Question: Question 1 (Show Excel steps) 2. Consider two people age 40. a. What is the expected number of years that both are alive? b. What

Question 1 (Show Excel steps)
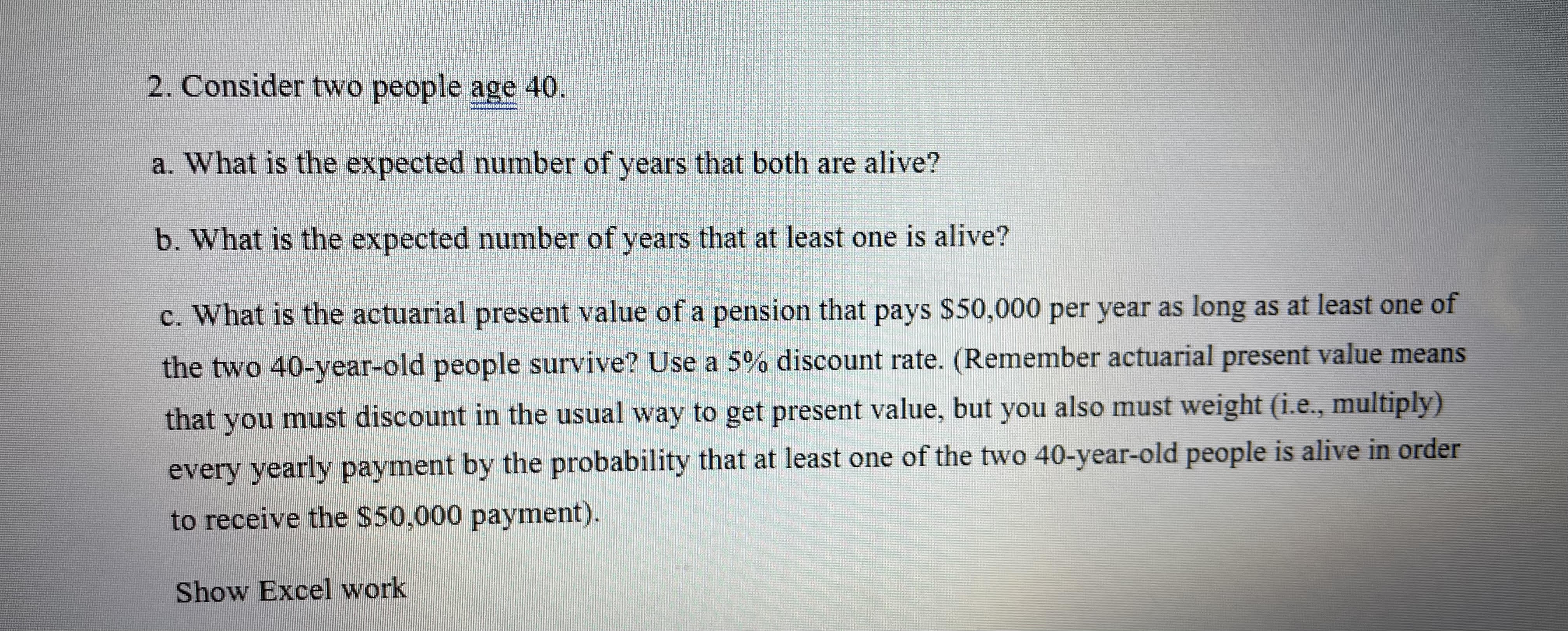

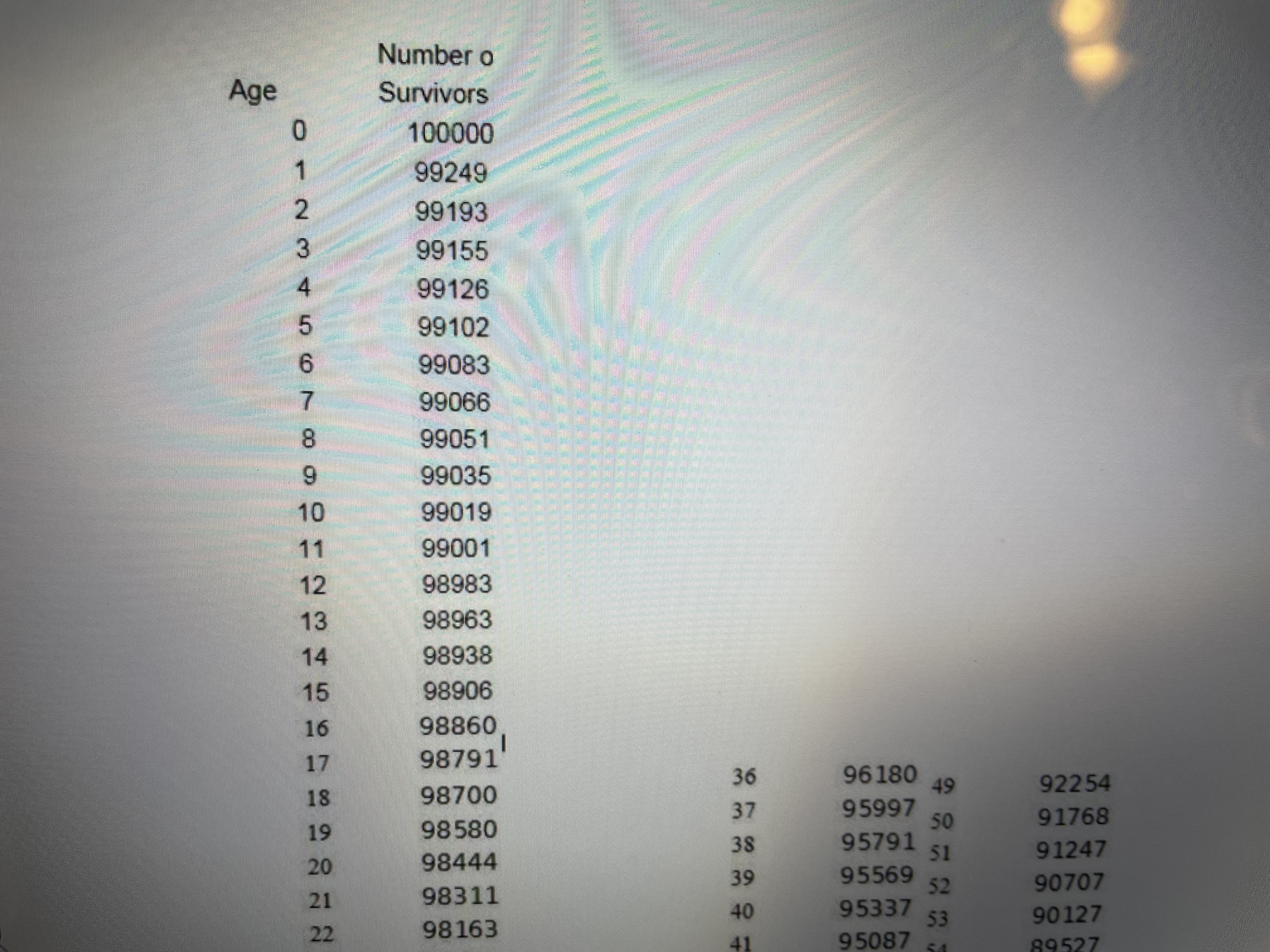
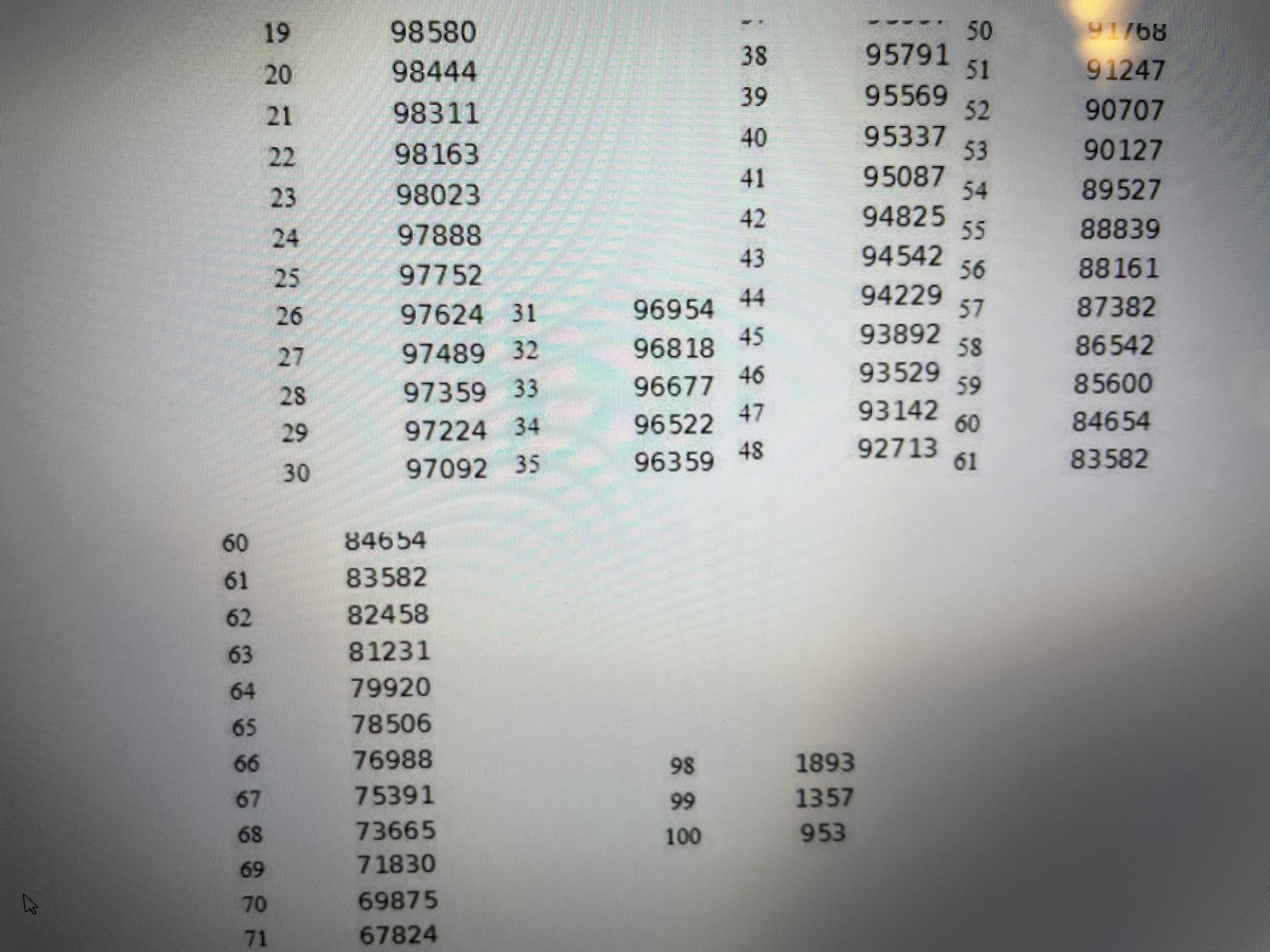
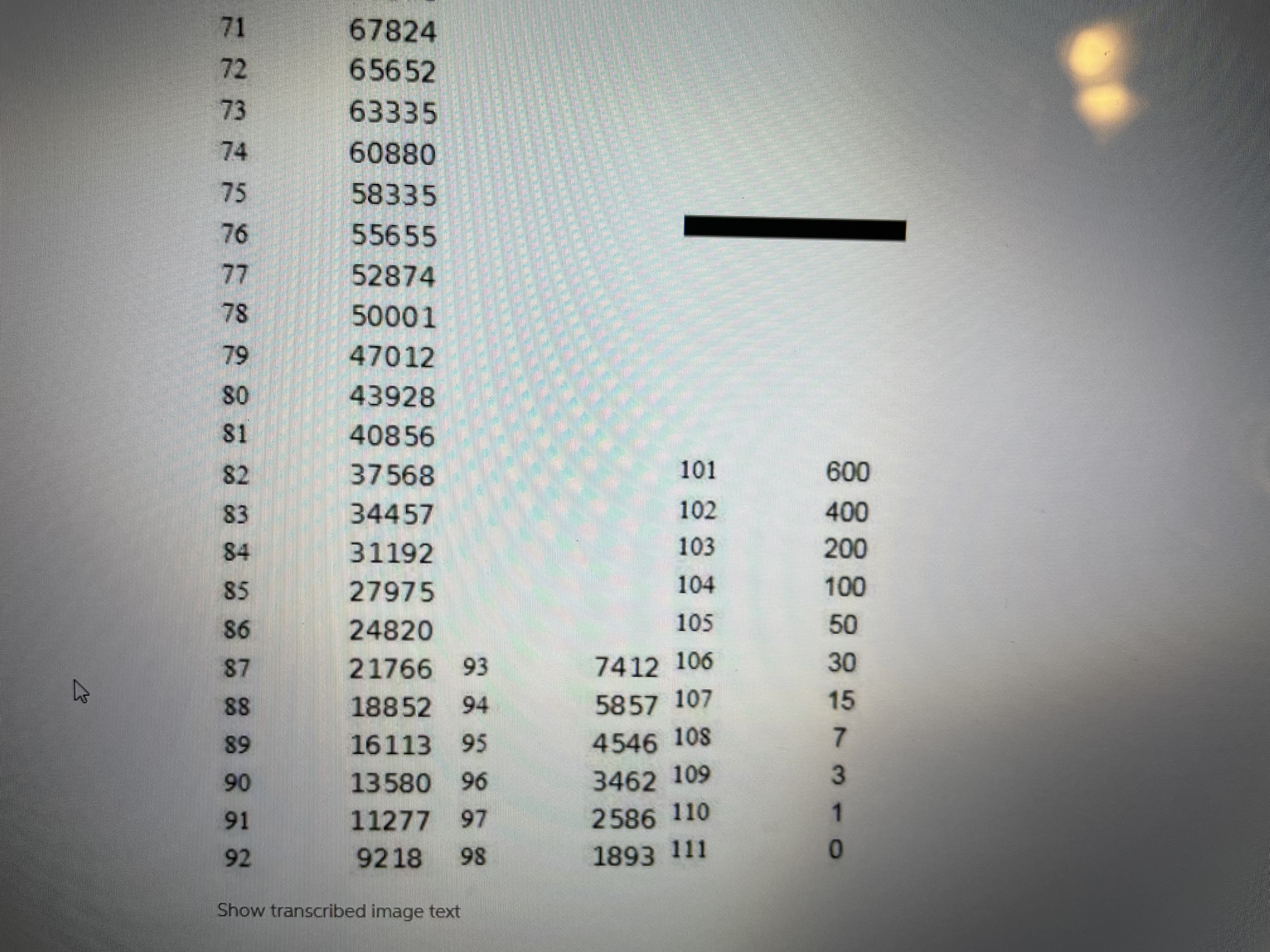
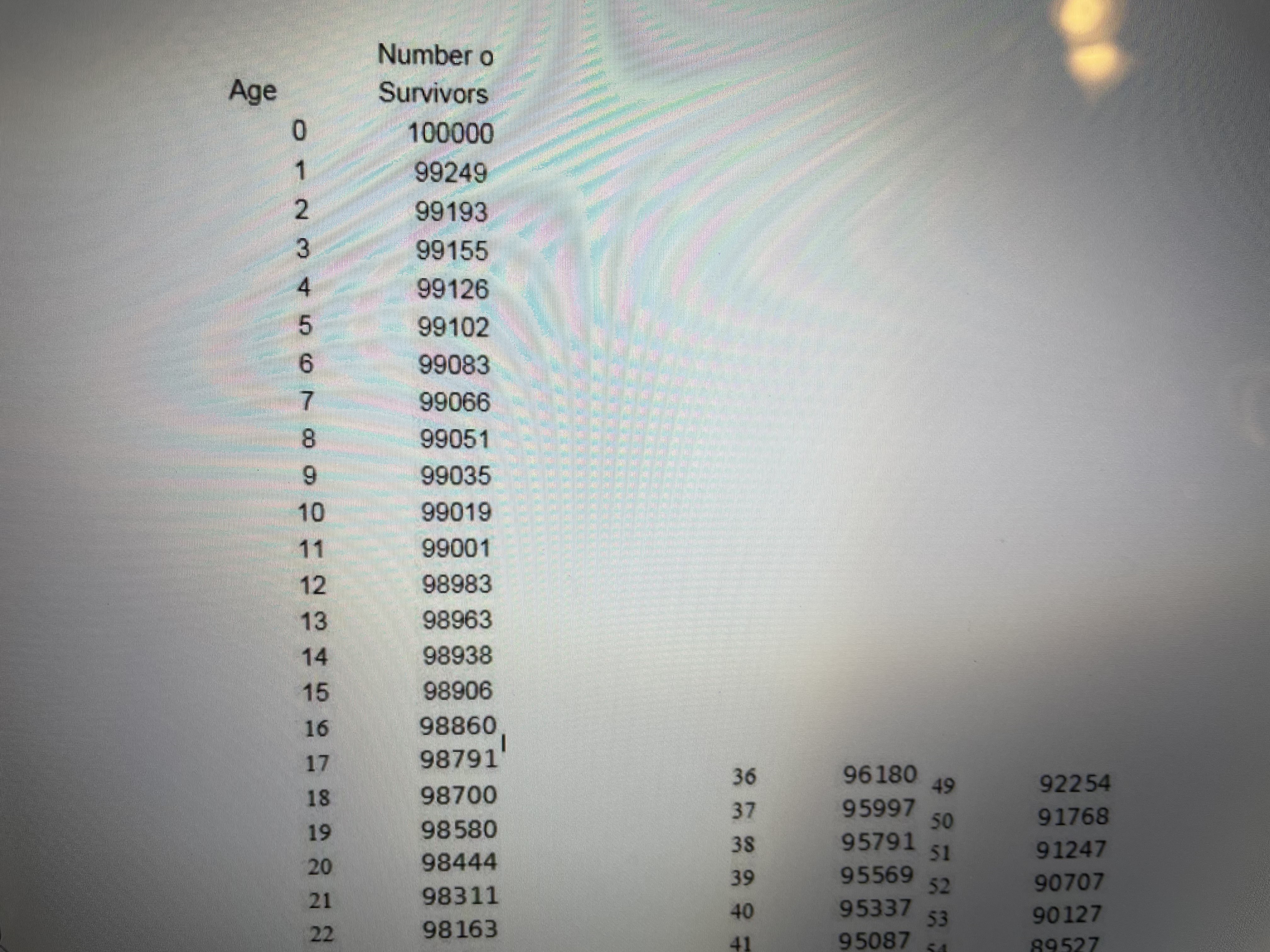
