Question: QUESTION 1 The one-dimensional classical wave equation is a second-order differential equation in True False QUESTION 2 The method of separation of variables involves assuming

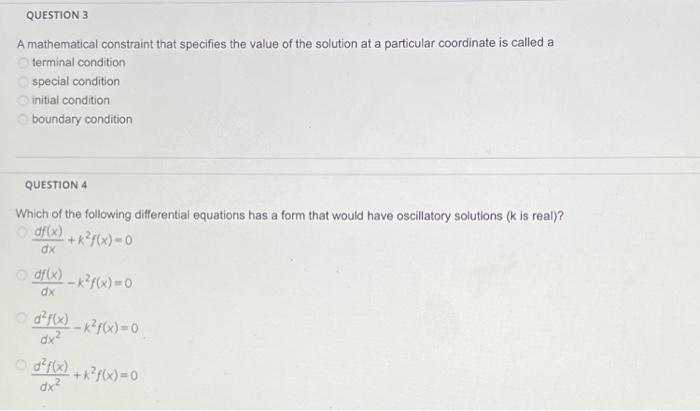

QUESTION 1 The one-dimensional classical wave equation is a second-order differential equation in True False QUESTION 2 The method of separation of variables involves assuming that the solutions can be written in the form, ulx.v) = x(x)+ (), then converting a partial differential equation into two ordinary differential equations True False QUESTION 3 A mathematical constraint that specifies the value of the solution at a particular coordinate is called a terminal condition special condition initial condition boundary condition QUESTION 4 Which of the following differential equations has a form that would have oscillatory solutions (k is real)? df(x) +*?(%) 0 dx of(x) --K/(x) = 0 dx df(x) _ k?f(x)=0 ?f dx d2F%) +k?f(x)=0 dx QUESTIONS If Ax) and g(x) are oscillatory solutions of a wave equation, then lineat.combinations of fand g will not necessarily be solutions of that equation True False QUESTION 6 A vibrating membrane with fixed edges is an example of a two-dimensional wave. True False
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


