Question: Question 1 Question 2 question 3 question 3 properly Q4 A decision maker is given a series of choices involving risk and time delays. You


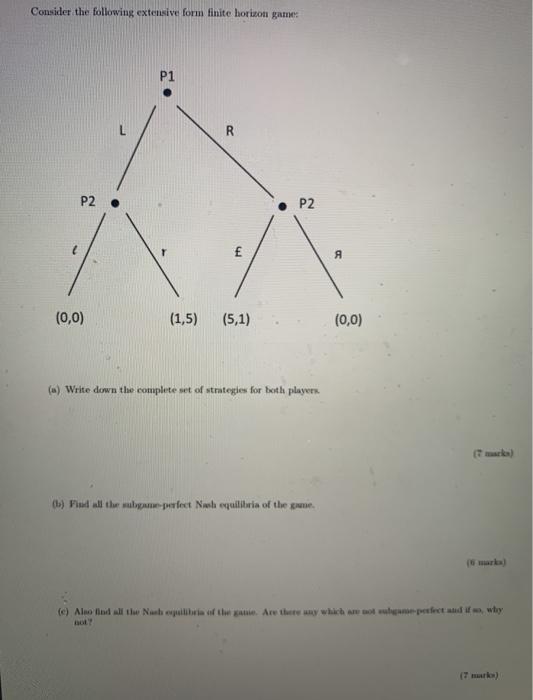


A decision maker is given a series of choices involving risk and time delays. You observe the following choice: (100..0.8:00) 100, where subscripts indicate years. (a) Derive the discount factor between periods 0 and 1 assuming discounted expected utility (DEU) with exponential discounting. (7 marks) (b) Suppose that we also observe (1000,0.6:00) 75). Is this decision maker risk-averse, risk-neutral, or risk-seeking? Explain your reasoning. (Hint: Use the discount factor you derived above.) (7 marks) (c) Now suppose that we observe (100,0.75:01) - 108. Given your answers to (a) and (b), does this decision maker display constant discounting? (6 mark) A decision maker is given a series of choices involving risk and time delays. You observe the following choice: (100,0.8:0.) 100,, where subscripts indicate years. (a) Derive the discount factor between periods 0 and 1 assuming discounted expected utility (DEU) with exponential discounting, (7 marks) (b) Suppose that we also observe (1000.0.600) - 75). Is this decision maker risk-averse, risk-neutral, or risk-seeking? Explain your reasoning. (Hint: Use the discount factor you derived above.) (7 marks) (c) Now suppose that we observe (100,0.75:01) - 108. Given your answers to (a) and (b), does this decision maker display constant discounting? (6 marks) Consider the following extensive form finite horizon game: P1 R P2. P2 A (0,0) (1,5) (5,1) (0,0) (a) Write down the complete set of strategies for both players (1) Pall the walpapefect No equilibria of the game. (e) Almind all the Northe game. Are there any which are not perfect and why Three firms, 1, 2, and 3, produce quantities 21. 22 and qs of the same good with market demand where Q=41 +92 +4s is the total market supply. The total costs of each firm are expressed as C(9) = 100+0.542 If the fins are in Cournot competition: (a) Find the Nash equilibrium quantities of the game. (10 marks) (b) Find the outcome which maximises the sum of the three firms' profits subject to a1 = 42 43- Why can this not be sustained in Nash equilibrium? (10 marks) Problem 3 Three firms, 1, 2 and 3. produce quantities 41 42 and of the same good with market demand P = 100 - 20, where Q=1+qa +93 is the total market supply. The total costs of each firm are expressed as C(96) = 109, +0.507 If the firms are in Cournot competition: (a) Find the Nash equilibrium quantities of the game. (10 marks) (b) Find the outcome which maximises the sum of the three firms' profits subject to q = 92 93. Why can this not be sustained in Nash equilibrium? (10 marks) Problem 4 Consider the following games. For all games, each pair of payoffs corresponds to Player 1. Player 2. For each of these games, identify The players' best responses . Any strictly or weakly dominated actions for either player Any pure-strategy Nash equilibria Player 2 A B 6.6 6, -6 7-1 --10, -1 B Player 1 (5 mrks) (b Player 2 B A-2, -10 8-3 B -6,0 Player 1 (5 marks) Player 2 A decision maker is given a series of choices involving risk and time delays. You observe the following choice: (100..0.8:00) 100, where subscripts indicate years. (a) Derive the discount factor between periods 0 and 1 assuming discounted expected utility (DEU) with exponential discounting. (7 marks) (b) Suppose that we also observe (1000,0.6:00) 75). Is this decision maker risk-averse, risk-neutral, or risk-seeking? Explain your reasoning. (Hint: Use the discount factor you derived above.) (7 marks) (c) Now suppose that we observe (100,0.75:01) - 108. Given your answers to (a) and (b), does this decision maker display constant discounting? (6 mark) A decision maker is given a series of choices involving risk and time delays. You observe the following choice: (100,0.8:0.) 100,, where subscripts indicate years. (a) Derive the discount factor between periods 0 and 1 assuming discounted expected utility (DEU) with exponential discounting, (7 marks) (b) Suppose that we also observe (1000.0.600) - 75). Is this decision maker risk-averse, risk-neutral, or risk-seeking? Explain your reasoning. (Hint: Use the discount factor you derived above.) (7 marks) (c) Now suppose that we observe (100,0.75:01) - 108. Given your answers to (a) and (b), does this decision maker display constant discounting? (6 marks) Consider the following extensive form finite horizon game: P1 R P2. P2 A (0,0) (1,5) (5,1) (0,0) (a) Write down the complete set of strategies for both players (1) Pall the walpapefect No equilibria of the game. (e) Almind all the Northe game. Are there any which are not perfect and why Three firms, 1, 2, and 3, produce quantities 21. 22 and qs of the same good with market demand where Q=41 +92 +4s is the total market supply. The total costs of each firm are expressed as C(9) = 100+0.542 If the fins are in Cournot competition: (a) Find the Nash equilibrium quantities of the game. (10 marks) (b) Find the outcome which maximises the sum of the three firms' profits subject to a1 = 42 43- Why can this not be sustained in Nash equilibrium? (10 marks) Problem 3 Three firms, 1, 2 and 3. produce quantities 41 42 and of the same good with market demand P = 100 - 20, where Q=1+qa +93 is the total market supply. The total costs of each firm are expressed as C(96) = 109, +0.507 If the firms are in Cournot competition: (a) Find the Nash equilibrium quantities of the game. (10 marks) (b) Find the outcome which maximises the sum of the three firms' profits subject to q = 92 93. Why can this not be sustained in Nash equilibrium? (10 marks) Problem 4 Consider the following games. For all games, each pair of payoffs corresponds to Player 1. Player 2. For each of these games, identify The players' best responses . Any strictly or weakly dominated actions for either player Any pure-strategy Nash equilibria Player 2 A B 6.6 6, -6 7-1 --10, -1 B Player 1 (5 mrks) (b Player 2 B A-2, -10 8-3 B -6,0 Player 1 (5 marks) Player 2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