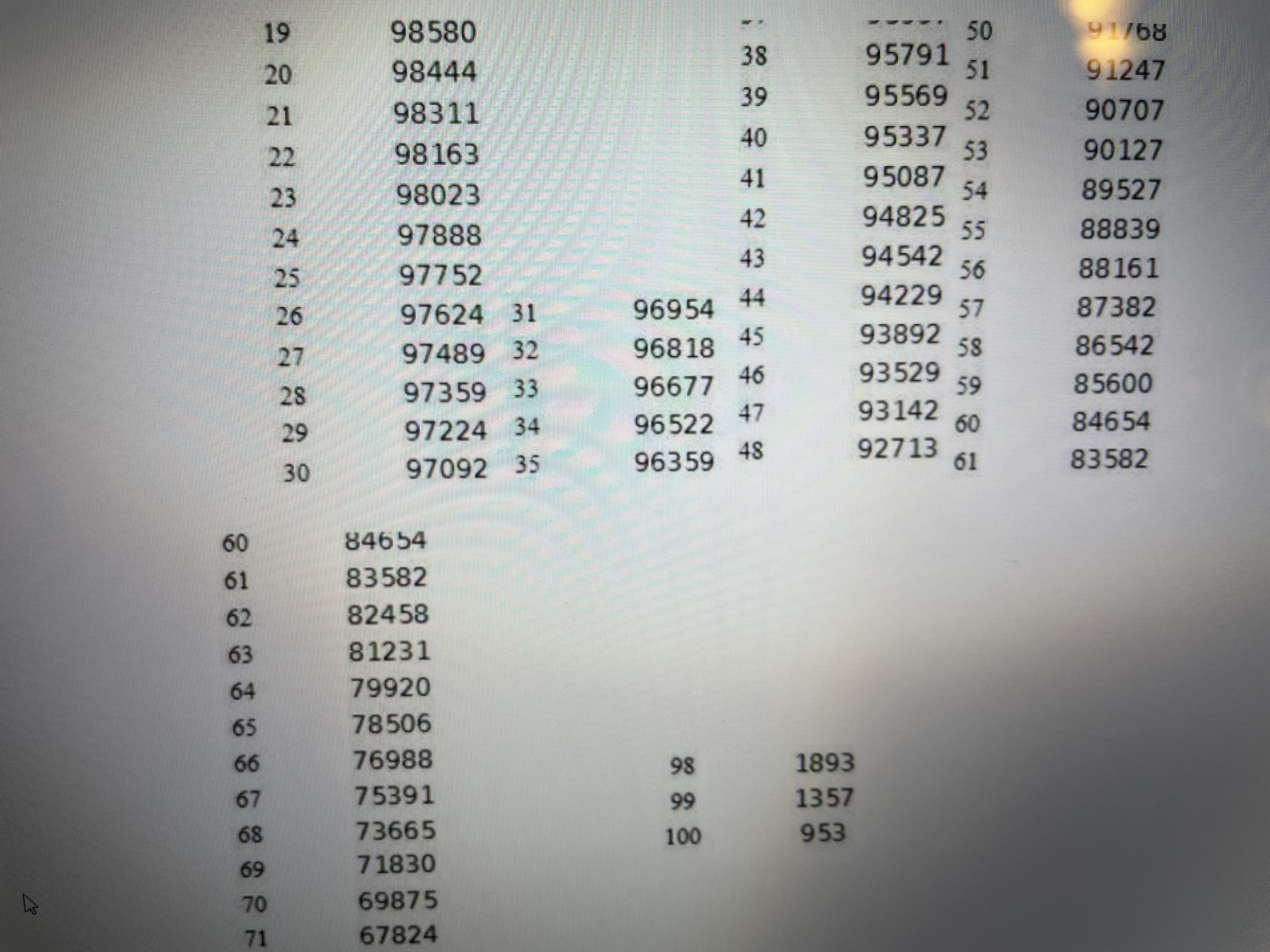
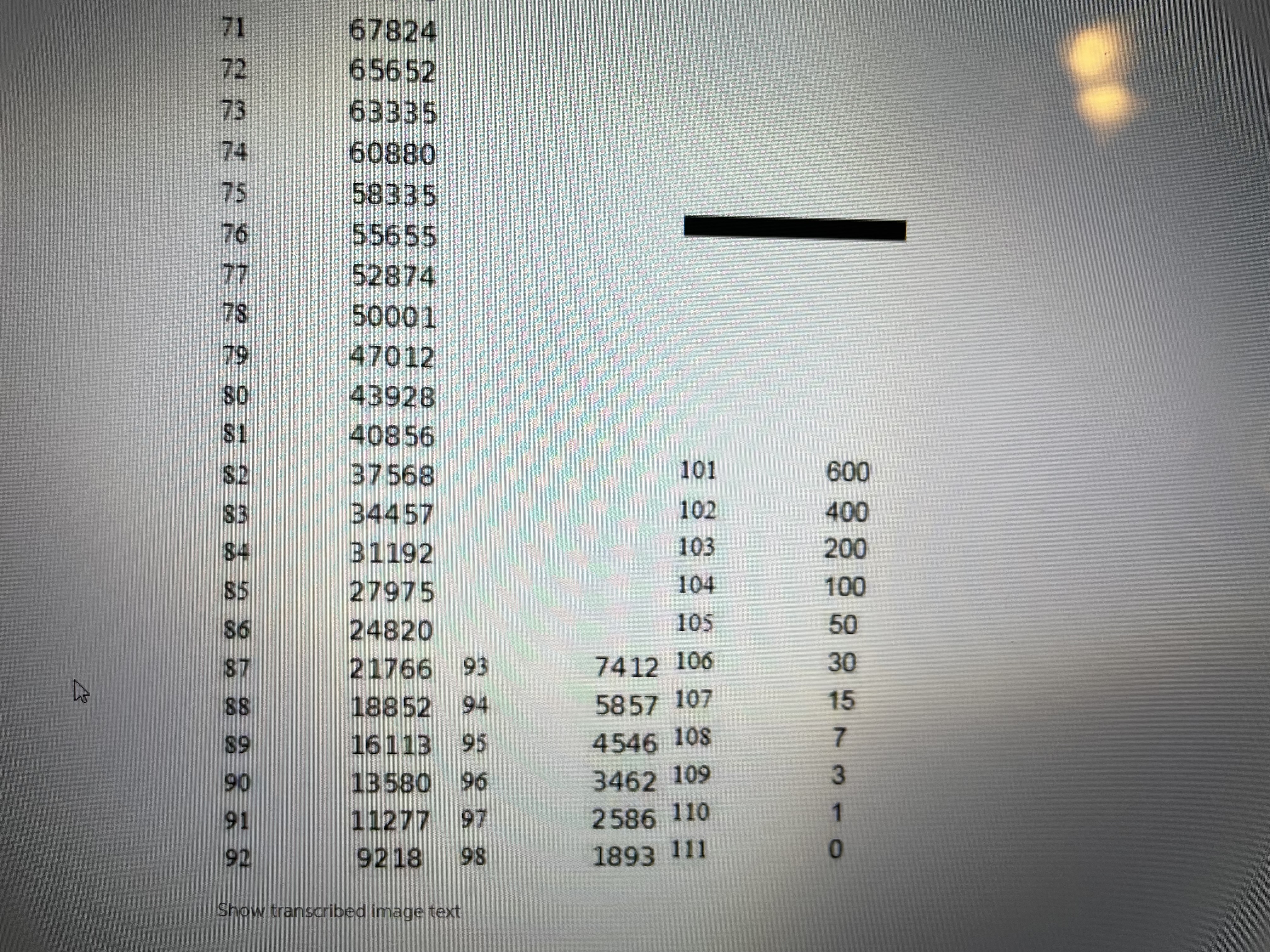
2. Consider two people age 40. a. What is the expected number of years that both are alive? b. What is the expected number of years that at least one is alive? c. What is the actuarial present value of a pension that pays $50,000 per year as long as at least one of the two 40-year-old people survive? Use