Question: Question 1: Question 2: Postfix notation (also known as Reverse Polish Notation or RPN in short) is a mathematical notation in which operators follow all
Question 1: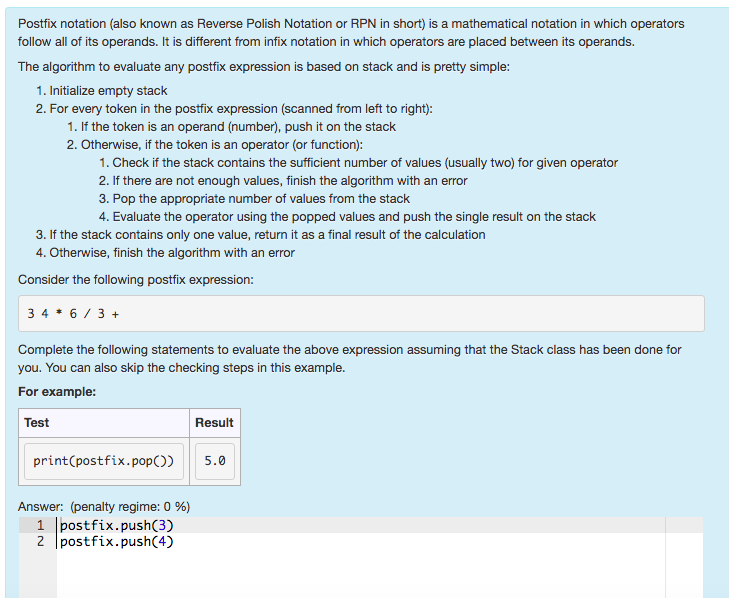
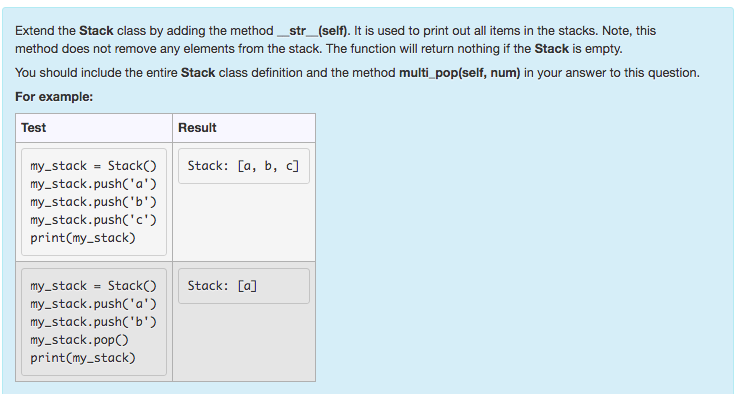
Question 2:
Postfix notation (also known as Reverse Polish Notation or RPN in short) is a mathematical notation in which operators follow all of its operands. It is different from infix notation in which operators are placed between its operands. The algorithm to evaluate any postfix expression is based on stack and is pretty simple: 1. Initialize empty stack 2. For every token in the postfix expression (scanned from left to right): 1. If the token is an operand (number), push it on the stack 2. Otherwise, if the token is an operator (or function): 1. Check if the stack contains the sufficient number of values (usually two) for given operator 2. If there are not enough values, finish the algorithm with an error 3. Pop the appropriate number of values from the stack 4. Evaluate the operator using the popped values and push the single result on the stack 3. If the stack contains only one value, return it as a final result of the calculation 4. Otherwise, finish the algorithm with an error Consider the following postfix expression: 34 613+ Complete the following statements to evaluate the above expression assuming that the Stack class has been done for you. You can also skip the checking steps in this example. For example: Test Result print(postfix.popO) 5.0 Answer: (penalty regime: 0 %) 1 postfix.push(3) 2 lpostfix.push(4)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


