Question: QUESTION 1) Run the following SQL statement to create a new table for inserting and storing the employees' salaries. Run the following statement to create
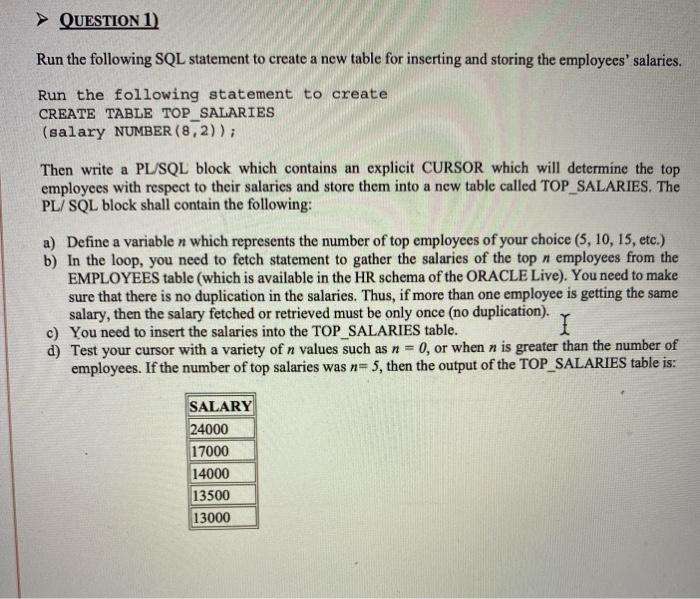

QUESTION 1) Run the following SQL statement to create a new table for inserting and storing the employees' salaries. Run the following statement to create CREATE TABLE TOP_SALARIES (salary NUMBER (8,2)); Then write a PL/SQL block which contains an explicit CURSOR which will determine the top employees with respect to their salaries and store them into a new table called TOP_SALARIES. The PL/SQL block shall contain the following: a) Define a variable n which represents the number of top employees of your choice (5, 10, 15, etc.) b) In the loop, you need to fetch statement to gather the salaries of the top n employees from the EMPLOYEES table (which is available in the HR schema of the ORACLE Live). You need to make sure that there is no duplication in the salaries. Thus, if more than one employee is getting the same salary, then the salary fetched or retrieved must be only once (no duplication). c) You need to insert the salaries into the TOP SALARIES table. I d) Test your cursor with a variety of n values such as n = 0, or when n is greater than the number of employees. If the number of top salaries was n=5, then the output of the TOP_SALARIES table is: SALARY 24000 17000 14000 13500 13000 QUESTION 2) Run the following SQL statement to create a new table for inserting and storing the employees' jobs. CREATE TABLE new jobs AS (SELECT * FROM HR.JOBS); Define the ADD_JOB procedure which will insert a new job into the NEW_JOBS table. The procedure takes two parameters, the Job ID and the Job Title. Invoke (call) the procedure twice, one with passing "MGR' as job ID and 'MANAGER' as a job title, and the second time by passing 'DBA' as a job ID and "DATABASE ADMINISTRATOR' as a job title. Test the new table NEW_JOBS to check that the procedure is working probably. QUESTION 1) Run the following SQL statement to create a new table for inserting and storing the employees' salaries. Run the following statement to create CREATE TABLE TOP_SALARIES (salary NUMBER (8,2)); Then write a PL/SQL block which contains an explicit CURSOR which will determine the top employees with respect to their salaries and store them into a new table called TOP_SALARIES. The PL/SQL block shall contain the following: a) Define a variable n which represents the number of top employees of your choice (5, 10, 15, etc.) b) In the loop, you need to fetch statement to gather the salaries of the top n employees from the EMPLOYEES table (which is available in the HR schema of the ORACLE Live). You need to make sure that there is no duplication in the salaries. Thus, if more than one employee is getting the same salary, then the salary fetched or retrieved must be only once (no duplication). c) You need to insert the salaries into the TOP SALARIES table. I d) Test your cursor with a variety of n values such as n = 0, or when n is greater than the number of employees. If the number of top salaries was n=5, then the output of the TOP_SALARIES table is: SALARY 24000 17000 14000 13500 13000 QUESTION 2) Run the following SQL statement to create a new table for inserting and storing the employees' jobs. CREATE TABLE new jobs AS (SELECT * FROM HR.JOBS); Define the ADD_JOB procedure which will insert a new job into the NEW_JOBS table. The procedure takes two parameters, the Job ID and the Job Title. Invoke (call) the procedure twice, one with passing "MGR' as job ID and 'MANAGER' as a job title, and the second time by passing 'DBA' as a job ID and "DATABASE ADMINISTRATOR' as a job title. Test the new table NEW_JOBS to check that the procedure is working probably
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