a 5% discount rate. (Remember actuarial present value means that you must discount in the usual way to get present value, but you also must weight (i.e., multiply) every yearly payment by the probability that at least one of the two 40-year-old people is alive in order to receive the $50,000 payment). Show Excel workLet x denote age, let denote the number of people alive at age x in the Male Survivors life table, and denotes the probability of still being alive j years after age x. Life expectancy at age x is until the end of the life table. That is, life expectancy at age is the sum of the probabilities of surviving additional years beyond age x until you reach the end of the life table plus .5 of a year (to center deaths between years at the mid points of years). Expected age at death for a person currently age x is the sum of x and life expectancy at age x. That is, expected age at death for a person currently age x is . Create an Excel spreadsheet which computes life expectancyes at ages x = 0, 20, 40, 60, 80 and the corresponding expected ages at death for these ages. Copy and paste your Excel work into a Word file in the detailed work part of the assignment. Let x denote age, let /, denote the number of people alive at age x in the Male Survivors life table, and py = "*denotes the probability of still being alive j years after agex. Life expectancy LE, at age x is LE, =.5+Pn+ Px2 + Pxa+... until the end of the life table. That is, life expectancy LE, at age is the sum of the probabilities of surviving additional years beyond age x until you reach the end of the life table plus .5 of a year (to center deaths between years at the mid points of years). Expected age at death for a person currently agex is the sum of x and life expectancy at agex. That is, expected age at death for a person currently age.x is x+LE,.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


