Question: Question 11 1 pts The Caesar Cipher is an example of: Shift Cipher Substitution Cipher Public Key Cryptography Asymmetric Encryption Question 12 1 pts The
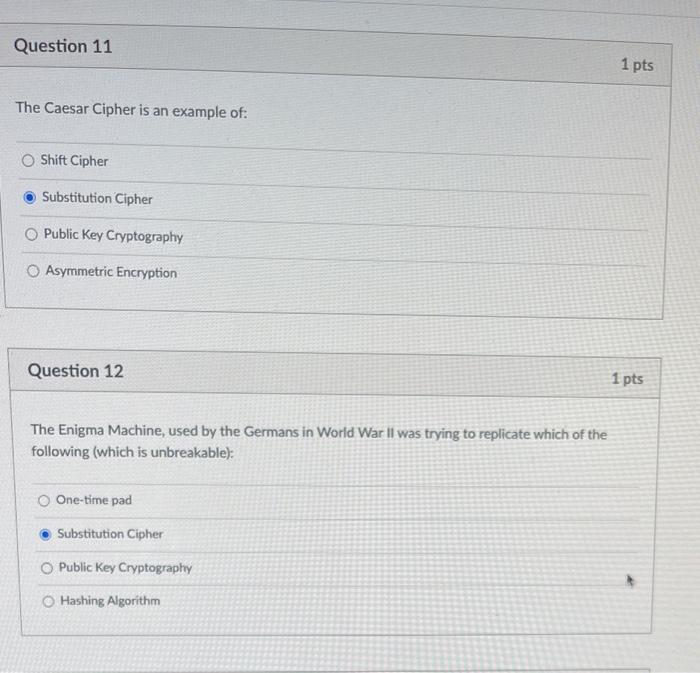
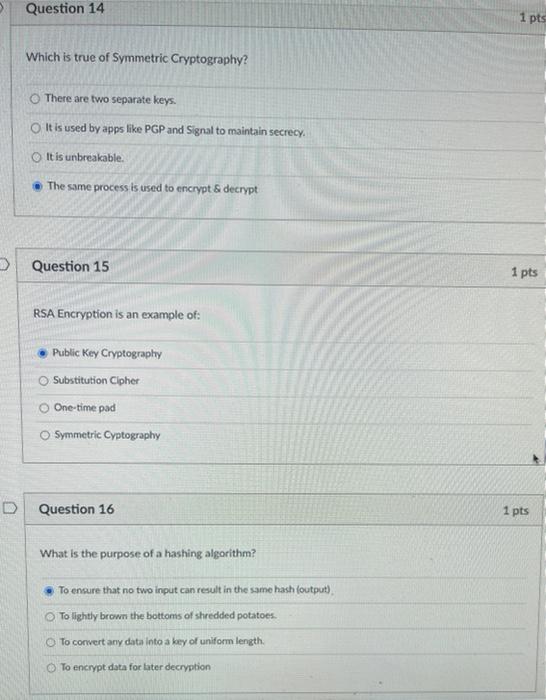
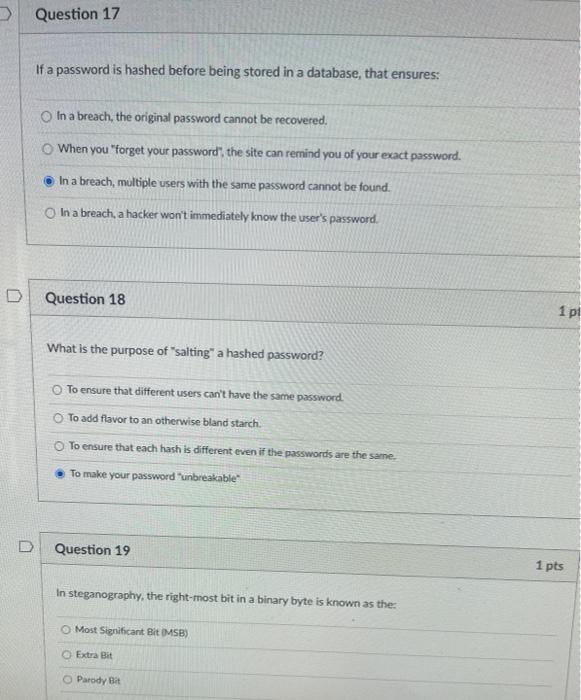
Question 11 1 pts The Caesar Cipher is an example of: Shift Cipher Substitution Cipher Public Key Cryptography Asymmetric Encryption Question 12 1 pts The Enigma Machine, used by the Germans in World War II was trying to replicate which of the following (which is unbreakable): One-time pad Substitution Cipher Public Key Cryptography Hashing Algorithm Question 14 1 pts Which is true of Symmetric Cryptography? There are two separate keys. It is used by apps like PGP and Signal to maintain secrecy. It is unbreakable The same process is used to encrypt & decrypt Question 15 1 pts RSA Encryption is an example of: Public Key Cryptography Substitution Cipher One-time pad Symmetric Cyptography D Question 16 1 pts What is the purpose of a hashing algorithm? To ensure that no two input can result in the same hash (output) To lightly brown the bottoms of shredded potatoes. To convert any data into a key of uniform length. To encrypt data for later decryption Question 17 If a password is hashed before being stored in a database, that ensures: In a breach the original password cannot be recovered. When you "forget your password", the site can remind you of your exact password. In a breach, multiple users with the same password cannot be found. In a breach, a hacker won't immediately know the user's password. D Question 18 1 p What is the purpose of "salting a hashed password? To ensure that different users can't have the same password. To add flavor to an otherwise bland starch. To ensure that each hash is different even if the passwords are the same. To make your password"unbreakable Question 19 1 pts In steganography, the right-most bit in a binary byte is known as the Most Significant Bit MSB) Extra Bit Parody Bit
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


