Question: Question 18 Given the following balanced equation, determine the rate of reaction with respect to O2 ]. 2O3(g)3O2(g) It is not possible to determine without
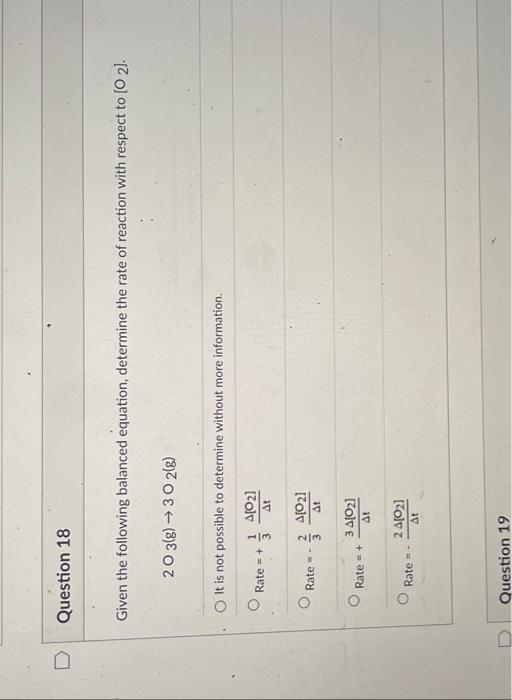
![reaction with respect to O2 ]. 2O3(g)3O2(g) It is not possible to](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f8d70c12728_01166f8d70bb14e7.jpg)
![determine without more information. Rate=+31t[O2]Rate=32t[O2]Rate=+t3[O2]Rate=t2[O2] 2SO2(g)+O2(g)2SO3(g) Rate=21t[SO2]Rate=+t2[SO2]Rate=t[SO2]Rate=+21t[SO2] It is not possible to](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f8d70ca06ac_01266f8d70c3b28c.jpg)




Question 18 Given the following balanced equation, determine the rate of reaction with respect to O2 ]. 2O3(g)3O2(g) It is not possible to determine without more information. Rate=+31t[O2]Rate=32t[O2]Rate=+t3[O2]Rate=t2[O2] 2SO2(g)+O2(g)2SO3(g) Rate=21t[SO2]Rate=+t2[SO2]Rate=t[SO2]Rate=+21t[SO2] It is not possible to determine without more information. The first-order reaction, 2N2O(g)2N2(g)+O2(g), has a rate constant equal to 0.76s1 at 1000K. How long will it take for the concentration of N2O to decrease to 12% of its initial concentration? 8.45 0.62.5 6.35 2.85 Given the following rate law, how does the rate of reaction change if the concentration of Y is doubled? Rate=k[X]2[Y]3 The rate of reaction will increase by a factor of 2 . The rate of reaction will increase by a factor of 4 . The rate of reaction will increase by a factor of 9. The rate of reaction will increase by a factor of 8 . The rate of reaction will remain unchanged. What is the overall order of the following reaction, given the rate law? 2NO(g)+H2(g)N2(g)+2H2O(g)Rate=k[NO]2[H2] Oth order 1st order 4th order 2nd order 3rd order Determine the rate law and the value of k for the following reaction using the data provided. 2N2O5(g)4NO2(g)+O2(g) Rate=1.6103M1/2s1[N2O5]1/2Rate=5.2103s1[N2O5]Rate=5.6102M1s1[N2O5]2Rate=6.0101M2s1[N2O5]3Rate=1.7102M1/251[N2O5]3/2 Determine the rate law and the value of k for the following reaction using the data provided. 2NO(g)+O2(g)2NO2(g) Rate=3.8M1/2s1[NO][O2]1/2Rate=3.1105M3s1[NO]2[O2]2Rate=1.7103M2s1[NO]2[O2]Rate=57M1s1[NO][O2]Rate=9.4103M2s1[NO][O2]2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


