best way maximize our probability model is to maximize the likelihood function. Likelihood methods can done on non-independ data, but we will not consider that case here. Given x,2,.. ,xn simple random sample of observations from unknown p then We define the likelihood as
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


